Microwaving offers a quick and convenient method for reheating meals, preserving nutrients with minimal cooking time. Steam ovens provide a gentler cooking process that retains moisture and enhances the texture of food, making them ideal for meal prepping fresh or frozen ingredients. Choosing between the two depends on the balance between speed and quality desired in meal preparation.
Table of Comparison
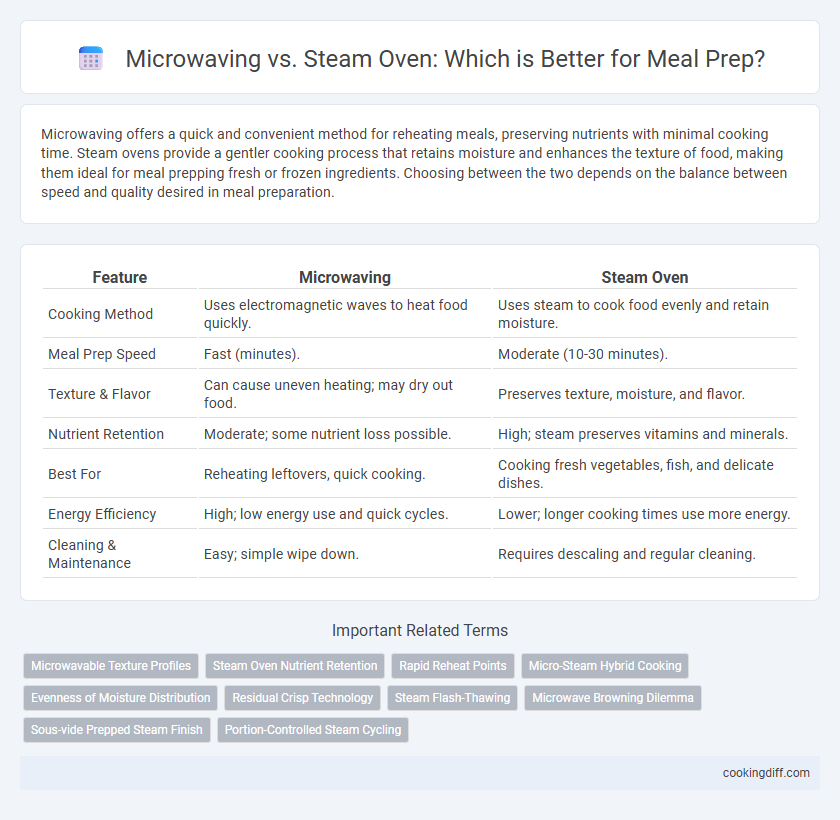
| Feature | Microwaving | Steam Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses electromagnetic waves to heat food quickly. | Uses steam to cook food evenly and retain moisture. |
| Meal Prep Speed | Fast (minutes). | Moderate (10-30 minutes). |
| Texture & Flavor | Can cause uneven heating; may dry out food. | Preserves texture, moisture, and flavor. |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate; some nutrient loss possible. | High; steam preserves vitamins and minerals. |
| Best For | Reheating leftovers, quick cooking. | Cooking fresh vegetables, fish, and delicate dishes. |
| Energy Efficiency | High; low energy use and quick cycles. | Lower; longer cooking times use more energy. |
| Cleaning & Maintenance | Easy; simple wipe down. | Requires descaling and regular cleaning. |
Introduction to Microwaving and Steam Oven Meal Prep
Microwaving offers rapid heating by agitating water molecules in food, making it a popular choice for quick meal prep. Steam ovens cook food using moist heat, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than microwaves.
- Microwaving Efficiency - Microwaves heat food faster than conventional ovens by directly targeting water molecules.
- Steam Oven Nutrient Retention - Steam ovens maintain higher levels of vitamins and minerals due to gentle cooking methods.
- Texture and Flavor - Steam ovens enhance moisture retention, resulting in tender and flavorful meals compared to microwaved food.
How Microwaves Work vs Steam Ovens
Microwaves heat food by emitting electromagnetic waves that cause water molecules to vibrate, generating heat quickly and efficiently. This rapid heating process makes microwaves ideal for reheating meals and cooking foods with high moisture content.
Steam ovens use steam to transfer heat, cooking food gently and evenly while preserving moisture and nutrients. Unlike microwaves, steam ovens maintain a consistent temperature and humidity level, which helps prevent drying out or overcooking. This method is particularly beneficial for meal prep involving vegetables, proteins, and delicate dishes.
Cooking Speed: Microwave vs Steam Oven
Which appliance offers faster cooking speed for meal prep, a microwave or a steam oven? Microwaves typically cook food in minutes by using electromagnetic waves that agitate water molecules, making them ideal for quick reheating and simple meals. Steam ovens, while slower with cooking times often 2-3 times longer, provide more even heat distribution and retain moisture, enhancing texture and flavor during meal preparation.
Nutrient Retention in Microwave and Steam Oven Cooking
Microwaving preserves nutrients by using shorter cooking times and minimal water, which reduces nutrient leaching. Steam ovens maintain nutrient retention by cooking food with moist heat, which helps preserve vitamins sensitive to oxidation and heat.
- Microwave cooking retains vitamin C - Short exposure to high heat prevents degradation of heat-sensitive vitamins.
- Steam ovens preserve B vitamins - Gentle steam heat minimizes nutrient loss compared to boiling or frying.
- Water usage impacts nutrient retention - Microwaving uses little to no water, limiting nutrient washout; steam ovens use moisture without direct water immersion.
Flavor and Texture: Comparing Results
Microwaving often results in uneven heating that can compromise flavor intensity and produce a slightly rubbery texture in foods. The rapid cooking process may cause moisture loss, diminishing the overall sensory appeal of the meal.
Steam ovens, however, utilize moist heat that preserves natural flavors and maintains food's tender, juicy texture by preventing drying out. This method enhances the retention of nutrients and produces a more consistent and flavorful meal preparation.
Meal Prep Versatility: What Can You Cook?
Microwaves excel at quickly reheating leftovers and cooking simple meals like steamed vegetables, scrambled eggs, and popcorn, making them ideal for basic meal prep tasks. Steam ovens offer greater versatility by enabling the cooking of a wider variety of dishes such as steamed fish, vegetables, rice, and even baked goods while retaining moisture and nutrients. Choosing between the two depends on whether speed or culinary variety and quality are prioritized during meal preparation.
Energy Efficiency: Microwave vs Steam Oven
Microwaves typically use 600 to 1200 watts of power, making them highly energy efficient for quick reheating and cooking tasks. Their short cooking times translate into lower overall energy consumption compared to steam ovens.
Steam ovens, while consuming more energy--usually around 1500 to 2000 watts--offer benefits in meal quality and moisture retention. Despite higher power usage, they can cook food more evenly, potentially reducing the need for reheating and saving energy in repeated meal prep.
Cleaning and Maintenance Requirements
Microwaving typically requires minimal cleaning, with most messes confined to splatters inside the cavity that can be easily wiped down with a damp cloth. Steam ovens demand more thorough maintenance due to the buildup of mineral deposits and moisture, necessitating regular descaling and gasket checks. Choosing between the two appliances depends on the balance between convenience in cleaning and the desired cooking outcomes.
Cost Analysis: Initial and Ongoing Expenses
Microwaving generally involves lower initial costs compared to steam ovens, making it a budget-friendly option for meal prep. However, steam ovens tend to have higher upfront prices but can offer energy efficiency that reduces ongoing utility expenses.
- Microwave Price Range - Basic models start as low as $50 while high-end units can cost up to $300.
- Steam Oven Cost - Premium steam ovens typically range from $1,000 to $3,000, reflecting advanced technology and features.
- Energy Consumption - Steam ovens use less energy over time due to their efficient water vapor cooking method, potentially lowering electricity bills.
Choosing between microwaving and steam ovens depends on balancing initial investment with long-term savings and cooking preferences.
Related Important Terms
Microwavable Texture Profiles
Microwaving rapidly heats food by agitating water molecules, often resulting in uneven texture profiles such as soggy exteriors and dry interiors, especially in dense meals. Unlike steam ovens that preserve moisture and deliver uniform softness, microwave cooking can cause toughening or rubbery textures in proteins and starchy components when reheated improperly.
Steam Oven Nutrient Retention
Steam ovens preserve nutrients more effectively than microwaving by using gentle steam heat that minimizes nutrient loss, especially vitamins C and B-complex. This cooking method retains moisture and antioxidants, promoting healthier meal prep with enhanced flavor and texture compared to microwaving.
Rapid Reheat Points
Microwaving offers rapid reheating by utilizing dielectric heating that excites water molecules, significantly reducing meal prep time compared to steam ovens. Steam ovens, while slower, provide even heat distribution and moisture retention, enhancing food texture but extending rapid reheat points beyond typical microwave durations.
Micro-Steam Hybrid Cooking
Micro-steam hybrid cooking combines the rapid heating of microwaving with the gentle moisture retention of steam ovens, enhancing nutrient preservation and meal texture for efficient meal prep. This method reduces cooking time significantly while delivering evenly cooked meals with improved flavor and juiciness compared to traditional microwave or steam-only cooking.
Evenness of Moisture Distribution
Microwaving often results in uneven moisture distribution, causing some parts of the food to become dry while others remain soggy. Steam ovens use controlled humidity to cook food uniformly, preserving moisture evenly throughout meals for better texture and taste.
Residual Crisp Technology
Residual Crisp Technology in steam ovens preserves food texture by maintaining heat to keep meals crispy after cooking, outperforming microwaves that often result in soggy leftovers. This innovation enhances meal prep efficiency by combining rapid cooking with prolonged crispness, ensuring a restaurant-quality finish without additional reheating steps.
Steam Flash-Thawing
Steam flash-thawing in steam ovens rapidly defrosts meals by using pressurized steam, preserving texture and nutrients better than microwaving, which can cause uneven heating and moisture loss. This method enhances meal prep efficiency by ensuring quicker, more uniform thawing and reducing cooking time compared to traditional microwave defrosting.
Microwave Browning Dilemma
Microwaving offers rapid reheating but often fails to produce the desirable browning and crisp texture that steam ovens achieve through convection and moisture control. The microwave browning dilemma stems from its inability to generate Maillard reactions without added browning agents or specialized microwave browning dishes.
Sous-vide Prepped Steam Finish
Microwaving rapidly reheats sous-vide prepped meals but may compromise texture and flavor, whereas finishing in a steam oven preserves moisture and enhances the delicate consistency through gentle steaming. Steam ovens provide controlled humidity and even heat distribution, optimizing meal prep by maintaining the sous-vide's precise doneness while improving surface texture and taste.
Microwaving vs Steam Oven for meal prep Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com