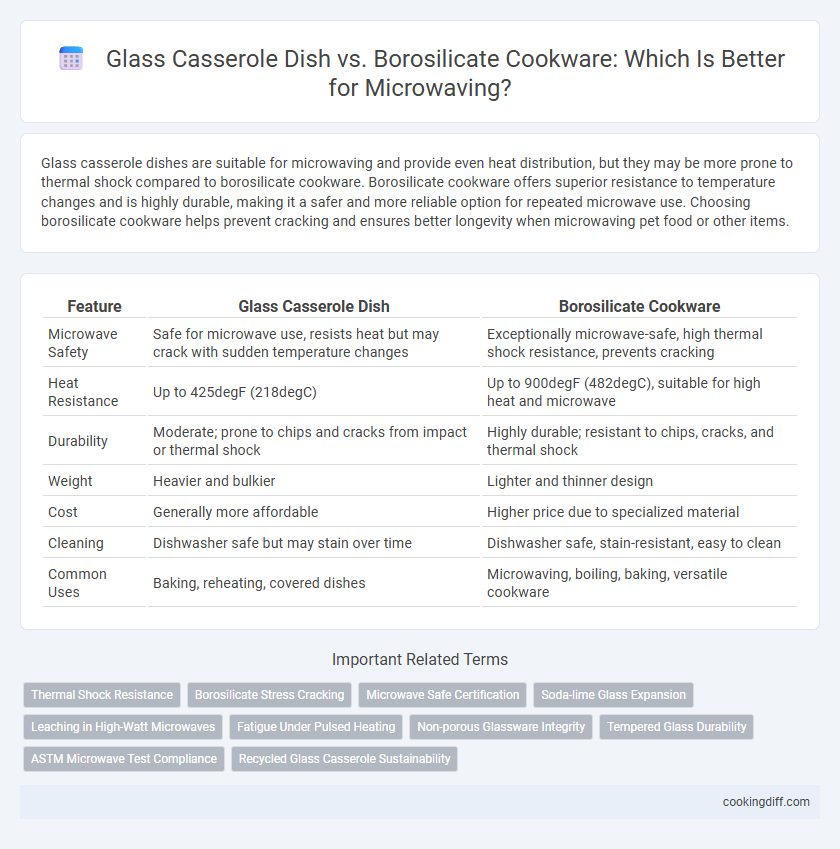
Glass casserole dishes are suitable for microwaving and provide even heat distribution, but they may be more prone to thermal shock compared to borosilicate cookware. Borosilicate cookware offers superior resistance to temperature changes and is highly durable, making it a safer and more reliable option for repeated microwave use. Choosing borosilicate cookware helps prevent cracking and ensures better longevity when microwaving pet food or other items.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Glass Casserole Dish | Borosilicate Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Microwave Safety | Safe for microwave use, resists heat but may crack with sudden temperature changes | Exceptionally microwave-safe, high thermal shock resistance, prevents cracking |
| Heat Resistance | Up to 425degF (218degC) | Up to 900degF (482degC), suitable for high heat and microwave |
| Durability | Moderate; prone to chips and cracks from impact or thermal shock | Highly durable; resistant to chips, cracks, and thermal shock |
| Weight | Heavier and bulkier | Lighter and thinner design |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Higher price due to specialized material |
| Cleaning | Dishwasher safe but may stain over time | Dishwasher safe, stain-resistant, easy to clean |
| Common Uses | Baking, reheating, covered dishes | Microwaving, boiling, baking, versatile cookware |
Introduction: Glass Casserole vs Borosilicate Cookware for Microwaving
Glass casserole dishes and borosilicate cookware are popular options for microwaving, each offering unique benefits. Understanding the differences in heat resistance and durability helps in choosing the best microwave-safe cookware.
- Glass casserole dishes - Made from soda-lime glass, these dishes are affordable and widely available but can be less resistant to thermal shock.
- Borosilicate cookware - Composed of boron and silica, this material offers superior resistance to temperature changes and is less likely to crack under microwave heat.
- Microwave safety - Both types are generally safe for microwave use, but borosilicate cookware provides enhanced durability for frequent or high-temperature heating.
What is Borosilicate Cookware?
Borosilicate cookware is made from a type of glass known for its high resistance to thermal shock, making it ideal for microwaving and oven use. Unlike regular glass casserole dishes, borosilicate glass can withstand sudden temperature changes without cracking or breaking.
This cookware type contains boron oxide, which enhances durability and heat resistance, often lasting longer than standard glass materials. Its chemical stability ensures no harmful substances leach into food when heated in the microwave.
Understanding Traditional Glass Casserole Dishes
Traditional glass casserole dishes are typically made from soda-lime glass, which is less resistant to thermal shock compared to borosilicate glass. When microwaving, soda-lime glass can crack or shatter due to rapid temperature changes, limiting its durability and safety. Understanding the material properties helps in selecting the appropriate cookware to prevent damage and ensure safe food heating in microwaves.
Heat Resistance: Borosilicate vs Regular Glass
| Heat Resistance | Glass Casserole Dish | Borosilicate Cookware |
|---|---|---|
| Thermal Shock Resistance | Lower resistance, prone to cracking under rapid temperature changes in microwave | High resistance, withstands sudden temperature shifts without cracking or breaking |
| Maximum Temperature Tolerance | Typically up to 140degC (284degF), limits use in high-heat microwaving | Can endure temperatures up to 400degC (752degF), ideal for intensive microwave cooking |
| Durability in Microwave | More susceptible to thermal damage and shattering during microwave use | Enhanced safety and longevity due to superior thermal stability |
Safety Considerations in the Microwave
Glass casserole dishes are generally safe for microwaving as they resist heat well but may shatter under sudden temperature changes. Borosilicate cookware offers superior thermal shock resistance, making it less likely to crack or break when exposed to rapid temperature shifts in the microwave.
Borosilicate glass contains silica and boron trioxide, which enhance durability and ensure even heat distribution during microwaving. Regular glass dishes typically have a lower tolerance to thermal stress, increasing the risk of breakage when exposed to high microwave heat. Choosing borosilicate cookware improves safety by minimizing the chance of accidents related to sudden temperature changes.
Impact on Food Taste and Quality
How does the choice between glass casserole dishes and borosilicate cookware affect food taste and quality when microwaving? Borosilicate cookware resists thermal shock better, preserving the original flavor and texture of food by maintaining even heat distribution. In contrast, standard glass casserole dishes may cause uneven cooking, potentially altering the taste and leading to inconsistent food quality.
Durability and Longevity
Glass casserole dishes primarily made from soda-lime glass offer good microwave safety but tend to be less durable, prone to cracking or breaking under rapid temperature changes. Borosilicate cookware, composed of silica and boron trioxide, exhibits superior thermal shock resistance, making it more robust for frequent microwaving.
Borosilicate glass cookware maintains its clarity and structural integrity over many years, resulting in greater longevity compared to standard glass casserole dishes. This extended durability reduces replacement frequency, offering a cost-effective and reliable option for microwave cooking.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Glass casserole dishes are generally easier to clean due to their smooth, non-porous surfaces that resist staining and odor retention. Borosilicate cookware offers higher durability and thermal shock resistance, making maintenance simpler over long-term use despite slightly more careful handling requirements.
- Smooth Surface - Glass casserole dishes have non-porous surfaces that prevent food from sticking, facilitating effortless cleaning.
- Thermal Shock Resistance - Borosilicate glass withstands rapid temperature changes, reducing the risk of cracking during cleaning and use.
- Durability and Maintenance - Borosilicate cookware's enhanced strength decreases the need for frequent replacements, lowering overall maintenance effort.
Cost Comparison
Glass casserole dishes generally cost less upfront compared to borosilicate cookware, making them a budget-friendly option for microwaving. Borosilicate cookware, while more expensive, offers superior durability and thermal resistance that may save money over time.
- Initial Cost - Glass casserole dishes are typically priced lower, around $10 to $25, depending on size and brand.
- Longevity - Borosilicate cookware can last significantly longer due to higher resistance to thermal shock.
- Value Over Time - Investing in borosilicate cookware reduces the frequency of replacements, potentially offsetting the higher purchase price.
Choosing between the two depends on balancing immediate budget constraints against long-term usage and durability benefits.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Shock Resistance
Borosilicate cookware exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to standard glass casserole dishes, allowing it to withstand rapid temperature changes in microwaving without cracking. This property makes borosilicate a safer and more durable choice for reheating or cooking foods directly from freezer to microwave.
Borosilicate Stress Cracking
Borosilicate cookware exhibits superior thermal shock resistance compared to glass casserole dishes, significantly reducing the risk of stress cracking during rapid temperature changes in microwaving. Stress cracks commonly occur in standard glass cookware due to uneven heating, whereas borosilicate's unique composition enhances durability and safety for microwave use.
Microwave Safe Certification
Glass casserole dishes often come with microwave-safe certifications such as FDA approval or UL listing, ensuring they can withstand high microwave temperatures without cracking. Borosilicate cookware, known for its thermal shock resistance, typically holds microwave-safe certifications from standards organizations like NSF and ISO, guaranteeing safe and durable use in microwave ovens.
Soda-lime Glass Expansion
Soda-lime glass casserole dishes often experience higher thermal expansion when microwaved, increasing the risk of cracking compared to borosilicate cookware, which has a much lower coefficient of thermal expansion and superior thermal shock resistance. This stability makes borosilicate glass ideal for microwave use, as it withstands rapid temperature changes without deforming or breaking.
Leaching in High-Watt Microwaves
Borosilicate cookware offers superior resistance to thermal shock and minimizes the risk of chemical leaching compared to standard glass casserole dishes when used in high-watt microwaves. High temperatures generated by powerful microwaves can cause some glass casserole dishes to release trace amounts of heavy metals or additives, whereas borosilicate glass maintains chemical stability under rapid heating conditions.
Fatigue Under Pulsed Heating
Borosilicate cookware exhibits superior resistance to fatigue under pulsed heating in microwaving compared to glass casserole dishes, due to its low thermal expansion coefficient and enhanced structural durability. This minimizes the risk of cracking and extends lifespan after repeated heating cycles in microwave ovens.
Non-porous Glassware Integrity
Borosilicate cookware maintains higher structural integrity under rapid temperature changes due to its low thermal expansion, making it less prone to cracking compared to regular glass casserole dishes. Non-porous borosilicate glass resists staining and odor absorption, ensuring long-term durability and safety during microwaving.
Tempered Glass Durability
Tempered glass casserole dishes offer enhanced durability and resistance to thermal shock during microwaving compared to standard glass, but borosilicate cookware provides superior strength and can withstand rapid temperature changes without cracking. Borosilicate glass's low coefficient of thermal expansion makes it the preferred choice for microwave cooking that requires frequent heating and cooling cycles.
ASTM Microwave Test Compliance
Glass casserole dishes and borosilicate cookware both exhibit high thermal shock resistance ideal for microwaving, but borosilicate cookware often surpasses standard ASTM Microwave Test Compliance due to its superior durability and resistance to sudden temperature changes. ASTM compliance ensures that these materials can safely endure the rapid heating and cooling cycles typical in microwave use without cracking or shattering, making borosilicate a preferred choice for microwave-safe cookware.
Glass casserole dish vs Borosilicate cookware for microwaving. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com