Roasting vegetables enhances their natural sweetness and produces a crispy exterior through dry heat, allowing for caramelization and rich flavor development. Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to achieve a similarly crisp texture with less oil, making it a quicker and healthier alternative. Both methods create crispy vegetables, but roasting often results in deeper flavor complexity while air frying offers convenience and reduced fat content.
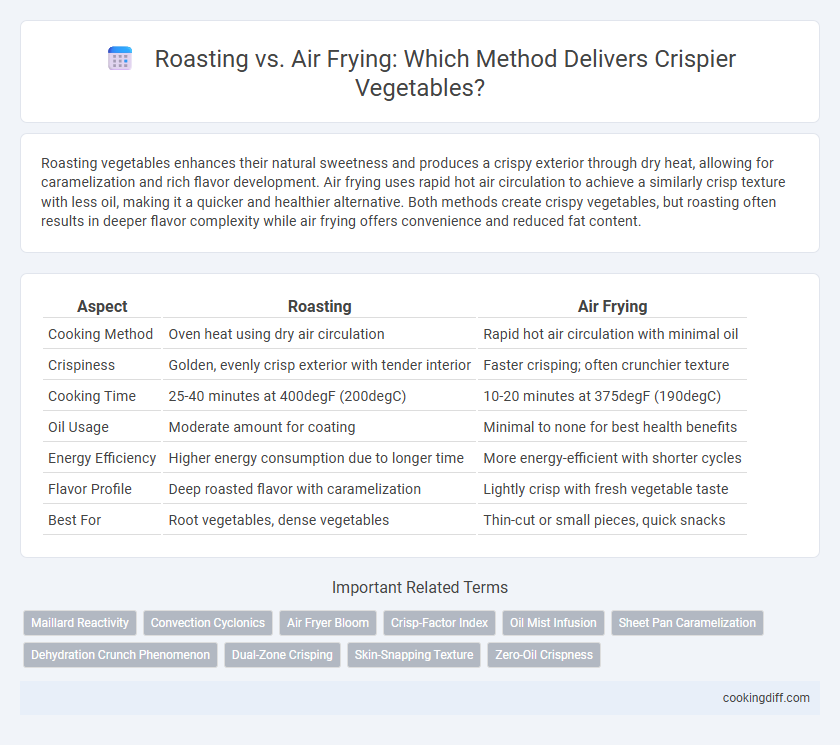
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Roasting | Air Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Oven heat using dry air circulation | Rapid hot air circulation with minimal oil |
| Crispiness | Golden, evenly crisp exterior with tender interior | Faster crisping; often crunchier texture |
| Cooking Time | 25-40 minutes at 400degF (200degC) | 10-20 minutes at 375degF (190degC) |
| Oil Usage | Moderate amount for coating | Minimal to none for best health benefits |
| Energy Efficiency | Higher energy consumption due to longer time | More energy-efficient with shorter cycles |
| Flavor Profile | Deep roasted flavor with caramelization | Lightly crisp with fresh vegetable taste |
| Best For | Root vegetables, dense vegetables | Thin-cut or small pieces, quick snacks |
Introduction: Roasting vs Air Frying for Crispy Vegetables
Roasting and air frying are popular methods for achieving crispy vegetables, each offering distinct techniques and results. Roasting uses dry heat in an oven to caramelize natural sugars, enhancing flavor and producing a tender interior with a crispy exterior. Air frying circulates hot air rapidly, creating a similar crispiness with less oil, making it a healthier alternative for quick vegetable preparation.
Comparing Cooking Techniques: Roasting and Air Frying
Roasting vegetables uses dry heat in an oven, which enhances natural sugars and creates a caramelized exterior. Air frying circulates hot air rapidly to achieve a crispy texture similar to frying but with less oil and faster cooking times.
- Heat Distribution - Roasting relies on radiant heat from the oven, allowing slow and even cooking of vegetables.
- Oil Usage - Air frying requires minimal oil to develop crispiness, making it a healthier alternative to traditional frying.
- Texture Outcome - Roasting provides a tender interior and caramelized edges, while air frying delivers a uniformly crispy outer layer quickly.
Texture and Crispiness: Which Method Wins?
Roasting vegetables in an oven uses dry heat that caramelizes sugars and browns the exterior, creating a deep, crunchy texture that air frying often cannot replicate. The high, consistent heat in roasting produces a thick, crispy layer while keeping the interior tender and moist.
Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to mimic frying effects with less oil, resulting in a lighter crispiness ideal for quick cooking. However, the texture tends to be thinner and less crunchy compared to the robust crispiness achieved through traditional roasting methods.
Flavor Development: Roasted vs Air-Fried Vegetables
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through Maillard reactions and caramelization, producing a rich, complex taste with crispy edges. This method intensifies natural sugars and develops deep, savory notes that air frying often cannot replicate.
Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation to create a crispy texture with less oil, preserving freshness but producing a milder flavor profile. While air-fried vegetables are crispy, they lack the depth and caramelized complexity characteristic of traditional roasting.
Oil Usage: Roasting vs Air Frying Efficiency
Roasting vegetables typically requires more oil to achieve a crispy texture, as the direct contact with the hot pan absorbs oil, enhancing flavor but increasing fat content. Air frying uses significantly less oil by circulating hot air around the food, producing crispiness with minimal added fat.
- Higher Oil Usage in Roasting - Roasting often involves coating vegetables in oil, resulting in greater oil absorption and higher calorie content.
- Lower Oil Requirement in Air Frying - Air frying achieves a crispy exterior by circulating hot air, reducing the need for excessive oil application.
- Efficiency in Oil Utilization - Air frying maximizes oil efficiency by requiring only a small amount of oil for crispiness, making it a healthier alternative to traditional roasting.
Time and Convenience: Which Is Faster and Easier?
Roasting vegetables typically takes 25-40 minutes depending on the oven temperature, while air frying reduces this time to about 15-20 minutes due to faster hot air circulation. Air fryers also preheat quickly, offering greater convenience for speedy meal preparation.
Roasting requires watching the oven and sometimes flipping the vegetables for even crispiness, which can be less hands-off compared to air frying. Air frying delivers consistent crisp results with minimal attention, making it ideal for busy schedules. Both methods produce crispy textures, but air frying wins in efficiency and ease of use.
Nutritional Differences: Roasted vs Air-Fried Veggies
How do the nutritional differences between roasted and air-fried vegetables affect their health benefits? Roasting vegetables can increase the concentration of certain antioxidants but may cause a slight loss of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C. Air frying uses less oil, resulting in lower calorie content and reduced fat intake compared to traditional roasting methods.
Equipment and Space: Oven vs Air Fryer
| Equipment | Space |
|---|---|
| Ovens provide larger capacity for roasting multiple trays of vegetables simultaneously, ideal for batch cooking and achieving even crispiness through consistent heat distribution. | Ovens require significant kitchen space and counter clearance, often needing built-in installation or dedicated countertop room. |
| Air fryers utilize rapid air circulation technology to crisp vegetables efficiently in a compact device, best suited for smaller portions. | Air fryers occupy minimal countertop space, making them convenient for kitchens with limited room and easy to store when not in use. |
Best Vegetables for Roasting and Air Frying
Roasting and air frying both enhance the crispiness of vegetables by using dry heat, but roasting typically suits dense, starchy vegetables while air frying excels with smaller, evenly sized pieces. Vegetables like Brussels sprouts, carrots, and sweet potatoes develop rich caramelization when roasted, whereas air frying is ideal for lighter, quicker-cooking options like zucchini and bell peppers.
- Roasted root vegetables - Carrots, potatoes, and beets gain a deep, sweet flavor and a tender yet crispy texture from dry oven heat.
- Air-fried softer vegetables - Zucchini, mushrooms, and bell peppers crisp quickly due to rapid hot air circulation in air fryers.
- Brussels sprouts and cauliflower - Both methods create crispy edges and maintain moisture, but roasting emphasizes caramelization, while air frying offers faster cooking times.
Choosing between roasting or air frying depends on the vegetable's density and desired texture for optimal crispiness.
Related Important Terms
Maillard Reactivity
Roasting vegetables enhances Maillard reactivity through prolonged high heat, producing deeper caramelization and a richer, more complex flavor profile compared to air frying. Air frying achieves crispiness faster by circulating hot air but may result in less intense Maillard browning due to shorter exposure times and lower surface temperatures.
Convection Cyclonics
Convection cyclonics in roasting evenly circulates hot air around vegetables, producing a uniformly crispy texture by promoting efficient moisture evaporation and caramelization. Air frying also uses convection technology but relies on higher-speed cyclonic airflows, creating a faster cooking process with a similar crispiness while reducing overall oil usage.
Air Fryer Bloom
Air Fryer Bloom technology enhances the air frying process by circulating hot air evenly, resulting in crispier vegetables with a perfectly roasted texture without excessive oil. Compared to traditional roasting, air frying reduces cooking time and boosts nutrient retention while delivering a crunchy exterior and tender interior.
Crisp-Factor Index
Roasting typically achieves a higher Crisp-Factor Index for vegetables by applying consistent dry heat that caramelizes sugars and dehydrates the surface, resulting in a more pronounced crispness. Air frying optimizes the Crisp-Factor Index by circulating hot air rapidly, creating a crispy exterior with less oil, but may yield less intense caramelization compared to traditional roasting.
Oil Mist Infusion
Roasting enhances vegetable crispiness through oil mist infusion, allowing even heat distribution and caramelization that locks in flavor and texture. Air frying uses rapid hot air circulation but provides less direct oil contact, resulting in a lighter crispy coating with reduced oil absorption.
Sheet Pan Caramelization
Roasting vegetables on a sheet pan enhances caramelization through direct contact with hot metal, creating Maillard reactions that develop deep, complex flavors and crispy edges. Air frying circulates hot air rapidly but often results in less intense caramelization and a different texture profile, favoring crispiness over the rich, browned exterior achieved by roasting.
Dehydration Crunch Phenomenon
Roasting enhances the dehydration crunch phenomenon by drawing out moisture from vegetables, intensifying their natural flavors and creating a crisp exterior through Maillard reactions. Air frying achieves similar crispness by circulating hot air rapidly, promoting dehydration with less oil but often yields a lighter texture compared to the deeper caramelization from traditional roasting.
Dual-Zone Crisping
Roasting enhances flavor through Maillard reactions but can result in uneven crispiness, while air frying uses circulating hot air to create a uniformly crispy texture. Dual-zone crisping technology combines both methods by allowing precise temperature control in separate zones, ensuring vegetables are evenly roasted with optimal crispy edges and tender interiors.
Skin-Snapping Texture
Roasting vegetables develops a skin-snapping texture by using dry, intense heat that caramelizes natural sugars and crisps the surface. Air frying achieves similar crispiness through rapid air circulation but may lack the deep caramelization and rich flavors produced by roasting.
Roasting vs Air frying for crispy vegetables Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com