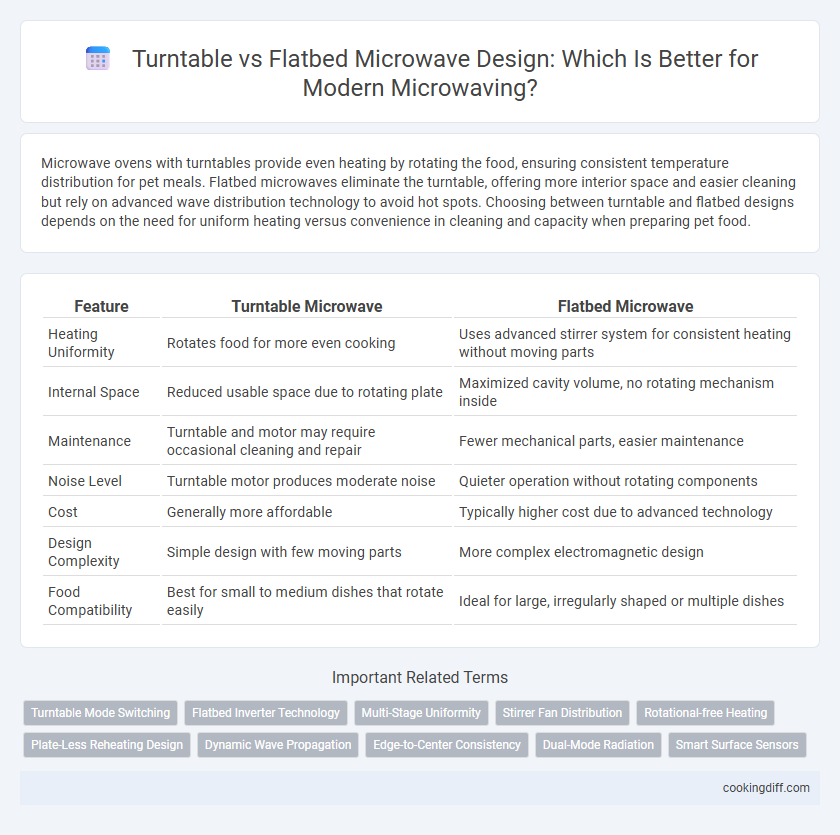
Microwave ovens with turntables provide even heating by rotating the food, ensuring consistent temperature distribution for pet meals. Flatbed microwaves eliminate the turntable, offering more interior space and easier cleaning but rely on advanced wave distribution technology to avoid hot spots. Choosing between turntable and flatbed designs depends on the need for uniform heating versus convenience in cleaning and capacity when preparing pet food.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Turntable Microwave | Flatbed Microwave |
|---|---|---|
| Heating Uniformity | Rotates food for more even cooking | Uses advanced stirrer system for consistent heating without moving parts |
| Internal Space | Reduced usable space due to rotating plate | Maximized cavity volume, no rotating mechanism inside |
| Maintenance | Turntable and motor may require occasional cleaning and repair | Fewer mechanical parts, easier maintenance |
| Noise Level | Turntable motor produces moderate noise | Quieter operation without rotating components |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Typically higher cost due to advanced technology |
| Design Complexity | Simple design with few moving parts | More complex electromagnetic design |
| Food Compatibility | Best for small to medium dishes that rotate easily | Ideal for large, irregularly shaped or multiple dishes |
Introduction to Microwave Design: Turntable vs Flatbed
Microwave ovens utilize two primary designs for heating: turntable and flatbed. Turntable microwaves rotate food on a spinning glass plate to ensure even heating through continuous movement.
Flatbed microwaves replace the rotating plate with a flat, stationary surface and use advanced microwave dispersion technology for uniform cooking. This design increases internal space and allows larger dishes to be heated without rotation constraints.
How Turntable Microwaves Work
Turntable microwaves use a rotating glass tray to evenly distribute microwave energy for consistent cooking results. This rotation helps reduce hot spots by moving food through varying electromagnetic fields inside the cavity.
- Rotating glass tray - The turntable spins food to ensure microwaves heat it uniformly from all angles.
- Microwave source placement - Microwaves are usually emitted from a fixed waveguide, with rotation compensating for uneven energy distribution.
- Design simplicity - The turntable mechanism is mechanically straightforward, making it cost-effective and reliable.
Understanding Flatbed Microwave Technology
Flatbed microwave technology eliminates the traditional turntable by using a rotating stirrer or a square waveguide to distribute microwaves evenly throughout the cavity, enhancing cooking uniformity and increasing usable space. This design allows for easier cleaning and more flexible placement of larger or irregularly shaped dishes compared to conventional turntable microwaves.
- Even Heating - Flatbed microwaves use a rotating stirrer to scatter microwaves uniformly, preventing hot or cold spots in food.
- Increased Capacity - Without a turntable mechanism, flatbed microwaves provide more flat surface area for larger or multiple dishes.
- Simple Maintenance - The flatbed design removes mechanical parts like turntables and rollers, simplifying cleaning and reducing malfunctions.
Understanding flatbed microwave technology helps consumers choose models that prioritize consistent cooking performance and convenience.
Cooking Performance: Evenness and Hot Spots
Turntable microwaves rotate food to enhance cooking evenness, reducing hot spots by allowing microwaves to distribute more uniformly. This mechanism helps prevent uneven heating, especially in irregularly shaped dishes.
Flatbed microwaves use advanced wave distribution technology without rotation, providing a larger and more flexible cooking area. This design minimizes hot spots more effectively by circulating microwaves through multiple sources, ensuring consistent heating throughout.
Usable Space and Interior Design
Microwave turntable designs often limit usable space due to the rotating mechanism occupying part of the interior, restricting the size and shape of cookware that fits comfortably. Flatbed microwaves maximize interior volume by eliminating the turntable, allowing for larger and more irregularly shaped dishes to be heated evenly with rotating wave technology. This interior design innovation enhances usability and flexibility, making flatbed models increasingly popular in modern kitchen appliances.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Turntable vs Flatbed
Turntable microwaves often accumulate food debris along the rotating mechanism, making cleaning more challenging compared to flatbed models. Flatbed microwaves feature a smooth, flat surface without a turntable, allowing for easier wiping and maintenance. The absence of moving parts in flatbed designs reduces mechanical issues and simplifies routine cleaning tasks.
Durability and Reliability Comparison
| Microwave Design | Durability | Reliability |
|---|---|---|
| Turntable | Prone to wear and tear due to moving parts such as the motor and roller ring, which may require replacements over time. | Consistent rotation ensures even heating but mechanical failures can disrupt performance, affecting long-term reliability. |
| Flatbed | Fewer mechanical parts increase structural durability, reducing risks of component failures compared to turntables. | Enhanced reliability with no moving parts; uniform microwave distribution achieved by engineered flatbed systems improves consistent cooking results. |
Suitability for Different Foods and Containers
Which microwave design is more suitable for heating diverse foods and containers, turntable or flatbed? Turntable microwaves excel in evenly cooking round containers and small to medium dishes by rotating the food, ensuring consistent heat distribution. Flatbed microwaves accommodate larger, irregularly shaped containers and multiple dishes simultaneously, providing more space and uniform heating without the need for rotation.
Energy Efficiency and Cooking Speed
Turntable microwaves distribute energy by rotating food, promoting even cooking but sometimes leading to longer cooking times due to variable energy exposure. Flatbed microwaves utilize a stationary glass plate and advanced stirrer technology to deliver uniform microwave distribution, improving energy efficiency and reducing cooking speed.
Energy efficiency in flatbed microwaves generally surpasses that of turntable models because the stationary design allows better utilization of microwave energy with minimal power loss. Cooking speed benefits from the flatbed's consistent wave distribution, which shortens heating cycles and improves overall performance. Consumers seeking faster and more energy-efficient microwave options typically prefer flatbed designs over traditional turntable units.
Related Important Terms
Turntable Mode Switching
Turntable mode switching in microwave design enhances even cooking by rotating food continuously, ensuring uniform heat distribution across all surfaces. This mechanism contrasts with flatbed microwaves, where the absence of rotation relies on advanced waveguide technology to minimize hot spots without mechanical movement.
Flatbed Inverter Technology
Flatbed microwave ovens equipped with inverter technology offer uniform cooking by eliminating the need for a turntable, providing more cooking space and easier cleaning. Inverter technology delivers precise and consistent power levels, enhancing cooking efficiency and preserving food texture compared to traditional turntable models.
Multi-Stage Uniformity
Microwaves with turntable designs enhance multi-stage uniformity by rotating food through varied microwave zones, reducing cold spots and ensuring even cooking. Flatbed microwaves utilize a rotating antenna beneath a stationary tray to distribute microwaves evenly, offering uniform energy exposure without mechanical movement.
Stirrer Fan Distribution
Turntable microwave designs rely on a rotating plate to evenly distribute microwave energy, while flatbed models use a stirrer fan system to scatter microwaves uniformly throughout the cavity, eliminating the need for rotation. The stirrer fan mechanism enhances cooking consistency by dispersing energy waves more effectively, reducing cold spots and improving overall heating performance compared to turntable systems.
Rotational-free Heating
Flatbed microwave designs enable rotational-free heating by utilizing advanced stirrer fans and even microwave distribution, eliminating the need for a turntable and providing uniform cooking results. Turntable microwaves rely on constant rotation to achieve even heat distribution but may cause uneven cooking in irregularly shaped containers.
Plate-Less Reheating Design
Flatbed microwave designs eliminate the traditional turntable, relying on rotating antennas or stirrers to distribute microwaves evenly for consistent heating without plate rotation. This plate-less reheating design enhances interior space, allows uniform cooking in larger or irregularly shaped containers, and simplifies cleaning compared to turntable-based models.
Dynamic Wave Propagation
Turntable microwaves promote dynamic wave propagation through rotation, ensuring more uniform heating by constantly changing the food's position relative to the microwave energy. Flatbed designs employ advanced wave distribution systems that eliminate the need for rotation, using integrated stirrer fans or multiple feed points to achieve consistent energy spread and reduce cold spots.
Edge-to-Center Consistency
Turntable microwaves provide better edge-to-center cooking consistency by rotating food, ensuring even heat distribution across the surface. Flatbed microwaves use advanced wave stirrer technology to eliminate hot spots, offering a uniform cooking experience without the need for a rotating plate.
Dual-Mode Radiation
Dual-mode radiation in microwave ovens enhances heating uniformity by combining turntable rotation with flatbed design, eliminating cold spots more effectively than either method alone. Integrating rotating waveguides with a stationary flatbed optimizes electromagnetic field distribution, improving cooking efficiency and food quality.
Turntable vs flatbed for microwave design. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com