Pressure-cooking uses high heat and steam to cook food quickly, preserving nutrients and tenderizing tough cuts, while sous vide relies on precise temperature control over an extended time to achieve even doneness and enhanced flavor infusion. Pressure-cooking is ideal for fast meal preparation and robust textures, whereas sous vide excels at delicate, consistent results with minimal moisture loss. Both methods offer unique benefits, making the choice dependent on desired cooking speed and texture.
Table of Comparison
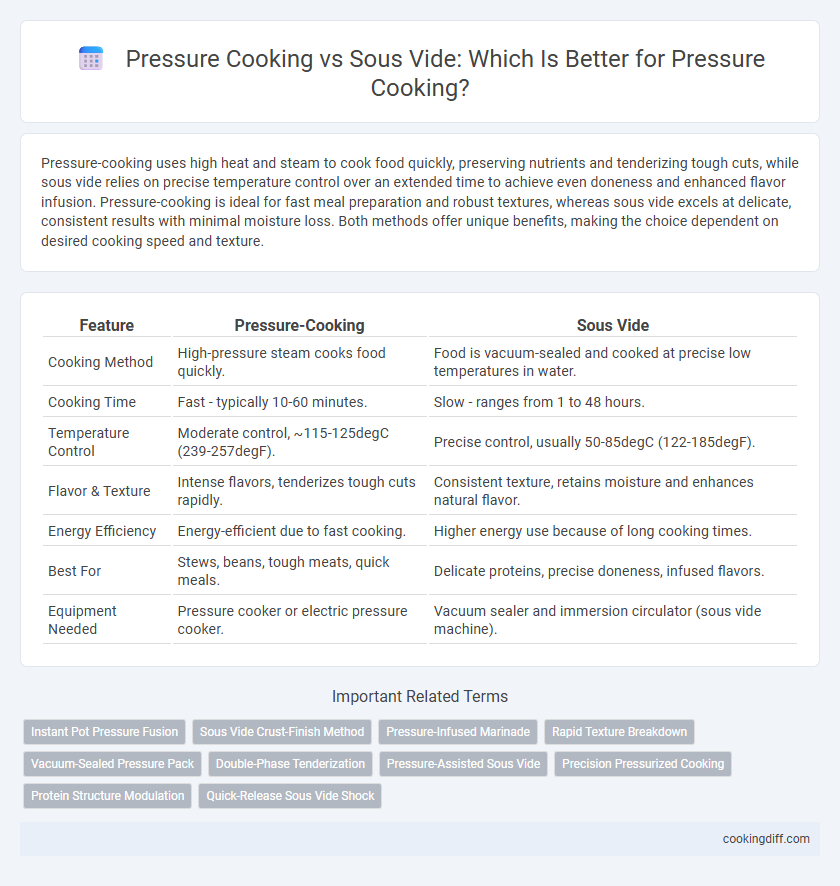
| Feature | Pressure-Cooking | Sous Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High-pressure steam cooks food quickly. | Food is vacuum-sealed and cooked at precise low temperatures in water. |
| Cooking Time | Fast - typically 10-60 minutes. | Slow - ranges from 1 to 48 hours. |
| Temperature Control | Moderate control, ~115-125degC (239-257degF). | Precise control, usually 50-85degC (122-185degF). |
| Flavor & Texture | Intense flavors, tenderizes tough cuts rapidly. | Consistent texture, retains moisture and enhances natural flavor. |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy-efficient due to fast cooking. | Higher energy use because of long cooking times. |
| Best For | Stews, beans, tough meats, quick meals. | Delicate proteins, precise doneness, infused flavors. |
| Equipment Needed | Pressure cooker or electric pressure cooker. | Vacuum sealer and immersion circulator (sous vide machine). |
Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide: Core Differences
Pressure-cooking uses high heat and steam pressure to cook food quickly, while sous vide relies on precise temperature control in a water bath for extended cooking times. Pressure-cooking excels at tenderizing tough cuts of meat in under an hour, whereas sous vide delivers consistent texture and flavor by cooking at low temperatures over several hours. Energy consumption varies, with pressure cookers requiring less time but higher heat, and sous vide appliances maintaining steady, lower temperatures for longer durations.
Cooking Times: Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide
Pressure-cooking significantly reduces cooking times by using high steam pressure to raise the boiling point of water, allowing food to cook up to 70% faster than traditional methods. Sous vide requires longer cooking times, often several hours, as it cooks food slowly at precise, lower temperatures to ensure even doneness and tenderness. For those prioritizing speed, pressure-cooking offers a time-efficient solution compared to the extended durations typical of sous vide cooking.
Flavor and Texture Outcomes Compared
Pressure-cooking intensifies flavors through rapid high-temperature steam, producing tender textures by breaking down tough fibers quickly. Sous vide gently cooks food at precise low temperatures, preserving natural moisture and enhancing subtle flavor nuances without overcooking.
- Flavor Intensity - Pressure-cooking concentrates bold, robust flavors due to high heat, while sous vide maintains delicate and nuanced taste profiles.
- Texture Precision - Pressure-cooking creates soft, fall-apart textures ideal for tough cuts, whereas sous vide yields uniform tenderness, retaining firmness and moisture.
- Cooking Control - Sous vide offers consistent, precise temperature control for repeatable texture outcomes, unlike the variable conditions of pressure-cooking.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Pressure-cooking preserves nutrients by using high heat and steam to cook food quickly, which minimizes nutrient loss compared to traditional methods. Sous vide cooking maintains nutrient levels by cooking food at precise, lower temperatures over a longer period, reducing degradation of heat-sensitive vitamins.
- Pressure-cooking - Retains water-soluble vitamins effectively due to reduced cooking time and sealed environment.
- Sous vide - Excels at preserving delicate nutrients by cooking food evenly at controlled temperatures below boiling point.
- Comparative advantage - Pressure-cooking is faster, while sous vide offers superior nutrient retention for heat-sensitive compounds.
Choosing between pressure-cooking and sous vide depends on balancing nutrient retention with cooking time and food texture preferences.
Equipment and Accessibility
Pressure cookers are widely available and generally more affordable than sous vide machines, making them accessible for everyday cooking. Sous vide equipment requires precise temperature control devices and immersion circulators, which can be more expensive and complex for beginners.
- Pressure Cooker Affordability - Pressure cookers come in various sizes and price ranges, suitable for most household budgets.
- Sous Vide Precision - Sous vide machines need specialized immersion circulators to maintain consistent low temperatures.
- Ease of Use - Pressure cookers operate with straightforward controls, unlike sous vide devices that may require digital programming.
Energy Efficiency: Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide
| Method | Energy Usage | Efficiency Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Pressure-Cooking | Uses high heat and pressure to cook food rapidly, significantly reducing cooking time and energy consumption compared to traditional methods. | Short cooking duration and insulation limit heat loss, maximizing energy efficiency in household kitchens. |
| Sous Vide | Maintains precise low temperatures over extended periods, resulting in continuous energy consumption despite moderate power requirements. | Long cooking times with constant heating and water circulation increase cumulative energy usage in professional and home settings. |
Versatility in Recipes
Which method offers greater versatility in recipes, pressure-cooking or sous vide? Pressure-cooking excels in preparing a wide array of meals quickly, from stews and soups to grains and tough cuts of meat, making it ideal for diverse culinary needs. Sous vide provides precise temperature control for delicate foods but generally requires longer cooking times and specialized equipment.
Safety Considerations for Both Methods
Pressure cooking involves high temperatures and sealed environments, requiring robust safety features like pressure release valves and locking lids to prevent accidents. Sous vide cooking operates at lower temperatures in water baths, minimizing risks but necessitating precise temperature control to avoid bacterial growth.
Both methods demand careful attention to food handling and equipment maintenance to ensure safety. Understanding the specific safety protocols for each technique is essential to reduce hazards and achieve optimal cooking results.
Cost Comparison and Investment
Pressure cookers generally require a lower initial investment compared to sous vide equipment, with prices starting as low as $50 for basic models. Sous vide systems, including immersion circulators and vacuum sealers, typically cost between $100 to $300, making pressure cooking more budget-friendly for beginners.
Long-term costs for pressure cooking remain minimal due to the absence of additional accessories and lower energy consumption. Sous vide cooking demands consistent use of vacuum bags and precise temperature controls, which can increase operational expenses over time. Evaluating both upfront costs and ongoing expenses makes pressure cooking a more economical choice for home cooks focused on cost efficiency.
Related Important Terms
Instant Pot Pressure Fusion
Instant Pot Pressure Fusion combines pressure-cooking and sous vide techniques to offer faster cooking times with precise temperature control, optimizing texture and flavor retention in meals. This hybrid appliance reduces nutrient loss typical in traditional pressure cooking while delivering the tender results associated with sous vide, making it ideal for versatile, efficient meal preparation.
Sous Vide Crust-Finish Method
The Sous Vide Crust-Finish Method combines precise temperature control from sous vide cooking with a quick pressure-cooking step to tenderize food rapidly while retaining moisture. This hybrid technique achieves a perfect balance of evenly cooked interiors and a flavorful, crispy crust that traditional pressure-cooking alone often lacks.
Pressure-Infused Marinade
Pressure-cooking significantly reduces marination time by infusing flavors rapidly under high pressure, enhancing the penetration of marinades compared to the slow, precise temperature control of sous vide. This method intensifies taste and tenderizes proteins swiftly, making pressure-infused marinades ideal for quick, flavorful meal preparation.
Rapid Texture Breakdown
Pressure-cooking uses high steam pressure to rapidly break down tough fibers in meats and vegetables, significantly reducing cooking time compared to sous vide. Sous vide relies on precise low-temperature water baths that slowly soften food textures, making pressure-cooking the ideal method for rapid texture breakdown.
Vacuum-Sealed Pressure Pack
Pressure-cooking with vacuum-sealed pressure packs significantly accelerates cooking times by creating an airtight environment that traps steam and intensifies heat penetration, unlike sous vide which relies on low-temperature water baths for gradual cooking. The vacuum-sealed bags used in pressure-cooking prevent moisture loss and retain nutrients more effectively compared to traditional ziplock bags used in sous vide, enhancing flavor concentration and texture.
Double-Phase Tenderization
Pressure-cooking achieves double-phase tenderization by combining high-temperature steam with intense pressure, rapidly breaking down tough connective tissues and collagen in meat. Sous vide offers precise temperature control for slow, uniform protein denaturation but lacks the rapid pressure-induced phase change that accelerates tenderization in pressure-cooking.
Pressure-Assisted Sous Vide
Pressure-assisted sous vide combines the precise temperature control of sous vide with elevated pressure to accelerate cooking times and enhance flavor infusion. This hybrid method preserves texture and nutrients more effectively than traditional pressure-cooking while delivering consistently tender and evenly cooked results.
Precision Pressurized Cooking
Pressure-cooking delivers rapid, high-temperature cooking by trapping steam under high pressure, which significantly reduces cooking times while preserving nutrients and flavors. Precision pressurized cooking, unlike sous vide's low, controlled temperatures, relies on variable pressure settings to achieve consistent, tender results in a fraction of the time.
Protein Structure Modulation
Pressure cooking rapidly alters protein structures through intense heat and high pressure, resulting in faster denaturation and breakdown of connective tissues compared to sous vide, which uses low, precise temperatures over extended periods to gently modulate protein texture and preserve moisture. This difference in heat application leads to pressure cooking producing tender, robust flavors quickly, while sous vide retains a more delicate, evenly cooked protein profile.
Pressure-cooking vs Sous vide for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com