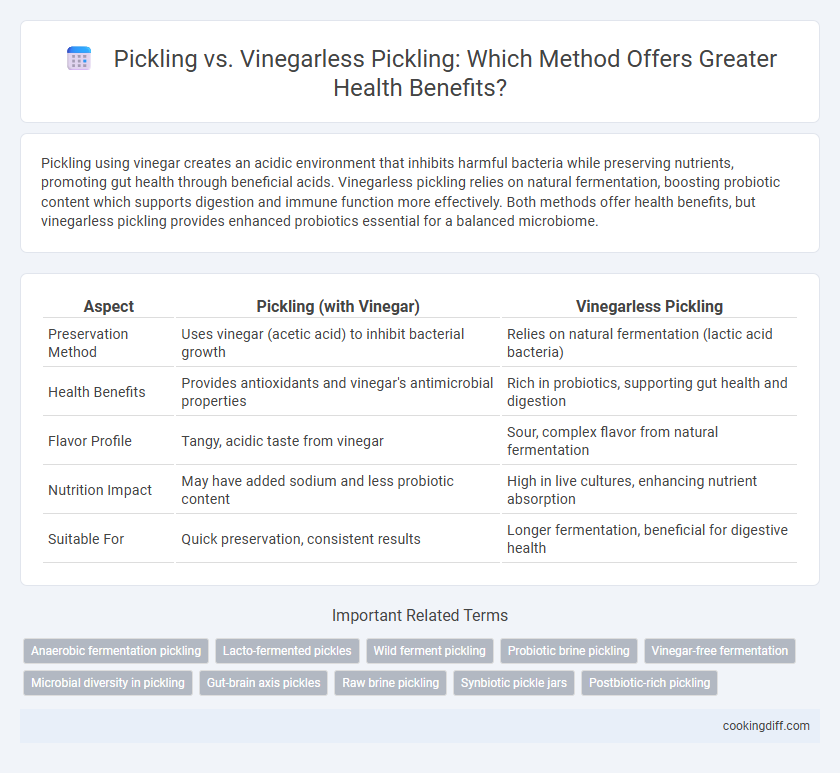
Pickling using vinegar creates an acidic environment that inhibits harmful bacteria while preserving nutrients, promoting gut health through beneficial acids. Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation, boosting probiotic content which supports digestion and immune function more effectively. Both methods offer health benefits, but vinegarless pickling provides enhanced probiotics essential for a balanced microbiome.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Pickling (with Vinegar) | Vinegarless Pickling |
|---|---|---|
| Preservation Method | Uses vinegar (acetic acid) to inhibit bacterial growth | Relies on natural fermentation (lactic acid bacteria) |
| Health Benefits | Provides antioxidants and vinegar's antimicrobial properties | Rich in probiotics, supporting gut health and digestion |
| Flavor Profile | Tangy, acidic taste from vinegar | Sour, complex flavor from natural fermentation |
| Nutrition Impact | May have added sodium and less probiotic content | High in live cultures, enhancing nutrient absorption |
| Suitable For | Quick preservation, consistent results | Longer fermentation, beneficial for digestive health |
Introduction to Pickling and Vinegarless Pickling
Pickling is a traditional preservation method that uses vinegar or brine to ferment and flavor vegetables, enhancing their shelf life and nutritional value. Vinegar-based pickling introduces beneficial acids and probiotics that support digestive health.
Vinegarless pickling relies on natural fermentation without added vinegar, often using salt and water to encourage lactic acid bacteria growth. This method can boost probiotic content further and reduce acidity, making it gentler on the stomach for sensitive individuals.
Traditional Pickling Methods Explained
Traditional pickling methods utilize natural fermentation processes, promoting beneficial probiotics that support gut health and enhance nutrient absorption. Unlike vinegarless pickling, which relies primarily on acidic solutions, fermented pickles develop complex flavors and maintain higher levels of vitamins like B and C. Consuming naturally fermented pickles can improve digestion, strengthen the immune system, and reduce inflammation more effectively than vinegar-based alternatives.
What Is Vinegarless Pickling?
| Vinegarless pickling, also known as lacto-fermentation, uses natural bacterial cultures to preserve vegetables by producing lactic acid instead of using vinegar. This method enhances the nutritional profile by increasing probiotics, which support gut health and improve digestion. It maintains the natural flavor and retains more vitamins compared to traditional vinegar pickling, making it a healthier alternative. |
Nutritional Profiles: Pickling vs Vinegarless Pickling
Pickling with vinegar typically preserves foods by creating an acidic environment that inhibits bacterial growth while adding antioxidants and vitamin C. Vinegarless pickling, often involving fermentation, enhances probiotic content which benefits gut health and digestion.
The nutritional profile of vinegar-based pickling includes lower calorie count and increased vitamin preservation due to the acidic medium. Vinegarless pickling boosts beneficial lactic acid bacteria, enhancing immune function and nutrient absorption. Both methods retain essential minerals, but vinegarl ess pickling contributes more to intestinal flora diversity and overall microbiome balance.
Impact on Gut Health and Probiotics
Traditional pickling with vinegar creates an acidic environment that inhibits probiotic growth, limiting gut health benefits. Vinegarless pickling encourages natural fermentation, fostering beneficial bacteria that enhance digestive health.
- Probiotic Preservation - Vinegarless pickling promotes Lactobacillus growth, essential for balancing gut microbiota.
- Digestive Enzyme Activity - Naturally fermented pickles contain enzymes that aid nutrient absorption and digestion.
- Immune System Support - Probiotics in vinegarless pickles help strengthen immune defenses by improving intestinal flora.
Sodium Content Comparison
Pickling traditionally involves soaking foods in a vinegar or brine solution that often contains high levels of sodium, which can contribute to increased blood pressure and heart disease risk. Vinegarless pickling, also known as lacto-fermentation, relies on natural bacteria to preserve foods without added salt, significantly reducing sodium content. Choosing vinegarless pickling methods can support heart health by minimizing sodium intake while preserving beneficial probiotics.
Antioxidant Retention in Pickled Foods
How does antioxidant retention compare between traditional pickling and vinegarless pickling methods? Vinegarless pickling, often utilizing fermentation, promotes higher levels of antioxidants like vitamin C and polyphenols due to the preservation of enzymatic activity. Traditional pickling with vinegar may reduce antioxidant content because of acidic exposure and heat during processing.
Potential Health Risks and Safety Precautions
Pickling with vinegar creates an acidic environment that inhibits harmful bacterial growth, reducing the risk of foodborne illness. Vinegarless pickling relies on fermentation, which requires precise control of conditions to prevent contamination and ensure safety.
- Risk of Botulism - Improperly fermented or low-acid products can harbor Clostridium botulinum, posing serious health risks.
- pH Monitoring - Maintaining a pH below 4.6 is essential in vinegar-based pickling to prevent microbial growth.
- Sanitation Practices - Sterilizing jars and using clean equipment is critical to minimize contamination in both pickling methods.
Suitability for Special Diets
Pickling traditionally uses vinegar, which can be high in acidity and sodium, potentially causing issues for individuals with acid reflux or hypertension. Vinegarless pickling, often utilizing fermentation, provides probiotics that support gut health and is generally better suited for low-sodium and low-acid diets.
- Low-Sodium Diets - Vinegarless pickling reduces sodium intake compared to vinegar-based methods.
- Gut Health - Fermentation in vinegarless pickling enhances probiotic content, benefiting digestion.
- Acid Sensitivity - Vinegarless pickles have lower acidity, making them more suitable for acid-sensitive individuals.
Choosing between pickling and vinegarless pickling depends on specific dietary restrictions and health goals.
Related Important Terms
Anaerobic fermentation pickling
Anaerobic fermentation pickling preserves beneficial probiotics by naturally fermenting vegetables without vinegar, enhancing gut health and boosting the immune system. This method increases levels of vitamin K and B vitamins, while reducing sodium content compared to traditional vinegar pickling.
Lacto-fermented pickles
Lacto-fermented pickles offer superior health benefits compared to vinegarless pickling by promoting beneficial probiotics that improve gut microbiota and enhance digestion. The natural fermentation process increases vitamin content and supports immune function without the high acidity typically found in vinegar-based methods.
Wild ferment pickling
Wild ferment pickling enhances gut health by promoting natural probiotic growth through lactic acid bacteria, unlike vinegarless pickling methods that may lack beneficial microbes. This traditional fermentation process increases nutrient bioavailability and supports a healthy digestive system more effectively than vinegar-based pickling.
Probiotic brine pickling
Probiotic brine pickling promotes gut health by encouraging beneficial bacteria growth, unlike vinegarless pickling which lacks this microbial fermentation process. The live cultures produced in brine pickling enhance digestion and boost the immune system, making it a healthier option compared to vinegar-based methods.
Vinegar-free fermentation
Vinegar-free fermentation in pickling enhances gut health by promoting beneficial probiotics, unlike traditional vinegar pickling which relies on acetic acid for preservation without probiotic formation. This natural fermentation process increases bioavailability of nutrients and supports the immune system through the growth of live, active cultures in fermented vegetables.
Microbial diversity in pickling
Pickling enhances microbial diversity by fostering beneficial lactic acid bacteria that promote gut health, whereas vinegarless pickling relies solely on natural fermentation, potentially increasing probiotics without the acidity of vinegar. This microbial richness supports improved digestion and boosts the immune system through the proliferation of diverse, health-supporting microbes.
Gut-brain axis pickles
Pickling with vinegar promotes probiotic-rich fermentation that supports the gut-brain axis by enhancing beneficial gut microbiota, whereas vinegarless pickling often retains more live bacteria and enzymes, offering superior gut microbiome modulation and improved cognitive function. Fermented pickles made without vinegar contain higher levels of lactic acid bacteria, which influence neurotransmitter production and reduce inflammation linked to mental health disorders.
Raw brine pickling
Raw brine pickling retains beneficial probiotics by fermenting vegetables in a saltwater solution, enhancing gut health and nutrient absorption compared to vinegarless pickling methods, which often lack these live cultures. This natural fermentation process also reduces sodium concentration relative to vinegar-based pickling, supporting cardiovascular wellness.
Synbiotic pickle jars
Synbiotic pickle jars combine traditional fermentation with probiotic cultures, enhancing gut health by promoting beneficial bacteria growth, unlike vinegarless pickling which focuses solely on natural fermentation without added acids. This method not only preserves nutrients but also boosts immune function and digestive balance more effectively than conventional vinegar-based pickling.
Pickling vs Vinegarless pickling for health benefits. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com