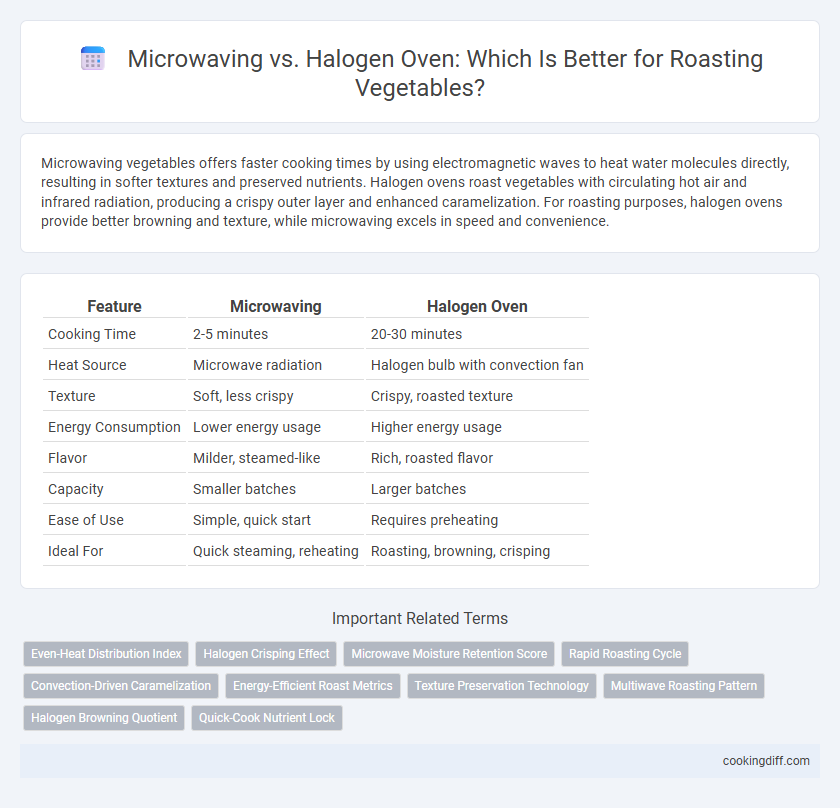
Microwaving vegetables offers faster cooking times by using electromagnetic waves to heat water molecules directly, resulting in softer textures and preserved nutrients. Halogen ovens roast vegetables with circulating hot air and infrared radiation, producing a crispy outer layer and enhanced caramelization. For roasting purposes, halogen ovens provide better browning and texture, while microwaving excels in speed and convenience.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Microwaving | Halogen Oven |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | 2-5 minutes | 20-30 minutes |
| Heat Source | Microwave radiation | Halogen bulb with convection fan |
| Texture | Soft, less crispy | Crispy, roasted texture |
| Energy Consumption | Lower energy usage | Higher energy usage |
| Flavor | Milder, steamed-like | Rich, roasted flavor |
| Capacity | Smaller batches | Larger batches |
| Ease of Use | Simple, quick start | Requires preheating |
| Ideal For | Quick steaming, reheating | Roasting, browning, crisping |
Introduction to Roasting Vegetables: Microwave vs Halogen Oven
Roasting vegetables enhances their natural flavors by caramelizing sugars and softening textures. Choosing between a microwave and a halogen oven affects cooking time, texture, and nutrient retention.
- Microwave Efficiency - Microwaves cook vegetables quickly using radiation, reducing overall cooking time.
- Halogen Oven Crispness - Halogen ovens use infrared heat to evenly roast and brown vegetables for a crispy exterior.
- Nutrient Preservation - Both methods preserve nutrients differently, with microwaves retaining more vitamins due to shorter cooking times.
Understanding these differences helps select the best method for perfectly roasted vegetables.
Cooking Time Comparison: Microwave vs Halogen Oven
Microwaving vegetables significantly reduces cooking time, often roasting them in 5 to 10 minutes depending on quantity and type. Halogen ovens typically require 15 to 25 minutes to achieve the same level of roasting, making microwaves faster for quick meals.
While microwaves excel in speed by using electromagnetic waves to heat food rapidly, halogen ovens rely on infrared light and convection to cook evenly and develop a crispy texture. The extended cooking time in halogen ovens allows for better caramelization and flavor enhancement in roasted vegetables. Choosing between the two depends on whether speed or texture is prioritized in the cooking process.
Energy Efficiency: Which Appliance Uses Less Power?
Microwaving vegetables typically uses less energy than a halogen oven because it cooks food faster by directly agitating water molecules. Halogen ovens require longer cooking times and circulating heat, which consumes more power overall.
- Microwave energy consumption - Microwaves generally use between 600 to 1200 watts of power, completing roasting tasks in a shorter duration.
- Halogen oven power usage - Halogen ovens operate around 1200 to 1700 watts and take longer due to convection heating.
- Efficiency comparison - The direct heating mechanism of microwaves results in higher energy efficiency compared to the indirect heat transfer in halogen ovens.
Texture and Flavor: How Each Method Affects Roasted Vegetables
Microwaving roasted vegetables typically results in a softer texture due to the rapid steam generation inside the food, which can diminish crispness. Halogen ovens use circulating hot air to achieve a more evenly roasted exterior, enhancing flavor through caramelization and maintaining a firmer texture. This makes halogen ovens preferable for those seeking a crispy, flavorful finish on roasted vegetables compared to the often moist outcome of microwaving.
Nutrient Retention: Microwaving vs Halogen Oven
Microwaving vegetables preserves more water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C due to shorter cooking times and reduced exposure to heat. Halogen ovens, while effective for roasting, may cause greater nutrient loss from prolonged high-temperature cooking.
- Microwaving retains vitamin C efficiently - Short cooking duration and minimal water use help preserve delicate nutrients.
- Halogen oven uses dry heat - This method can degrade heat-sensitive antioxidants during roasting.
- Microwaving reduces mineral leaching - Limited exposure to water prevents loss of essential minerals compared with some oven methods.
Ease of Use and Convenience
| Microwaving | Offers rapid cooking with simple controls and minimal preparation time, making it highly convenient for roasting vegetables quickly. |
| Halogen Oven | Provides evenly roasted vegetables with preset functions but requires more monitoring and longer cooking times compared to microwaving. |
| Comparison | Microwaving excels in ease of use due to faster cook times and straightforward operation; halogen ovens offer better texture but are less convenient for quick meals. |
Cleanup and Maintenance
Microwaving vegetables requires minimal cleanup as most dishes are cooked in microwave-safe containers that are easy to wash. The lack of additional parts means there is little maintenance beyond regular cleaning of the microwave interior.
In contrast, halogen ovens have removable trays and racks that need thorough cleaning after each use to prevent food residue buildup. Regular maintenance also includes wiping down the halogen bulb and fan area, which can be more time-consuming than microwaving cleanup.
Versatility: Other Uses Beyond Roasting Vegetables
Which appliance offers greater versatility beyond roasting vegetables? A halogen oven excels with its ability to bake, grill, and toast various foods, while microwaves primarily focus on reheating and defrosting. Halogen ovens provide a broader range of cooking techniques, making them more adaptable for different kitchen tasks.
Cost Analysis: Initial Investment and Long-term Savings
Microwaving offers a lower initial investment, with basic models priced significantly less than halogen ovens. Halogen ovens, while more expensive upfront, provide energy-efficient roasting that can reduce long-term electricity costs when used regularly. Evaluating cost-effectiveness depends on frequency of use and desired cooking quality, with microwaving suitable for budget-conscious consumers and halogen ovens ideal for those prioritizing energy savings.
Related Important Terms
Even-Heat Distribution Index
Microwaving often results in uneven heating patterns due to microwave penetration variability, leading to inconsistent roasting of vegetables, whereas halogen ovens provide a higher Even-Heat Distribution Index by circulating hot air evenly around the food. This superior heat circulation in halogen ovens ensures uniformly roasted vegetables with consistent texture and flavor compared to the spotty heat distribution typical of microwaving.
Halogen Crisping Effect
Halogen ovens deliver superior roasting results for vegetables by utilizing intense halogen heat that creates a crisp, golden exterior while maintaining a tender interior, unlike microwaves which often result in uneven cooking and lack of crispness. The halogen crisping effect leverages convection and infrared radiation to efficiently caramelize vegetable surfaces, enhancing flavor and texture beyond the capabilities of standard microwaving.
Microwave Moisture Retention Score
Microwaving vegetables scores higher on the Microwave Moisture Retention Score, preserving more water content and resulting in juicier, tender vegetables compared to the drier texture often produced by halogen oven roasting. This moisture retention enhances both the nutritional value and flavor profile of the vegetables when microwaved.
Rapid Roasting Cycle
Microwaving offers a rapid roasting cycle that significantly reduces cooking time by using electromagnetic waves to heat vegetables quickly and evenly. In contrast, halogen ovens rely on convection and infrared heat, which, although providing a crispy texture, generally require longer roasting times.
Convection-Driven Caramelization
Halogen ovens utilize convection heat to evenly roast vegetables, enabling deeper caramelization and enhanced flavor development compared to microwaving. Microwaving primarily heats water molecules quickly without generating the dry, circulating heat necessary for the Maillard reaction that defines caramelized textures.
Energy-Efficient Roast Metrics
Microwaving uses significantly less energy than halogen ovens, typically consuming 600-1200 watts compared to 1400-1700 watts in halogen cooking, making it more energy-efficient for roasting vegetables. The quicker cooking time of microwaves--often reducing roasting from 30-40 minutes to 10-15 minutes--also lowers overall energy use, contributing to a smaller carbon footprint.
Texture Preservation Technology
Halogen ovens utilize intense infrared heat to roast vegetables evenly while maintaining a crispy exterior and tender interior, preserving texture through controlled radiant heat. Microwaving relies on dielectric heating, which can cause uneven moisture distribution, often resulting in softer, less textured vegetables lacking the distinct roasted crunch.
Multiwave Roasting Pattern
The Multiwave Roasting Pattern in microwaving ensures even heat distribution by using multiple microwave sources, resulting in uniformly roasted vegetables with a crisp texture. Unlike halogen ovens that rely on radiant heat, microwaving with multiwave technology reduces cooking time while preserving nutrients and enhancing flavor.
Halogen Browning Quotient
Halogen ovens achieve superior roasting results compared to microwaves due to their higher Halogen Browning Quotient, which measures efficient heat distribution and caramelization on vegetable surfaces. The intense infrared radiation in halogen ovens promotes even browning and crispy textures that microwaves, relying primarily on electromagnetic waves, often fail to replicate.
Microwaving vs Halogen Oven for roasting vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com