Microwave ovens reheat food quickly by using electromagnetic waves that excite water molecules, making them ideal for convenience and speed. Steam ovens use moist heat to gently warm food, preserving texture and preventing drying, which is beneficial for delicate dishes. Choosing between the two depends on whether speed or food quality is the priority during reheating.
Table of Comparison
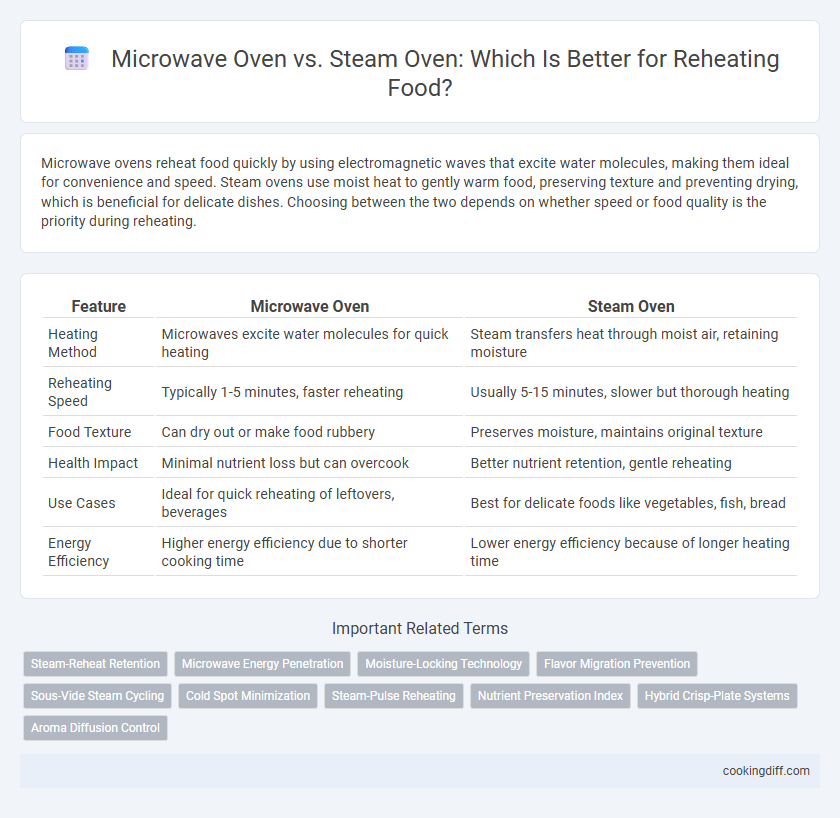
| Feature | Microwave Oven | Steam Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Method | Microwaves excite water molecules for quick heating | Steam transfers heat through moist air, retaining moisture |
| Reheating Speed | Typically 1-5 minutes, faster reheating | Usually 5-15 minutes, slower but thorough heating |
| Food Texture | Can dry out or make food rubbery | Preserves moisture, maintains original texture |
| Health Impact | Minimal nutrient loss but can overcook | Better nutrient retention, gentle reheating |
| Use Cases | Ideal for quick reheating of leftovers, beverages | Best for delicate foods like vegetables, fish, bread |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy efficiency due to shorter cooking time | Lower energy efficiency because of longer heating time |
Understanding Microwave Ovens for Reheating
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to excite water molecules within food, generating heat rapidly and evenly for efficient reheating. This technology preserves moisture while significantly reducing reheating time compared to conventional methods.
Microwave ovens are best suited for reheating a variety of foods quickly without altering texture or flavor drastically. Their ability to penetrate food layers ensures uniform warmth, minimizing cold spots often encountered in other reheating appliances.
How Steam Ovens Reheat Food
Steam ovens reheat food by using moist heat, which penetrates food evenly and preserves moisture. This method reduces the risk of drying out or overcooking, unlike conventional microwave ovens that heat by agitating water molecules rapidly.
- Even Heating - Steam ovens distribute heat gently, ensuring food heats through without cold spots.
- Maintains Moisture - The steam prevents food from losing its natural juices, keeping texture and flavor intact.
- Retains Nutrients - Lower reheating temperatures help preserve vitamins sensitive to heat compared to microwave reheating.
The use of steam ovens results in reheated food that is more tender, flavorful, and nutritionally superior to that reheated by microwaves.
Speed Comparison: Microwave vs Steam Oven
Microwave ovens reheat food significantly faster, typically completing the process in 2 to 5 minutes due to rapid electromagnetic wave penetration. Steam ovens require 10 to 20 minutes as they rely on moist heat to evenly warm food, preserving texture and moisture. For quick reheating, microwaves offer unparalleled speed, while steam ovens provide gentle cooking at the cost of longer times.
Food Quality and Texture After Reheating
Microwave ovens reheat food rapidly by agitating water molecules, which can result in uneven heating and a soggy or rubbery texture, especially in crispy or baked items. This method often compromises food quality by reducing moisture retention and altering texture negatively.
Steam ovens use moist heat to gently reheat food, preserving its original texture and moisture content, making it ideal for delicate dishes and leftovers that benefit from a tender, fresh taste. The steam method enhances food quality by maintaining juiciness and preventing dryness commonly caused by microwaving.
Retaining Nutrients: Microwave vs Steam Oven
| Reheating Method | Impact on Nutrient Retention |
|---|---|
| Microwave Oven | Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly, preserving water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C better than conventional methods due to shorter cooking times but may unevenly heat food, potentially causing nutrient degradation in hot spots. |
| Steam Oven | Steam ovens reheat food using moist heat, which helps retain moisture and preserves heat-sensitive nutrients such as B vitamins and antioxidants more effectively while maintaining food texture and flavor integrity. |
Convenience and Ease of Use
Microwave ovens provide rapid reheating with simple one-button controls, making them highly convenient for quick meals. Steam ovens require slightly longer cooking times and involve water setup, but they preserve moisture and texture more effectively. For ease of use, microwaves dominate due to their speed and straightforward operation, ideal for busy lifestyles.
Safety Considerations in Reheating
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but may cause uneven heating, potentially leaving cold spots where bacteria can survive. Steam ovens reheat food more evenly with moist heat, reducing the risk of foodborne illness by thoroughly warming all parts.
Microwaving requires careful stirring and checking of food temperature to ensure safety, as underheated areas can promote bacterial growth. Steam ovens maintain consistent heat, making them safer for reheating delicate or dense foods without drying them out. Choosing the appropriate method depends on balancing reheating speed with ensuring food reaches safe temperatures throughout.
Suitable Foods for Each Reheating Method
Microwave ovens excel at quickly reheating foods with high moisture content like soups, stews, and pasta, preserving their texture and flavor. Steam ovens provide gentle, even heating ideal for delicate items such as rice, vegetables, and baked goods, preventing dryness and maintaining moisture.
- Microwave Oven - Best for reheating soups, casseroles, and pasta due to rapid heating and moisture retention.
- Steam Oven - Ideal for rice, steamed vegetables, and pastries, ensuring even warmth without drying out.
- Food Texture - Microwave can cause uneven heating and tough spots in dense foods, while steam ovens maintain softness and moistness.
Energy Efficiency: Which Uses Less Power?
Microwave ovens typically use less energy than steam ovens due to their rapid heating mechanisms. Steam ovens require more power to generate and maintain steam, leading to higher energy consumption during reheating.
- Microwave Oven Efficiency - Uses electromagnetic waves to directly heat food, resulting in shorter cooking times and lower energy use.
- Steam Oven Power Demand - Consumes more electricity to produce steam and maintain temperature, increasing overall energy consumption.
- Energy Cost Comparison - Microwaves generally reduce electricity costs for reheating compared to steam ovens, making them more energy-efficient appliances.
Related Important Terms
Steam-Reheat Retention
Steam ovens provide superior steam-reheat retention by evenly distributing moist heat, preserving food texture and preventing drying during reheating. Microwave ovens often cause uneven heating and moisture loss, resulting in drier, less palatable leftovers.
Microwave Energy Penetration
Microwave ovens utilize microwave radiation that penetrates food to agitate water molecules, resulting in rapid and uniform heating compared to steam ovens, which rely on external steam heat conduction primarily affecting food surfaces. The deeper energy penetration of microwaves ensures faster reheating with reduced nutrient loss, while steam ovens may provide gentler heating but often require longer times for thorough internal warming.
Moisture-Locking Technology
Microwave ovens use electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly but often cause moisture loss, resulting in drier textures. In contrast, steam ovens employ moisture-locking technology by circulating steam during reheating, preserving food's natural hydration and ensuring a juicier, more evenly heated meal.
Flavor Migration Prevention
Microwave ovens rapidly heat food by agitating water molecules, which can cause uneven temperature distribution and potential flavor migration between different ingredients. Steam ovens use moist heat that cooks food more gently and evenly, preserving original flavors and preventing cross-contamination of tastes during reheating.
Sous-Vide Steam Cycling
Microwave ovens quickly reheat food using electromagnetic waves but can cause uneven heating and moisture loss, affecting texture and taste. Steam ovens employing sous-vide steam cycling gently circulate steam under controlled temperatures, preserving food's moisture and flavor while ensuring even reheating.
Cold Spot Minimization
Microwave ovens often create cold spots due to uneven microwaving patterns, leading to inconsistent reheating and potential food safety risks. Steam ovens utilize moist heat and convection to evenly distribute temperature, effectively minimizing cold spots and ensuring thorough reheating of food.
Steam-Pulse Reheating
Steam-pulse reheating in steam ovens preserves food moisture and texture more effectively than microwave ovens, which often cause uneven heating and dryness. This method uses controlled bursts of steam combined with precise temperature regulation, ensuring consistent warmth without overcooking or drying out meals.
Nutrient Preservation Index
Microwave ovens rapidly reheat food by agitating water molecules, resulting in moderate nutrient retention with a Nutrient Preservation Index (NPI) typically around 70-80%. Steam ovens utilize moist heat, preserving nutrients more effectively by minimizing nutrient leaching and oxidation, often achieving an NPI of 85-95%, making them superior for nutrient-sensitive reheating.
Hybrid Crisp-Plate Systems
Hybrid crisp-plate systems in microwave ovens combine microwave energy with a crisping element to deliver faster reheating while maintaining a crunchy texture, outperforming steam ovens that primarily reheat with moist heat. This technology ensures even heating and browning, making microwave ovens with hybrid crisp-plates ideal for reheating foods that benefit from a crispy finish without the sogginess often associated with steam ovens.
Microwave Oven vs Steam Oven for reheating food Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com