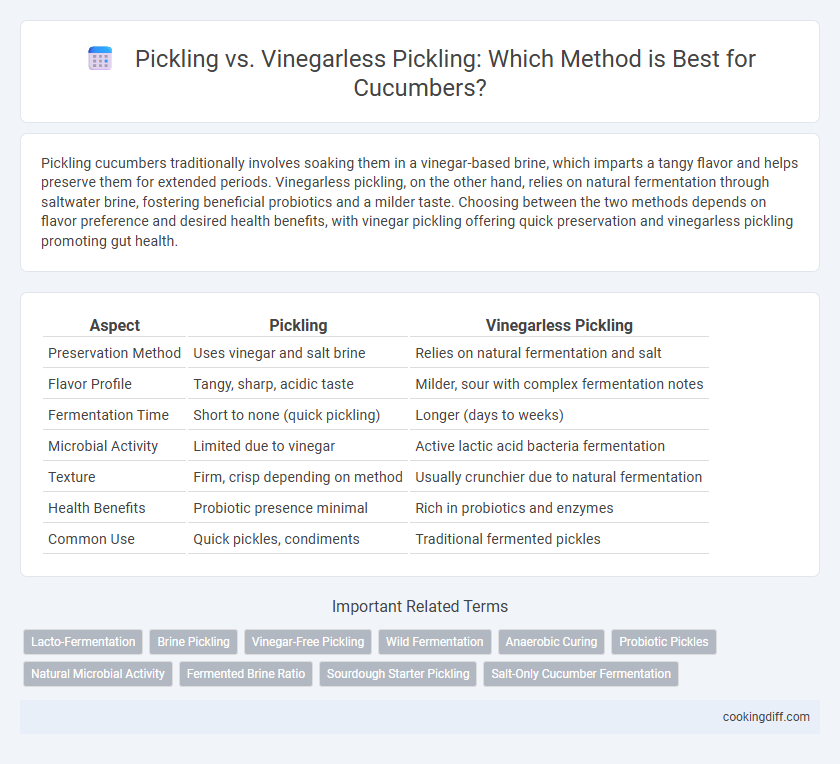
Pickling cucumbers traditionally involves soaking them in a vinegar-based brine, which imparts a tangy flavor and helps preserve them for extended periods. Vinegarless pickling, on the other hand, relies on natural fermentation through saltwater brine, fostering beneficial probiotics and a milder taste. Choosing between the two methods depends on flavor preference and desired health benefits, with vinegar pickling offering quick preservation and vinegarless pickling promoting gut health.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pickling | Vinegarless Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Preservation Method | Uses vinegar and salt brine | Relies on natural fermentation and salt |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, sharp, acidic taste | Milder, sour with complex fermentation notes |
| Fermentation Time | Short to none (quick pickling) | Longer (days to weeks) |
| Microbial Activity | Limited due to vinegar | Active lactic acid bacteria fermentation |
| Texture | Firm, crisp depending on method | Usually crunchier due to natural fermentation |
| Health Benefits | Probiotic presence minimal | Rich in probiotics and enzymes |
| Common Use | Quick pickles, condiments | Traditional fermented pickles |
Introduction to Cucumber Pickling Methods
Cucumber pickling involves preserving cucumbers through fermentation or acidic brining to enhance flavor and shelf life. Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation without added vinegar, creating a distinct tang and beneficial probiotics.
- Traditional Pickling - Uses vinegar for immediate acidity, ensuring quick preservation and a sharp taste.
- Vinegarless Pickling - Depends on lactic acid fermentation, which develops complex flavors over time.
- Health Benefits - Vinegarless pickles offer probiotics that support digestive health, unlike vinegar-based methods.
Choosing between these methods depends on desired flavor profiles and preservation preferences.
What is Traditional Vinegar Pickling?
Traditional vinegar pickling involves immersing cucumbers in a solution of vinegar, water, salt, and spices to achieve preservation and flavor enhancement. This method relies on the acidity of vinegar to inhibit bacterial growth and create a distinctive tangy taste.
- Acidic Environment - Vinegar creates an acidic environment that preserves cucumbers by preventing the growth of harmful bacteria.
- Flavor Infusion - The mixture of vinegar with herbs and spices penetrates the cucumbers, imparting a sharp, tangy flavor.
- Shorter Processing Time - Vinegar pickling typically requires less time compared to natural fermentation methods, making it faster to produce pickles.
Understanding Vinegarless Pickling (Lacto-Fermentation)
Vinegarless pickling, or lacto-fermentation, preserves cucumbers through natural fermentation using salt and water, promoting beneficial lactic acid bacteria. This method enhances flavor complexity and probiotic benefits compared to traditional vinegar-based pickling.
- Lacto-Fermentation Process - Involves submerging cucumbers in a salt brine that encourages the growth of lactobacillus bacteria, producing natural acidity.
- Health Benefits - Rich in probiotics that support gut health and improve digestion, unlike vinegar pickling which lacks live cultures.
- Flavor Development - Produces a tangy, robust flavor profile with depth that vinegar does not impart, adding unique taste to cucumbers.
Ingredient Differences: Vinegar vs. Salt Brine
| Pickling Method | Main Ingredient | Flavor Profile | Preservation Mechanism |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Pickling | Vinegar | Tangy and acidic with a sharp bite | Acidic environment from vinegar inhibits bacterial growth |
| Vinegarless Pickling | Salt brine | Complex, sour, and mildly effervescent due to natural fermentation | Lactic acid produced by fermentation preserves cucumbers |
Taste Profiles: Tangy vs. Savory Cucumbers
Pickling cucumbers with vinegar creates a tangy flavor profile characterized by sharp acidity and a crisp bite, enhancing their refreshing qualities. This method intensifies the cucumber's natural brightness while imparting a classic pickled sourness that balances sweetness and saltiness.
Vinegarless pickling relies on lacto-fermentation, producing a more savory, umami-rich taste with subtle sour notes from naturally developed lactic acid. This process results in cucumbers with a complex, mildly tangy flavor and a tender texture that highlights earthier, deeper flavor nuances.
Health Benefits: Probiotics and Preservation
Pickling cucumbers using traditional fermentation methods promotes the growth of probiotics, which support gut health and improve digestion. Vinegarless pickling preserves cucumbers naturally through lactic acid bacteria, enhancing beneficial microflora without adding acidity from vinegar.
Probiotic-rich pickles contribute to a balanced microbiome and strengthen the immune system by increasing beneficial bacteria in the gut. Vinegarless pickling maintains the natural enzymes and vitamins in cucumbers, providing higher nutritional value compared to vinegar-based pickling. Both methods extend shelf life, but fermentation-based pickling offers superior health benefits through live cultures and natural preservation.
Texture and Crunch: Which Method Wins?
Which pickling method provides a better texture and crunch for cucumbers? Traditional pickling uses vinegar that helps preserve the firmness, resulting in a crisp bite. Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation, producing a tangy flavor with slightly softer but still pleasantly crunchy cucumbers.
Safety Considerations in Pickling Processes
Pickling cucumbers using traditional vinegar-based methods ensures a low pH environment that effectively inhibits the growth of harmful bacteria like Clostridium botulinum, enhancing food safety. Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation, requiring precise salt concentrations and controlled temperatures to prevent the risk of spoilage and pathogens. Proper hygiene and storage conditions are critical in both methods to maintain the safety and quality of pickled cucumbers.
Popular Recipes for Each Pickling Style
Traditional pickling of cucumbers typically involves a vinegar-based brine, featuring popular recipes like classic dill pickles and bread-and-butter pickles, which balance acidity with flavors such as garlic, dill, and sugar. These recipes are favored for their crisp texture and tangy taste, making them staples in many households.
Vinegarless pickling, also known as lacto-fermentation, relies on natural bacteria to ferment cucumbers, resulting in recipes like traditional German sauerkraut-style pickles and Korean cucumber kimchi. The process enhances probiotic content and produces a complex, sour flavor profile without the sharpness of vinegar.
Related Important Terms
Lacto-Fermentation
Lacto-fermentation preserves cucumbers by naturally producing lactic acid through beneficial bacteria, enhancing flavor complexity and probiotic benefits compared to vinegarless pickling methods that rely more on salt brines without the same microbial activity. This process supports gut health and creates a tangy, crisp texture distinct from traditional vinegar-based pickled cucumbers.
Brine Pickling
Brine pickling preserves cucumbers in a saltwater solution that promotes fermentation by lactic acid bacteria, enhancing flavor complexity and crispness without the sharpness of vinegar. Vinegarless pickling relies exclusively on this natural fermentation process, resulting in probiotic-rich cucumbers with a balanced, tangy taste distinct from the more acidic profile of vinegar-based pickles.
Vinegar-Free Pickling
Vinegar-free pickling for cucumbers relies on fermentation through natural lactic acid bacteria, producing a tangy flavor without added vinegar, which enhances probiotic benefits and creates a complex, mildly sour taste profile. This method preserves the cucumbers' crisp texture while allowing the development of unique enzymatic compounds, making it a favored technique in traditional kosher dills and homemade pickles.
Wild Fermentation
Wild fermentation in vinegarless pickling relies on naturally occurring lactic acid bacteria on cucumber skins to create a tangy flavor and preserve the cucumbers without added vinegar. This traditional method enhances probiotic content and develops complex, naturally balanced sourness unparalleled in vinegar-based pickling.
Anaerobic Curing
Pickling cucumbers through anaerobic curing involves fermenting them in a saltwater brine, promoting lactic acid bacteria growth while preventing oxygen exposure, which enhances flavor development and preservation without vinegar. Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation under airtight conditions, producing probiotic-rich cucumbers with a distinct tang compared to traditional vinegar-based methods.
Probiotic Pickles
Probiotic pickles, created through traditional pickling without vinegar, harness natural fermentation by Lactobacillus bacteria, enhancing gut health with beneficial probiotics. Vinegarless pickling preserves the cucumbers' natural enzymes and live cultures, differentiating it from vinegar-based methods that lack probiotic benefits.
Natural Microbial Activity
Pickling cucumbers through traditional methods relies on natural microbial activity, where lactic acid bacteria ferment sugars to produce a distinctive tang and preserve the cucumbers. Vinegarless pickling enhances this natural fermentation process by maintaining an alkaline environment that supports beneficial bacteria growth without introducing acetic acid.
Fermented Brine Ratio
Fermented brine ratio in traditional pickling typically involves a higher salt concentration, around 5-8% by weight, to encourage beneficial lactic acid bacteria growth essential for fermentation. Vinegarless pickling relies exclusively on this fermented brine, whereas vinegar-based pickling mixes lower salt brine with acetic acid vinegar, resulting in different flavor profiles and preservation mechanisms.
Sourdough Starter Pickling
Pickling cucumbers with sourdough starter enhances natural fermentation by leveraging wild yeast and lactic acid bacteria, resulting in a complex, tangy flavor compared to traditional vinegar-based methods. Vinegarless pickling with sourdough starter preserves probiotics and creates a crunchy texture while maintaining nutritional benefits absent in vinegar-preserved cucumbers.
Pickling vs Vinegarless Pickling for cucumbers Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com