Roasting fish typically involves cooking it evenly using dry heat, often in an oven or over an open flame, preserving its natural flavors and moisture. Coal roasting infuses the fish with a distinct smoky aroma and charred texture due to the direct exposure to hot charcoal, enhancing its richness and depth. Choosing between the two methods depends on the desired flavor profile and cooking environment.
Table of Comparison
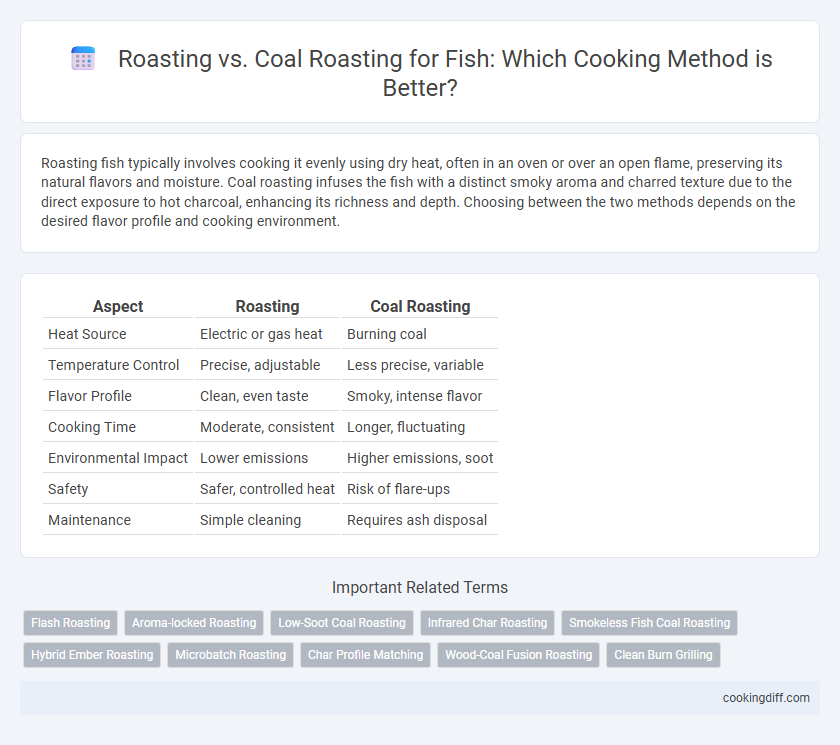
| Aspect | Roasting | Coal Roasting |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Electric or gas heat | Burning coal |
| Temperature Control | Precise, adjustable | Less precise, variable |
| Flavor Profile | Clean, even taste | Smoky, intense flavor |
| Cooking Time | Moderate, consistent | Longer, fluctuating |
| Environmental Impact | Lower emissions | Higher emissions, soot |
| Safety | Safer, controlled heat | Risk of flare-ups |
| Maintenance | Simple cleaning | Requires ash disposal |
Overview: Roasting vs Coal Roasting for Fish
Roasting fish involves cooking it evenly with dry heat, typically in an oven or over an open flame, enhancing its natural flavors and retaining moisture. Coal roasting imparts a smoky aroma and distinct charred taste due to direct exposure to burning coal, often preferred for traditional or outdoor settings. Both methods affect texture and flavor differently, with coal roasting providing a more intense, rustic finish compared to the cleaner, more controlled heat of standard roasting.
Flavor Profiles: Traditional Roasting vs Coal Roasting
| Roasting Method | Flavor Profile |
| Traditional Roasting | Produces a delicate, evenly cooked flavor with subtle caramelization that highlights the fish's natural sweetness and moisture. |
| Coal Roasting | Imparts a smoky, robust taste with a slightly charred exterior, enhancing the fish with complex, earthy undertones and a crisp texture. |
Cooking Techniques: Methods and Tools
Roasting fish uses dry heat typically in an oven or over an open flame, preserving moisture while achieving a crispy exterior, ideal for delicate flavors. Coal roasting, on the other hand, involves direct exposure to charcoal heat, imparting a smoky aroma and intensifying the taste through natural smoke infusion.
Cooking tools for roasting include roasting pans, racks, and ovens that provide controlled temperature settings, ensuring even cooking. Coal roasting requires specialized grills or coal braziers that allow for precise placement of fish over glowing embers, enhancing flavor complexity. Selecting between these methods depends on desired flavor profiles and available equipment, with each technique offering distinct culinary advantages.
Temperature Control in Both Methods
Roasting fish allows precise temperature control through ovens or grills, maintaining consistent heat to ensure even cooking and moisture retention. Coal roasting relies on managing the distance and intensity of charcoal heat, which can introduce variability but imparts a smoky flavor. Temperature sensors and adjustable vents improve control in coal roasting, yet electric or gas roasting offers superior accuracy for delicate fish preparation.
Health Implications: Roasting vs Coal Roasting
Roasting fish using an electric or gas oven produces fewer harmful compounds compared to coal roasting, reducing exposure to carcinogens such as polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbons (PAHs) and benzopyrenes. These toxic substances are often released during coal roasting due to incomplete combustion and direct contact with smoke.
Health risks from coal-roasted fish include increased chances of respiratory issues and long-term diseases due to inhaled smoke particles and carcinogenic residues on the food surface. Opting for roasting methods with controlled temperatures and cleaner fuel sources supports safer consumption and better overall health outcomes.
Texture and Moisture Differences in Fish
Roasting fish typically results in a firmer texture with retained moisture due to controlled heat exposure, while coal roasting imparts a smokier flavor but can lead to drier, flakier flesh. The intense, uneven heat from coal roasting often causes faster moisture loss compared to the gentler heat of conventional roasting.
- Texture Differences - Roasting maintains a tender yet firm fish texture, whereas coal roasting often produces a drier, more brittle surface.
- Moisture Retention - Controlled roasting techniques help preserve internal moisture better than the direct, high heat from coal roasting.
- Flavor Impact - Coal roasting enhances smoky flavors but can compromise juiciness, contrasting with the balanced moisture of roasted fish.
Time Efficiency: Which Method is Faster?
Roasting fish using conventional methods typically requires less time than coal roasting, with average cooking durations ranging from 10 to 15 minutes depending on the fish size and heat intensity. This efficiency stems from the direct heat application in ovens or grills, which allows for consistent temperature control and faster heat penetration.
In contrast, coal roasting involves slower cooking times of approximately 20 to 30 minutes due to the gradual and uneven heat distribution from burning coal. The extended roasting time is often preferred for imparting smoky flavors but is less efficient when time is a critical factor in food preparation.
Recommended Fish Types for Each Method
Roasting fish over direct heat evenly cooks delicate fillets, making it ideal for lean, flaky species. Coal roasting imparts a smoky flavor and is perfect for firmer, oil-rich fish that can withstand longer cooking times without drying out.
- Salmon for Roasting - Its rich texture holds moisture well during high-heat roasting, producing tender results.
- Sea Bass for Coal Roasting - Firm flesh absorbs smoky notes while maintaining structural integrity over coals.
- Trout for Roasting - Its fine flakes cook quickly and evenly in roasting, preserving natural flavors.
Choosing the appropriate fish type enhances the roasting method's effectiveness and flavor profile.
Environmental Impact: Roasting vs Coal Roasting
How does the environmental impact of roasting compare to coal roasting for fish? Roasting fish using electric or gas methods produces significantly fewer carbon emissions and reduces air pollutants compared to traditional coal roasting. Coal roasting releases higher levels of particulate matter and greenhouse gases, contributing to environmental degradation and health risks.
Related Important Terms
Flash Roasting
Flash roasting preserves the delicate texture and natural flavors of fish by rapidly exposing it to high heat, minimizing moisture loss and preventing overcooking compared to traditional coal roasting. Unlike coal roasting, flash roasting reduces smoke and char, resulting in a cleaner taste and a more evenly cooked fish with enhanced nutritional retention.
Aroma-locked Roasting
Aroma-locked roasting preserves the natural oils and enhances the delicate flavors of fish by using controlled heat and minimal smoke, unlike coal roasting, which imparts a stronger, smoky taste but can sometimes overpower the fish's subtle aromas. This method ensures a tender texture and a rich, fresh seafood aroma, offering a refined culinary experience without the heavy smokiness typical of coal roasting.
Low-Soot Coal Roasting
Low-soot coal roasting for fish significantly reduces particulate emissions compared to traditional roasting methods, ensuring a cleaner cooking environment and enhanced flavor retention. This method leverages controlled combustion technology to minimize soot production while maintaining optimal roasting temperatures, preserving the fish's texture and nutritional value.
Infrared Char Roasting
Infrared char roasting offers a cleaner, more efficient method for cooking fish compared to traditional coal roasting by using radiant heat to evenly sear while preserving moisture and flavor. This technique reduces smoke emissions and cooking time, enhancing taste and texture without the intense flare-ups often associated with coal roasting.
Smokeless Fish Coal Roasting
Smokeless fish coal roasting leverages advanced ventilation and high-quality charcoal to minimize smoke emissions while enhancing the fish's natural flavors and achieving an even, crispy texture. This method contrasts traditional coal roasting by significantly reducing harmful pollutants, making it a healthier and more environmentally friendly option without compromising taste or aroma.
Hybrid Ember Roasting
Hybrid ember roasting combines the intense heat of coal roasting with the controlled temperature of traditional roasting, enhancing the natural flavors and texture of fish by providing a smoky aroma and evenly cooked flesh. This method reduces charring and retains moisture better than coal roasting alone, resulting in juicier, more flavorful fish with a perfect balance of crisp skin and tender interior.
Microbatch Roasting
Microbatch roasting offers precise temperature control and uniform heat distribution, enhancing flavor complexity and preserving delicate fish textures compared to coal roasting, which can introduce inconsistent heat and smoky off-flavors. This method reduces contamination risks and allows for detailed profiling of fish roast characteristics, making it ideal for artisanal culinary applications.
Char Profile Matching
Roasting fish with traditional wood enhances flavor complexity through natural char profile matching, delivering subtle smoky notes that complement the fish's oils. Compared to coal roasting, wood roasting provides a more nuanced char, preserving delicate textures while imparting a balanced aroma that elevates the overall taste experience.
Wood-Coal Fusion Roasting
Wood-coal fusion roasting for fish combines the smoky aroma of charcoal with the rich, natural flavors imparted by hardwood, enhancing both texture and taste. This hybrid method ensures even heat distribution and retains moisture, resulting in a perfectly roasted fish with a balanced, deep smoky essence.
Roasting vs Coal Roasting for fish. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com