Pressure Cooker and Ceramic Pressure Cooker both offer efficient cooking under high pressure, but ceramic models excel in even heat distribution and are less prone to sticking, making them ideal for delicate meals. Pressure Cookers typically heat up faster and are often more durable due to metal construction, suitable for heavier dishes requiring longer cooking times. Choosing between the two depends on your cooking preferences, with ceramic pressure cookers favored for gentle, flavorful results and standard pressure cookers for robust, quick pressure-cooking.
Table of Comparison
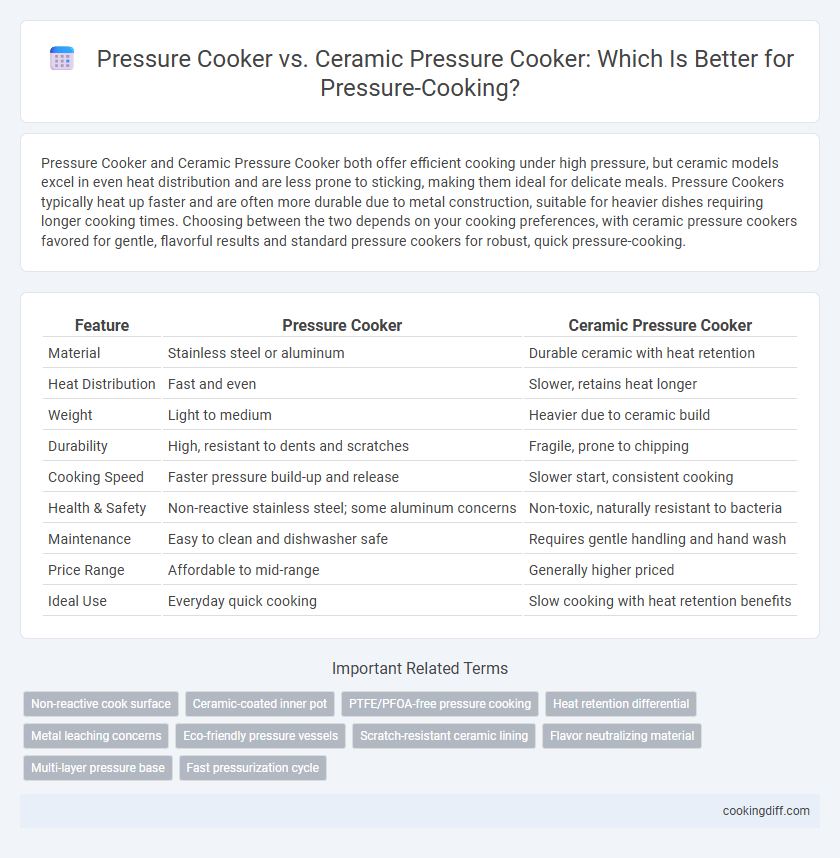
| Feature | Pressure Cooker | Ceramic Pressure Cooker |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Stainless steel or aluminum | Durable ceramic with heat retention |
| Heat Distribution | Fast and even | Slower, retains heat longer |
| Weight | Light to medium | Heavier due to ceramic build |
| Durability | High, resistant to dents and scratches | Fragile, prone to chipping |
| Cooking Speed | Faster pressure build-up and release | Slower start, consistent cooking |
| Health & Safety | Non-reactive stainless steel; some aluminum concerns | Non-toxic, naturally resistant to bacteria |
| Maintenance | Easy to clean and dishwasher safe | Requires gentle handling and hand wash |
| Price Range | Affordable to mid-range | Generally higher priced |
| Ideal Use | Everyday quick cooking | Slow cooking with heat retention benefits |
Introduction to Pressure Cookers and Ceramic Pressure Cookers
Pressure cookers utilize steam pressure to cook food quickly and efficiently, preserving nutrients and flavors. Ceramic pressure cookers feature a non-metallic, heat-retentive ceramic pot that ensures even cooking and easy cleanup. Choosing between traditional and ceramic pressure cookers depends on cooking preferences, material durability, and heat distribution needs.
Material Composition: Steel vs Ceramic
Pressure cookers are commonly constructed from stainless steel, known for its durability, heat conductivity, and resistance to corrosion, ensuring efficient and long-lasting cooking performance. Ceramic pressure cookers, however, feature an inner pot made from ceramic material that offers non-reactive cooking surfaces, which prevents food from absorbing metallic tastes and promotes even heat distribution.
Steel pressure cookers are prized for their strength and ability to withstand high pressure safely, making them ideal for rapid cooking and frequent use. Ceramic models provide a healthier cooking alternative by minimizing the risk of chemical leaching, but they tend to be more fragile and less resistant to thermal shock compared to steel counterparts.
Heat Retention and Distribution Differences
Pressure cookers typically use metal construction to provide rapid heat distribution and efficient heat retention, while ceramic pressure cookers excel at maintaining consistent heat over longer periods due to their thicker walls. The metal pressure cooker heats up and cools down quickly, offering precision in temperature control compared to the slower thermal response of ceramic models.
- Metal Pressure Cookers Provide Quick Heat Distribution - They allow food to cook evenly and rapidly by efficiently transferring heat through stainless steel or aluminum materials.
- Ceramic Pressure Cookers Offer Superior Heat Retention - Their denser ceramic walls hold heat longer, maintaining steady cooking temperatures without frequent energy input.
- Metal Cookers Enable Faster Temperature Adjustments - Their quick heat response supports precise control during pressure cooking cycles compared to the slower thermal adjustments in ceramic cookers.
Cooking Performance and Food Quality
Pressure cookers provide rapid and consistent cooking by maintaining high steam pressure, which significantly reduces cooking time while preserving nutrients. Ceramic pressure cookers distribute heat more evenly and retain moisture better, resulting in enhanced food texture and flavor. Both types offer excellent cooking performance, but ceramic models often yield superior food quality due to their non-reactive and gentle heating properties.
Safety Features Comparison
Pressure cookers typically include multiple safety mechanisms such as pressure release valves, locking lids, and gasket release systems to prevent accidental opening and over-pressurization. Ceramic pressure cookers enhance safety with natural heat retention properties and often incorporate non-toxic, chemical-free materials that reduce the risk of harmful fumes.
While traditional pressure cookers rely heavily on mechanical safety features, ceramic pressure cookers emphasize both mechanical and material safety by using durable, heat-resistant ceramic coatings that resist cracking and bursting. The combination of these factors makes ceramic pressure cookers a safer alternative for users concerned about long-term health and safety risks during pressure cooking.
Durability and Longevity
Pressure cookers made from stainless steel are renowned for their exceptional durability, resisting dents and corrosion over years of use. Ceramic pressure cookers, while offering aesthetic appeal and non-toxic cooking surfaces, tend to have more fragile exteriors that may chip or crack under heavy use.
- Stainless Steel Durability - Stainless steel pressure cookers maintain structural integrity and resist rust, ensuring long-lasting performance.
- Ceramic Fragility - Ceramic-coated pressure cookers are prone to chipping and cracking if mishandled or subjected to sudden impacts.
- Wear Resistance - Steel models withstand repeated heating cycles without degrading, while ceramic coatings can wear down over time, reducing their longevity.
Choosing stainless steel pressure cookers generally guarantees superior durability and longer lifespan compared to ceramic options.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Which pressure cooker offers greater ease of cleaning and maintenance, traditional pressure cookers or ceramic pressure cookers? Ceramic pressure cookers typically feature non-stick surfaces that simplify residue removal and reduce scrubbing time. Traditional pressure cookers often require more thorough cleaning due to stainless steel or aluminum construction, which can retain food particles more stubbornly.
Health and Non-Toxicity Considerations
| Material Composition | Pressure Cookers are typically made of stainless steel or aluminum, which may release trace metals under high heat, while Ceramic Pressure Cookers use a non-reactive, inorganic ceramic coating that prevents metal leaching. |
| Health Impact | Ceramic Pressure Cookers offer non-toxic cooking surfaces free from PFOA, PTFE, and other harmful chemicals, reducing risk of exposure to toxic substances common in traditional metal pressure cookers with synthetic coatings. |
| Durability and Maintenance | Stainless steel models withstand high pressure and frequent use but may require careful cleaning to avoid corrosion; ceramics provide excellent heat retention without degrading or releasing toxins, though they need gentle handling to prevent chipping. |
Cost and Value for Money
Pressure cookers generally offer a lower upfront cost compared to ceramic pressure cookers, making them more accessible for budget-conscious consumers. Traditional pressure cookers typically use stainless steel or aluminum, which are durable and provide excellent heat conductivity at a more affordable price point.
Ceramic pressure cookers often have a higher initial cost due to their non-toxic, eco-friendly materials and aesthetic appeal. They provide even heat distribution and excellent resistance to high temperatures, which can enhance cooking quality and longevity. For users prioritizing long-term health benefits and modern design, the higher price of ceramic options can represent better value for money despite the premium cost.
Related Important Terms
Non-reactive cook surface
Ceramic pressure cookers feature a non-reactive cooking surface that prevents food from interacting with metal ions, preserving flavors and nutrients better than traditional stainless steel pressure cookers. The non-reactive ceramic coating also reduces the risk of corrosion and is ideal for cooking acidic foods without imparting metallic tastes.
Ceramic-coated inner pot
Ceramic-coated inner pots in pressure cookers offer superior non-stick properties and chemical-free cooking compared to traditional stainless steel or aluminum inner pots. These ceramic coatings ensure even heat distribution, reduce the risk of food sticking or scorching, and provide an eco-friendly, easy-to-clean surface ideal for pressure cooking various recipes.
PTFE/PFOA-free pressure cooking
Pressure cookers made with ceramic materials are typically free from PTFE and PFOA, offering a non-toxic, eco-friendly alternative to traditional metal pressure cookers that may contain these chemicals in their non-stick coatings. Ceramic pressure cookers provide safe, chemical-free pressure-cooking while maintaining heat efficiency and durability, making them ideal for health-conscious users.
Heat retention differential
Pressure cookers with traditional metal construction exhibit superior heat retention compared to ceramic pressure cookers, enabling faster cooking times and better energy efficiency. Ceramic pressure cookers often lose heat more rapidly due to their material properties, which can result in longer cooking durations and less consistent pressure maintenance.
Metal leaching concerns
Metal pressure cookers may pose risks of metal leaching into acidic or high-temperature foods, potentially affecting taste and safety, while ceramic pressure cookers offer a non-reactive cooking surface that minimizes such concerns and preserves food purity. Choosing ceramic pressure cookers reduces exposure to heavy metals like nickel and chromium, commonly found in stainless steel variants, ensuring healthier pressure-cooking outcomes.
Eco-friendly pressure vessels
Ceramic pressure cookers offer an eco-friendly alternative to traditional metal pressure cookers by utilizing non-toxic, recyclable materials that reduce environmental impact. Their natural, chemical-free composition ensures safer cooking, while maintaining efficient heat retention and pressure performance comparable to stainless steel models.
Scratch-resistant ceramic lining
Pressure cookers with scratch-resistant ceramic lining offer enhanced durability and prevent abrasion from metal utensils, ensuring a longer-lasting non-stick surface compared to traditional metal or Teflon-lined models. Ceramic pressure cookers also provide even heat distribution and chemical-free cooking, making them a safer and more sustainable choice for high-pressure cooking environments.
Flavor neutralizing material
Pressure cookers with stainless steel or aluminum interiors are preferred over ceramic pressure cookers for their flavor-neutralizing properties, ensuring true taste preservation during cooking. Ceramic pressure cookers can sometimes impart subtle flavors or absorb odors, making stainless steel options superior for maintaining the integrity of diverse dishes.
Multi-layer pressure base
A multi-layer pressure base enhances heat distribution and retention in both traditional pressure cookers and ceramic pressure cookers, but ceramic models often incorporate a reinforced multi-layer base combining aluminum and stainless steel for superior durability and even cooking. This design ensures efficient pressure buildup and temperature control, optimizing cooking performance while preventing hotspots.
Pressure Cooker vs Ceramic Pressure Cooker for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com