Quick pressure-cooking rapidly tenderizes food by using high temperature and pressure, making it ideal for fast meal preparation. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure to achieve evenly cooked, tender results while preserving moisture and flavor. This method allows for enhanced texture and taste compared to traditional quick pressure-cooking techniques.
Table of Comparison
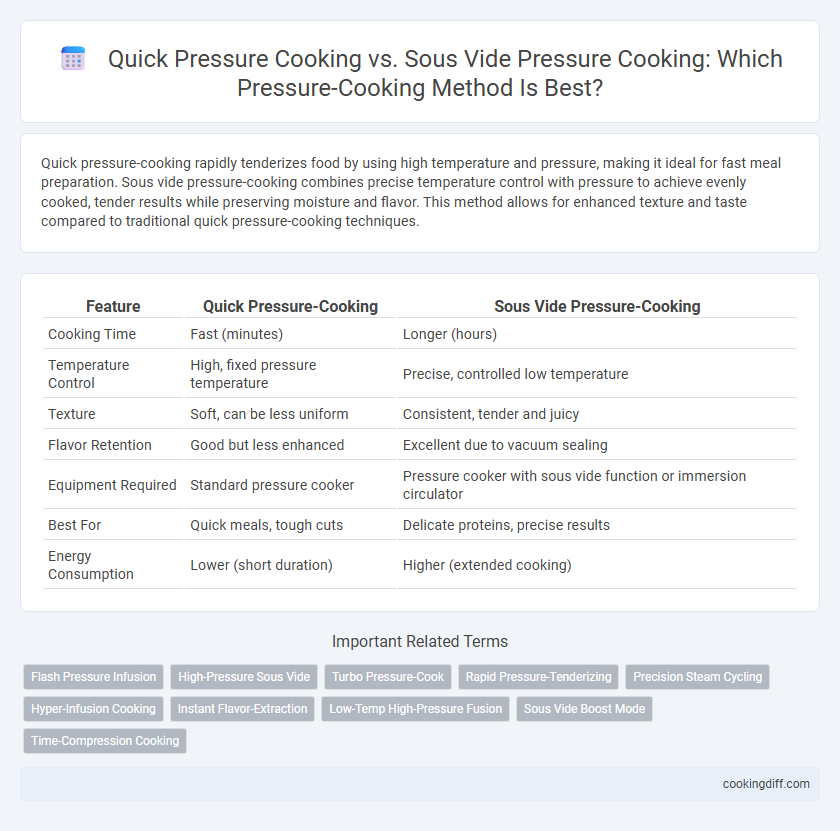
| Feature | Quick Pressure-Cooking | Sous Vide Pressure-Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Time | Fast (minutes) | Longer (hours) |
| Temperature Control | High, fixed pressure temperature | Precise, controlled low temperature |
| Texture | Soft, can be less uniform | Consistent, tender and juicy |
| Flavor Retention | Good but less enhanced | Excellent due to vacuum sealing |
| Equipment Required | Standard pressure cooker | Pressure cooker with sous vide function or immersion circulator |
| Best For | Quick meals, tough cuts | Delicate proteins, precise results |
| Energy Consumption | Lower (short duration) | Higher (extended cooking) |
Quick Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide Pressure-Cooking: An Overview
What are the key differences between quick pressure-cooking and sous vide pressure-cooking? Quick pressure-cooking uses high heat and pressure to drastically reduce cooking time, making it ideal for meals requiring fast preparation. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure, resulting in tender, evenly cooked dishes with enhanced flavor retention.
Speed of Cooking: Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide Methods
Quick pressure-cooking reduces cooking time by utilizing high steam pressure, often completing meals in under 30 minutes, compared to traditional methods. This method is ideal for tenderizing tough cuts of meat rapidly without sacrificing flavor.
Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure, resulting in evenly cooked dishes but requires longer cooking durations, typically 1 to 4 hours. While slower, this technique enhances texture and retains nutrients better than quick pressure-cooking.
Temperature Control in Quick Pressure-Cooking and Sous Vide
Quick pressure-cooking operates at high temperatures, typically around 121degC (250degF), enabling rapid cooking by increasing steam pressure. This method lacks precise temperature control, as it primarily relies on time and pressure settings rather than gradual temperature adjustments.
Sous vide pressure-cooking combines pressure with precise temperature control, maintaining water baths at specific temperatures, often between 55degC to 85degC (131degF to 185degF), for even and consistent cooking. This technique ensures delicate proteins and vegetables retain texture and nutrients, minimizing overcooking compared to quick pressure heat spikes.
Flavor Retention: Comparing Quick and Sous Vide Pressure-Cooking
Quick pressure-cooking uses high heat and rapid pressure changes to lock in flavors quickly, often resulting in slightly diminished aromatic complexity compared to sous vide pressure-cooking. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with gentle pressure, enhancing flavor retention by evenly infusing spices and juices over extended cooking periods. Both methods reduce cooking time significantly, but sous vide pressure-cooking delivers superior depth and consistency in flavor profiles.
Texture Differences: Quick vs Sous Vide Pressure-Cooked Foods
Quick pressure-cooking results in foods with a firmer texture due to high heat applied over a short period. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure, producing tender, evenly cooked textures that retain moisture. The slow, gentle cooking of sous vide pressure methods minimizes fiber breakdown, enhancing mouthfeel compared to rapid pressure-cooking techniques.
Nutrient Preservation: Which Pressure-Cooking Method Wins?
Quick pressure-cooking uses high heat and pressure for a short time, which can cause some nutrient loss. Sous vide pressure-cooking applies controlled low temperature over a longer period, better preserving vitamins and minerals.
- Quick pressure-cooking - Rapid cooking at high pressure may degrade heat-sensitive nutrients like vitamin C and folate.
- Sous vide pressure-cooking - Precise temperature control helps retain more antioxidants and water-soluble vitamins.
- Nutrient retention comparison - Studies show sous vide pressure-cooking often preserves nutritional quality better than traditional quick pressure methods.
Equipment Requirements: Quick Pressure-Cookers vs Sous Vide Setups
Quick pressure-cookers are compact, all-in-one devices designed for rapid cooking using high-pressure steam. Sous vide pressure-cooking requires additional equipment, including a precision immersion circulator and vacuum sealer, to maintain exact temperature control within sealed bags.
- Quick Pressure-Cookers - Typically consist of a sealed pot with a built-in pressure regulator to expedite cooking times.
- Sous Vide Equipment - Involves a water bath with a digital temperature controller for consistent low-temperature cooking.
- Complementary Devices - Sous vide methods often need vacuum sealers to remove air and ensure food safety during pressure application.
Recipe Versatility for Quick and Sous Vide Pressure-Cooking
Quick pressure-cooking offers broad recipe versatility by significantly reducing cooking times for a variety of dishes such as stews, beans, and tough cuts of meat. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure to enhance flavors and textures, ideal for delicate proteins and complex recipes.
- Quick pressure-cooking versatility - Suitable for fast preparation of soups, grains, and braised dishes with consistent results.
- Sous vide precision - Enables slow, controlled cooking for enhanced tenderness and flavor infusion in meats and vegetables.
- Recipe flexibility - Both methods accommodate a range of cuisines, but sous vide pressure-cooking excels in gourmet and intricate recipes.
Choosing between quick and sous vide pressure-cooking depends on whether speed or culinary precision is the priority in recipe versatility.
Energy Efficiency: Quick Pressure-Cooking vs Sous Vide
Quick pressure-cooking uses high heat and pressure to cook food rapidly, significantly reducing cooking time and energy consumption compared to traditional methods. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure, resulting in longer cooking durations but optimized energy use through consistent, lower temperature maintenance.
Quick pressure-cooking maximizes energy efficiency by cutting down total cooking time, which directly lowers electricity or gas usage. Sous vide pressure-cooking's energy efficiency stems from its steady heat application and airtight environment that minimizes heat loss. Both methods offer energy advantages, but quick pressure-cooking tends to be more efficient for rapid meals while sous vide excels in precision cooking with moderate energy savings.
Related Important Terms
Flash Pressure Infusion
Quick pressure-cooking utilizes high pressure and temperature to rapidly tenderize and infuse flavors into food, while sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure to enhance flavor absorption through Flash Pressure Infusion technology. This method accelerates marinade penetration by using rapid pressure cycling, resulting in intensified taste profiles and improved texture without overcooking.
High-Pressure Sous Vide
High-pressure sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with elevated pressure to tenderize proteins faster while preserving moisture and flavor better than traditional quick pressure-cooking. This method enhances texture and nutrient retention by using lower temperatures over longer times under pressure, ideal for delicate foods requiring gentle cooking.
Turbo Pressure-Cook
Turbo Pressure-Cook delivers rapid cooking times by combining high-pressure steam with increased temperature, significantly speeding up the process compared to traditional sous vide pressure-cooking, which uses precise temperature control for even cooking but requires longer durations. This makes Turbo Pressure-Cook ideal for meals needing quick turnaround without sacrificing tenderness or flavor, outperforming sous vide methods in efficiency and convenience.
Rapid Pressure-Tenderizing
Quick pressure-cooking rapidly breaks down collagen and connective tissues in meat through high-temperature steam, drastically reducing cooking time for tender results. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise low-temperature water bath control with subsequent pressure cooking, enhancing flavor infusion while still achieving rapid pressure-tenderizing effects.
Precision Steam Cycling
Quick pressure-cooking relies on high, consistent pressure and temperature to rapidly cook food, whereas sous vide pressure-cooking integrates precise steam cycling control to maintain exact temperature settings for even doneness and enhanced texture. Precision steam cycling optimizes moisture retention and flavor infusion by modulating steam pressure in defined intervals, making sous vide pressure-cooking superior for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Hyper-Infusion Cooking
Quick pressure-cooking accelerates the Hyper-Infusion process by rapidly breaking down food fibers and allowing flavors to penetrate deeply in a short time. Sous vide pressure-cooking enhances Hyper-Infusion through precise temperature control, facilitating gradual and uniform flavor absorption without overcooking.
Instant Flavor-Extraction
Quick pressure-cooking rapidly intensifies flavors by using high heat and pressure to extract essential oils and nutrients from ingredients in a fraction of traditional cooking time. Sous vide pressure-cooking combines precise temperature control with pressure to evenly infuse flavors while retaining moisture and texture, resulting in a more delicate and consistent flavor profile.
Low-Temp High-Pressure Fusion
Quick pressure-cooking relies on high pressure and temperature to rapidly cook food, while sous vide pressure-cooking combines low-temperature precision with elevated pressure to achieve a unique fusion of texture and flavor retention. This Low-Temp High-Pressure Fusion method enhances moisture retention and tenderizes proteins more effectively than traditional pressure-cooking techniques.
Sous Vide Boost Mode
Sous Vide Boost Mode in pressure-cooking enhances precision temperature control by combining rapid pressure heating with sous vide immersion, resulting in evenly cooked meals with superior texture and flavor retention. This method outperforms traditional quick pressure-cooking by minimizing moisture loss and preventing overcooking, ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Quick pressure-cooking vs Sous vide pressure-cooking for pressure-cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com