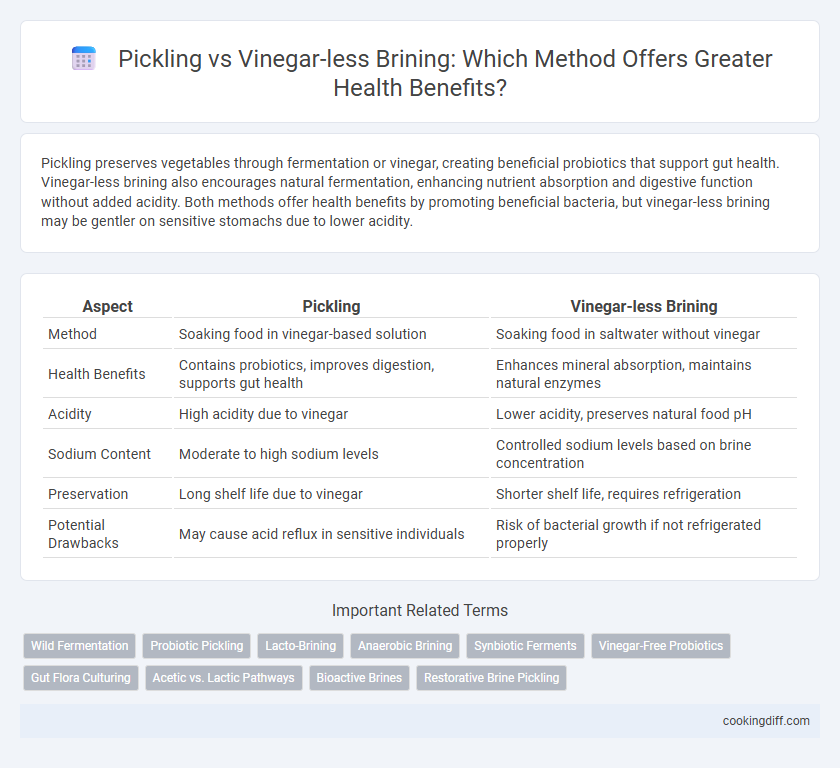
Pickling preserves vegetables through fermentation or vinegar, creating beneficial probiotics that support gut health. Vinegar-less brining also encourages natural fermentation, enhancing nutrient absorption and digestive function without added acidity. Both methods offer health benefits by promoting beneficial bacteria, but vinegar-less brining may be gentler on sensitive stomachs due to lower acidity.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pickling | Vinegar-less Brining |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Soaking food in vinegar-based solution | Soaking food in saltwater without vinegar |
| Health Benefits | Contains probiotics, improves digestion, supports gut health | Enhances mineral absorption, maintains natural enzymes |
| Acidity | High acidity due to vinegar | Lower acidity, preserves natural food pH |
| Sodium Content | Moderate to high sodium levels | Controlled sodium levels based on brine concentration |
| Preservation | Long shelf life due to vinegar | Shorter shelf life, requires refrigeration |
| Potential Drawbacks | May cause acid reflux in sensitive individuals | Risk of bacterial growth if not refrigerated properly |
Introduction to Pickling and Vinegar-less Brining
Pickling involves preserving food in an acidic solution, typically vinegar, which inhibits bacterial growth and extends shelf life. Vinegar-less brining uses saltwater and natural fermentation to enhance flavor and probiotic content without added acids.
- Pickling creates an acidic environment - This prevents spoilage by inhibiting the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Vinegar-less brining relies on natural fermentation - Beneficial bacteria produce lactic acid, promoting gut health through probiotics.
- Both methods preserve food differently - Pickling offers immediate acid-based preservation, while vinegar-less brining develops flavor and probiotics over time.
Core Differences: Pickling with Vinegar vs. Brining without Vinegar
Pickling with vinegar preserves foods by creating an acidic environment that inhibits bacterial growth, enhancing shelf life and adding a distinctive tangy flavor. Vinegar's acetic acid content also supports digestion and provides antimicrobial properties, making pickled products a healthful choice for gut health.
Vinegar-less brining relies on salt and water to draw moisture from foods, promoting the growth of beneficial lactic acid bacteria through natural fermentation. This process can enhance probiotic content, improve nutrient absorption, and support immune function without the acidity of vinegar. Both methods offer unique health benefits, but pickling with vinegar prioritizes acidity and preservation, while vinegar-less brining focuses on fermentation and probiotic development.
Nutrient Retention in Pickled vs. Brined Foods
Pickling preserves vegetables by fermenting them in vinegar or brine, which can affect nutrient retention differently compared to vinegar-less brining methods. Vinegar-less brining tends to better retain water-soluble vitamins, while pickling in vinegar may lead to some nutrient loss but enhances probiotic content.
- Water-soluble Vitamins Retention - Vinegar-less brining helps maintain higher levels of vitamin C and B vitamins by avoiding acidic degradation.
- Probiotic Development - Pickling with vinegar or fermentation promotes beneficial bacteria that support gut health but may reduce some nutrient levels.
- Mineral Preservation - Both methods generally retain minerals like potassium and magnesium effectively due to minimal heat exposure.
Gut Health and Probiotics: Brining versus Vinegar Pickling
| Pickling Methods | Gut Health Impact | Probiotic Content |
| Vinegar Pickling | Preserves food using acetic acid; lowers pH, inhibits harmful bacteria growth. | Generally lacks live probiotics due to high acidity and heat during processing. |
| Vinegar-less Brining | Relies on natural fermentation with salt promoting beneficial bacterial growth. | Rich in lactic acid bacteria, enhances gut microbiome and probiotic intake. |
Sodium Content and Health Impact in Both Methods
Pickling typically involves high sodium content due to the use of salt and vinegar, which can contribute to increased blood pressure and cardiovascular risks if consumed excessively. Vinegar-less brining often uses lower sodium levels by relying on salt and water without acidic vinegar, potentially reducing the risk of hypertension while still preserving food effectively. Choosing vinegar-less brining can be a healthier alternative by minimizing sodium intake and supporting better heart health without sacrificing flavor.
Antioxidant Levels After Pickling and Brining
Pickling significantly preserves antioxidant levels in vegetables due to the fermentation process, which enhances bioavailability. Vinegar-less brining also maintains antioxidants but often results in lower retention compared to traditional pickling.
- Fermentation Effect - Enhances antioxidant compounds by promoting beneficial microbial activity during pickling.
- Acidity Role - Vinegar's acetic acid in pickling stabilizes antioxidants better than saltwater alone.
- Health Impact - Higher antioxidant retention in pickled foods supports better reduction of oxidative stress in the body.
Choosing pickling over vinegar-less brining optimizes antioxidant intake for improved health benefits.
Effects on Blood Sugar Management
Pickling using vinegar creates an acidic environment that can help lower the glycemic index of foods, potentially supporting better blood sugar control. Vinegar-less brining relies on salt and fermentation, which may also improve gut health but has less direct impact on blood sugar regulation. Studies indicate that consuming vinegar-based pickled foods may aid in stabilizing post-meal blood glucose levels more effectively than vinegar-free brines.
Impact on Food Safety and Preservation
Pickling involves fermenting or soaking food in an acidic solution like vinegar, which lowers pH and inhibits harmful bacteria growth, enhancing food safety and long-term preservation. Vinegar-less brining relies on salt and water, promoting beneficial lactic acid bacteria fermentation that also preserves food by creating an anaerobic environment.
Pickling with vinegar provides immediate acidity, ensuring rapid microbial control, whereas vinegar-less brining requires time for microbial action to lower pH levels for safe preservation. Both methods effectively extend shelf life, but vinegar pickling offers a quicker and more consistent microbial barrier against spoilage and pathogens.
Flavor and Texture: Health Implications
Which method better preserves flavor and texture while offering health benefits--pickling or vinegar-less brining? Pickling enhances flavor with a tangy, probiotic-rich profile that supports gut health, while vinegar-less brining maintains a milder taste and crispier texture by relying on salt and natural fermentation. Both methods reduce sodium compared to conventional brines, but pickling provides additional antioxidants and beneficial bacteria that boost digestive wellness.
Related Important Terms
Wild Fermentation
Wild fermentation pickling promotes beneficial probiotics by naturally developing lactic acid bacteria, which enhances gut health and boosts the immune system. Vinegar-less brining relies on these live cultures instead of acetic acid, providing superior digestion support and increased nutrient absorption compared to traditional vinegar-based pickling.
Probiotic Pickling
Probiotic pickling preserves beneficial bacteria such as Lactobacillus, enhancing gut health and boosting the immune system, whereas vinegar-less brining lacks these live cultures and primarily affects texture and flavor. Consuming probiotic pickled foods supports digestion and nutrient absorption, offering more substantial health benefits compared to vinegar-based or vinegar-less methods.
Lacto-Brining
Lacto-brining leverages beneficial lactic acid bacteria to ferment vegetables, enhancing gut health by increasing probiotics and reducing harmful pathogens, unlike traditional pickling which commonly uses vinegar that lacks these probiotic benefits. Vinegar-less lacto-brining also maintains higher vitamin content and antioxidants, offering superior nutritional advantages compared to standard vinegar pickling methods.
Anaerobic Brining
Pickling involves anaerobic brining where cucumbers ferment in a saltwater solution, promoting the growth of beneficial probiotics that support gut health and improve digestion. Vinegar-less brining relies on natural lacto-fermentation without acidic preservatives, enhancing nutrient absorption and reducing inflammation compared to traditional vinegar-based pickling methods.
Synbiotic Ferments
Synbiotic ferments produced through pickling combine probiotics and prebiotics, enhancing gut health and immune function more effectively than vinegar-less brining, which lacks live microbial cultures. The presence of beneficial bacteria in pickled foods supports digestive balance and nutrient absorption, offering superior health benefits compared to non-fermented, vinegar-free brined products.
Vinegar-Free Probiotics
Vinegar-less brining promotes the growth of natural probiotics by fermenting vegetables in a saltwater solution, enhancing gut health and boosting the immune system without the acidity of vinegar. Unlike traditional pickling, which uses vinegar to preserve food, vinegar-free fermentation supports a diverse microbiome by allowing beneficial bacteria like Lactobacillus to thrive.
Gut Flora Culturing
Pickling promotes the growth of beneficial probiotic bacteria such as Lactobacillus, which supports a diverse and healthy gut microbiome, enhancing digestion and immune function. Vinegar-less brining, while effective for flavor and preservation, lacks the natural fermentation process that cultivates these gut-friendly microbes, offering less impact on gut flora diversity and overall gut health.
Acetic vs. Lactic Pathways
Pickling using vinegar involves acetic acid pathways that provide antimicrobial properties and consistent acidity, supporting gut health through controlled pH levels. Vinegar-less brining relies on lactic acid fermentation, which enhances probiotic benefits by promoting beneficial bacteria growth and improving nutrient absorption.
Bioactive Brines
Pickling with bioactive brines enhances the concentration of probiotics and antioxidants, promoting gut health and reducing inflammation compared to vinegar-less brining, which mainly relies on salt for preservation without boosting beneficial microbial growth. The presence of bioactive compounds such as polyphenols and lactic acid bacteria in traditional pickling brines contributes to improved digestion and stronger immune function through natural fermentation processes.
Pickling vs Vinegar-less brining for health benefits. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com