A carbon steel skillet offers superior heat retention and even cooking, making it ideal for frying compared to a standard frying pan. Its durability and natural non-stick seasoning improve with use, delivering better browning and crispiness for fried foods. While a frying pan is versatile and easy to handle, a carbon steel skillet provides enhanced control over temperature and searing quality.
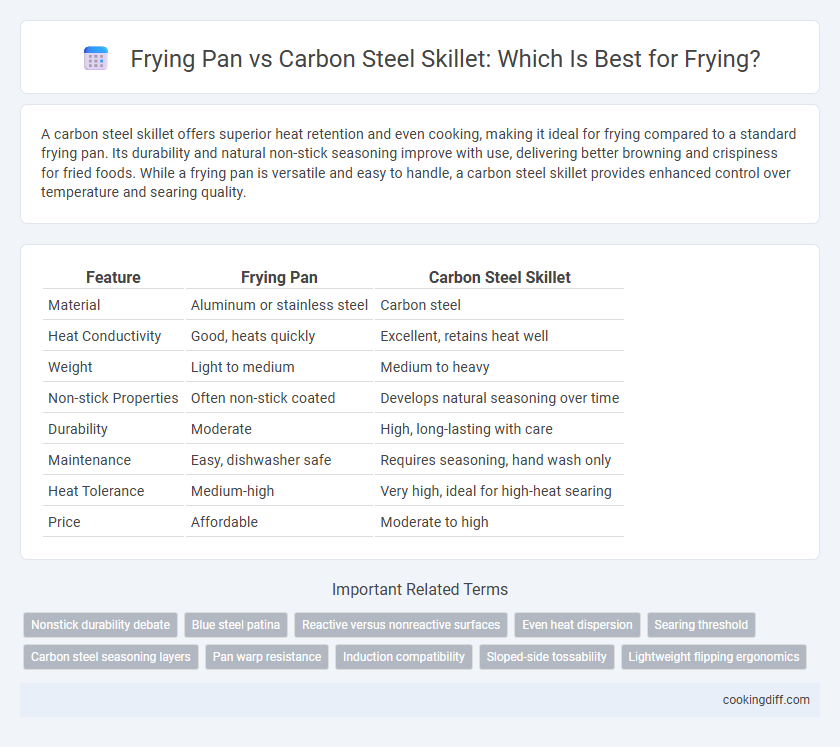
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Frying Pan | Carbon Steel Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Aluminum or stainless steel | Carbon steel |
| Heat Conductivity | Good, heats quickly | Excellent, retains heat well |
| Weight | Light to medium | Medium to heavy |
| Non-stick Properties | Often non-stick coated | Develops natural seasoning over time |
| Durability | Moderate | High, long-lasting with care |
| Maintenance | Easy, dishwasher safe | Requires seasoning, hand wash only |
| Heat Tolerance | Medium-high | Very high, ideal for high-heat searing |
| Price | Affordable | Moderate to high |
Introduction: Frying Pan vs Carbon Steel Skillet
Choosing between a frying pan and a carbon steel skillet affects cooking performance and food flavor. Both tools serve frying purposes but differ in heat conduction, durability, and maintenance.
- Frying Pan - Typically made from aluminum or stainless steel, offering non-stick surfaces and lightweight design.
- Carbon Steel Skillet - Known for superior heat retention and natural non-stick seasoning over time.
- Usability - Frying pans require less seasoning, while carbon steel skillets demand regular care for longevity.
Understanding these differences helps optimize frying results based on cooking needs.
Material Composition and Heat Conductivity
Carbon steel skillets are composed primarily of iron and carbon, offering excellent heat conductivity and rapid temperature adjustments suitable for frying. Traditional frying pans often use aluminum or stainless steel, which may distribute heat unevenly compared to carbon steel. The superior thermal responsiveness of carbon steel allows for precise control over cooking temperatures, making it ideal for frying tasks that require quick searing or consistent heat retention.
Weight and Maneuverability Comparison
Frying pans are generally lighter and easier to maneuver compared to carbon steel skillets, which tend to be heavier due to their dense material. This weight difference affects the ease of flipping and tossing food during cooking.
- Weight Difference - Frying pans typically weigh less, enhancing user comfort during prolonged cooking sessions.
- Maneuverability - Carbon steel skillets offer superior heat retention but require more effort to handle because of their heavier weight.
- User Preference - Lightweight frying pans are preferred for quick, agile cooking, while carbon steel skillets are favored for their sturdy feel and heat control.
Non-Stick Properties and Seasoning Needs
Frying pans with non-stick coatings offer superior food release, requiring minimal oil and easy cleaning, ideal for low-fat cooking. Conversely, carbon steel skillets lack built-in non-stick surfaces, relying on proper seasoning to develop a natural, durable non-stick layer over time.
Seasoning carbon steel skillets involves applying oil and heating to create a polymerized coating that improves with use, enhancing flavor and browning. Non-stick frying pans need no seasoning, but their coatings can degrade with high heat or metal utensils, limiting longevity compared to well-maintained carbon steel skillets.
Heat Retention and Distribution Efficiency
Carbon steel skillets excel in heat retention and provide even heat distribution, making them ideal for consistent frying temperatures. Traditional frying pans often have uneven heat distribution, which can cause hot spots and affect cooking performance.
- Carbon steel skillet heat retention - Carbon steel retains heat efficiently due to its density and thickness, maintaining stable temperatures during frying.
- Heat distribution in carbon steel - The material's excellent thermal conductivity ensures uniform heat across the cooking surface, preventing uneven cooking.
- Frying pan heat inconsistencies - Many frying pans are made from materials with lower thermal conductivity, leading to slower heat response and uneven hot spots.
Versatility Across Cooking Methods
Frying pans are designed for quick, even heating and excel at sauteing and frying delicate foods, while carbon steel skillets offer superior heat retention suitable for searing and browning. Carbon steel skillets can also be used over higher heat and in the oven, providing greater versatility across cooking methods.
Frying pans often have non-stick coatings that limit high-heat applications but simplify cooking and cleanup. Carbon steel skillets develop a natural seasoning over time, enhancing flavor and making them ideal for a wide range of techniques from frying to roasting.
Suitability for Different Heat Sources
Which cookware is more suitable for various heat sources when frying? Frying pans with non-stick coatings are ideal for electric and glass stovetops due to their even heat distribution and ease of use. Carbon steel skillets excel on gas and induction cooktops, offering superior heat retention and quick responsiveness to temperature changes.
Durability and Longevity in the Kitchen
Carbon steel skillets offer superior durability compared to traditional frying pans due to their robust construction and ability to withstand high temperatures without warping. These skillets develop a natural non-stick patina over time, enhancing their longevity and making them ideal for frequent use in busy kitchens. While frying pans may require replacement after frequent use, carbon steel skillets can last decades with proper care and seasoning.
Maintenance and Care Requirements
Frying pans with non-stick coatings require gentle cleaning and avoidance of metal utensils to prevent surface damage. Carbon steel skillets demand regular seasoning and thorough drying to maintain their natural non-stick layer and prevent rust.
Maintaining a carbon steel skillet involves periodic oiling after each use to preserve its patina and enhance durability. Frying pans with non-stick surfaces typically need less seasoning but are more susceptible to scratches and degradation from high heat. Proper care extends the lifespan and performance of both cookware types, ensuring optimal frying results.
Related Important Terms
Nonstick durability debate
Carbon steel skillets develop a natural nonstick patina with proper seasoning and use, offering superior nonstick durability compared to frying pans coated with synthetic nonstick surfaces that wear out over time. Unlike traditional frying pans that may require frequent replacement due to coating degradation, carbon steel skillets enhance their cooking performance and longevity through consistent seasoning and maintenance.
Blue steel patina
A carbon steel skillet develops a distinctive blue steel patina after repeated frying, enhancing its natural non-stick properties and corrosion resistance, which is crucial for maintaining optimal cooking performance. Compared to standard frying pans, this patina formation significantly improves heat retention and flavor development, making carbon steel skillets a preferred choice for frying enthusiasts.
Reactive versus nonreactive surfaces
Carbon steel skillets have reactive surfaces that can interact with acidic foods, potentially altering flavors and causing discoloration, while traditional nonreactive frying pans with stainless steel or nonstick coatings prevent chemical reactions, preserving the original taste and appearance of ingredients during frying. Choosing between these depends on cooking preferences and the types of food prepared, as reactive pans develop a natural seasoning that enhances flavor over time, whereas nonreactive pans offer consistent, neutral performance.
Even heat dispersion
Carbon steel skillets provide superior even heat dispersion due to their high thermal conductivity, ensuring consistent cooking without hot spots. Frying pans, especially those with non-stick coatings, often have uneven heat distribution, which can negatively affect the frying process and food quality.
Searing threshold
A carbon steel skillet offers a higher searing threshold than a typical non-stick frying pan, allowing for better browning and enhanced flavor development when cooking at high temperatures. Its superior heat retention and even heat distribution make it ideal for achieving a perfect sear on meats and vegetables without sticking.
Carbon steel seasoning layers
Carbon steel skillets develop natural non-stick seasoning layers that improve with use, providing excellent heat retention and distribution ideal for frying. Unlike typical frying pans with synthetic coatings, the seasoning on carbon steel prevents food from sticking while enhancing flavor through polymerized oil layers.
Pan warp resistance
Carbon steel skillets offer superior warp resistance compared to typical frying pans due to their thicker gauge and sturdier construction, maintaining flatness even under high heat. Frying pans made from thinner materials often warp quickly, compromising heat distribution and cooking performance.
Induction compatibility
Carbon steel skillets offer excellent induction compatibility due to their magnetic properties, ensuring efficient and even heat distribution essential for frying. In contrast, traditional frying pans made from non-magnetic materials like aluminum often require a special base to work on induction cooktops, limiting their versatility.
Sloped-side tossability
Carbon steel skillets feature sloped sides designed to enhance tossability during frying, allowing for easy flipping and stirring of ingredients without spills. In contrast, traditional frying pans often have flatter sides, which can limit efficient tossing and may require using a spatula for food movement.
Frying pan vs carbon steel skillet for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com