Microwaving vegetables offers quick cooking with minimal nutrient loss due to shorter cooking times and reduced water use. Food steamers preserve more vitamins and minerals by gently cooking with steam, preventing nutrient leaching. Choosing between the two depends on your priorities: speed and convenience versus nutrient retention and texture quality.
Table of Comparison
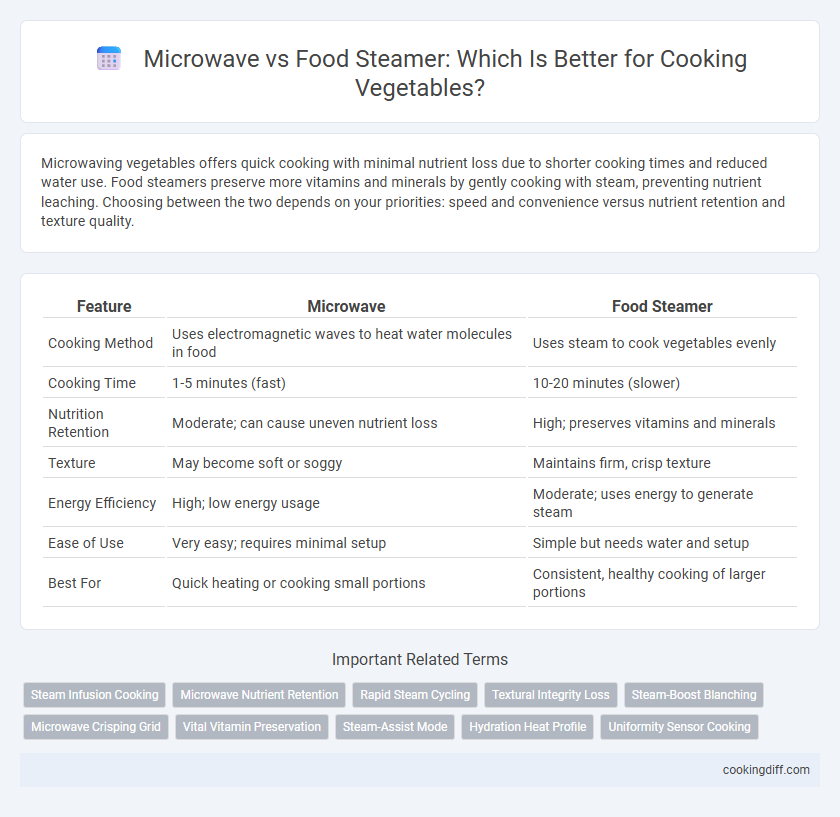
| Feature | Microwave | Food Steamer |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses electromagnetic waves to heat water molecules in food | Uses steam to cook vegetables evenly |
| Cooking Time | 1-5 minutes (fast) | 10-20 minutes (slower) |
| Nutrition Retention | Moderate; can cause uneven nutrient loss | High; preserves vitamins and minerals |
| Texture | May become soft or soggy | Maintains firm, crisp texture |
| Energy Efficiency | High; low energy usage | Moderate; uses energy to generate steam |
| Ease of Use | Very easy; requires minimal setup | Simple but needs water and setup |
| Best For | Quick heating or cooking small portions | Consistent, healthy cooking of larger portions |
Introduction: Microwave vs Food Steamer for Vegetables
Microwaving and steaming are popular cooking methods for vegetables, each offering unique benefits in terms of nutrient retention and cooking time. Understanding the differences helps in choosing the best technique for preserving flavor and texture.
- Microwave Cooking - Uses electromagnetic waves to rapidly heat water molecules within vegetables, reducing cooking time and preserving nutrients.
- Food Steamer - Cooks vegetables gently with steam, maintaining texture and vitamins without using added fats.
- Nutrient Preservation - Both methods retain more nutrients compared to boiling, with steaming often slightly better for water-soluble vitamins.
Nutrient Retention: Steaming vs Microwaving
Which method retains more nutrients when cooking vegetables, microwaving or steaming? Steaming is widely recognized for preserving water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex more effectively due to its gentle cooking process. Microwaving uses less water and shorter cooking times, which can also help retain nutrients but may cause uneven heating and nutrient loss in some cases.
Cooking Time Comparison
Microwaving vegetables typically reduces cooking time more than using a traditional food steamer, often taking just 3 to 5 minutes. Steamers generally require 10 to 15 minutes to achieve similar tenderness, depending on vegetable type and quantity.
- Faster Heating - Microwaves heat water molecules inside vegetables quickly, speeding up the cooking process.
- Energy Efficiency - Shorter microwaving times save energy compared to longer steaming sessions.
- Texture Control - Steaming allows for gentler heat application, which can better preserve texture despite longer cooking.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Microwaving vegetables tends to retain more of their natural flavor by quickly heating them without water dilution, preserving crispness and vibrant color. In contrast, a food steamer gently softens vegetables, enhancing moisture content but sometimes resulting in a milder taste and softer texture.
Microwave cooking uses high-frequency waves to heat water molecules within the vegetables, which helps lock in nutrients and creates a firmer bite compared to steaming. Food steamers cook vegetables by surrounding them with hot vapor, which can cause slight nutrient leaching but often leads to more uniformly tender results. Choosing between these methods depends on whether you prioritize retaining a vegetable's original texture or achieving a more delicate softness in your dish.
Energy Efficiency: Microwave vs Steamer
Microwaves generally use less energy compared to food steamers when cooking vegetables due to their shorter cooking times and focused heat application. Steamers, while effective for even cooking, consume more electricity by continuously heating water to generate steam.
- Microwave energy consumption - Microwaves typically use 600 to 1200 watts, efficiently converting energy directly into the food.
- Steamer power usage - Steamers often draw 800 to 1500 watts to maintain a steady steam flow during cooking.
- Cooking duration impact - Shorter cooking times in microwaves reduce overall energy use compared to the longer steaming process.
Choosing a microwave for vegetable cooking is generally more energy-efficient than using a food steamer due to its quicker heat delivery and lower power consumption.
Convenience and Ease of Use
Microwaves offer unparalleled convenience by cooking vegetables quickly using minimal preparation time, making them ideal for busy schedules. Food steamers require slightly more setup and monitoring but provide precise control over texture and nutrient retention. Both methods are user-friendly, though microwaves excel in speed while steamers prioritize consistent, gentle cooking.
Suitability for Different Vegetables
Microwaving is ideal for quick cooking of softer vegetables like spinach and zucchini, preserving nutrients through minimal water use and shorter cooking times. Food steamers suit a broader range of vegetables, including dense varieties like carrots and broccoli, ensuring even cooking while maintaining texture and flavor. Steaming also reduces nutrient loss in fibrous vegetables, making it preferable for health-conscious preparations.
Maintenance and Cleaning
| Microwave | Requires minimal cleaning; typically involves wiping the interior with a damp cloth to remove splatters and spills, with occasional deodorizing using vinegar or lemon water. The built-in turntable and rack are usually dishwasher safe, simplifying maintenance. Microwaves do not accumulate mineral deposits, reducing the need for descaling compared to steamers. |
| Food Steamer | Demands thorough cleaning after each use to remove food residues from steaming trays and water reservoirs, preventing mold and bacteria growth. Detachable parts often require handwashing or dishwasher cleaning, and periodic descaling is necessary to eliminate mineral buildup caused by water vapor. Maintenance is more intensive compared to microwaves due to the water-based cooking method and multiple components. |
Cost Analysis: Microwave vs Steamer
Microwaves generally cost less upfront, with average prices ranging from $50 to $200, compared to food steamers, which typically cost between $30 and $150. However, microwaves consume more electricity per use, averaging around 700 to 1200 watts, whereas steamers use about 400 to 800 watts, leading to potential energy savings over time.
Maintenance and replacement parts for microwaves are usually more expensive, increasing the total cost of ownership. Food steamers require minimal upkeep, making them a more cost-effective option for long-term vegetable cooking.
Related Important Terms
Steam Infusion Cooking
Steam infusion cooking in microwaves rapidly heats vegetables by embedding steam directly into the food, preserving nutrients and enhancing texture more effectively than traditional food steamers. Unlike conventional steamers, microwave steam infusion minimizes cooking time and reduces water usage, resulting in vibrant, evenly cooked vegetables with superior flavor retention.
Microwave Nutrient Retention
Microwaving vegetables preserves nutrients more effectively than steaming by using less water and shorter cooking times, which helps retain water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Studies show microwaved vegetables can retain up to 90% of their nutrients, whereas steaming typically results in slightly lower nutrient retention due to prolonged heat exposure.
Rapid Steam Cycling
Microwave ovens utilize rapid steam cycling to quickly heat and cook vegetables by generating steam inside a sealed environment, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional steaming methods. Food steamers, while efficient in producing consistent steam, typically lack the quick steam cycling capability, resulting in longer cooking times and potential nutrient loss compared to microwave steaming.
Textural Integrity Loss
Microwaving vegetables often results in greater textural integrity loss due to uneven heating and rapid moisture evaporation, causing sogginess or mushiness. Food steamers maintain crispness and firmness by gently cooking with moist heat, preserving cell structure and nutrients more effectively.
Steam-Boost Blanching
Steam-boost blanching in a microwave combines rapid heating with steam infusion, preserving nutrients and vibrant colors more effectively than traditional steaming. This method reduces cooking time while enhancing texture, making microwaving a superior choice for preparing crisp, nutrient-rich vegetables.
Microwave Crisping Grid
A microwave crisping grid enhances vegetable texture by promoting even browning and crisping, contrasting with the gentle steaming process of a food steamer that preserves moisture and nutrients without browning. Using a crisping grid in microwaving delivers a roasted flavor and crispy exterior, making it ideal for achieving a satisfying crunch that steaming alone cannot produce.
Vital Vitamin Preservation
Microwaving vegetables preserves vital vitamins like vitamin C and folate more effectively due to shorter cooking times and minimal water use, reducing nutrient leaching. Food steamers also retain nutrients well by using gentle heat and steam, but may require longer cooking, which can slightly diminish some heat-sensitive vitamins.
Steam-Assist Mode
Steam-Assist Mode in microwaves combines rapid heating with steam injection, preserving nutrients and texture in vegetables more effectively than traditional microwave cooking. Compared to standalone food steamers, this mode saves time and energy while delivering evenly cooked, tender, and flavorful vegetables.
Hydration Heat Profile
Microwaving uses electromagnetic waves to quickly heat water molecules inside vegetables, resulting in uneven hydration and potential nutrient loss due to rapid temperature spikes. In contrast, a food steamer applies gentle, consistent steam heat that maintains optimal hydration and preserves texture and nutrients by slowly raising the temperature.
Microwave vs Food Steamer for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com