Roasting vegetables enhances their natural sweetness and creates a caramelized, crispy texture that intensifies flavors through dry heat. Steam infusion, on the other hand, preserves the vegetable's moisture and delicate nutrients, resulting in a tender and vibrant dish with a lighter taste. Choosing between roasting and steam infusion depends on whether you prioritize bold, roasted flavors or fresh, nutrient-retentive qualities in your vegetables.
Table of Comparison
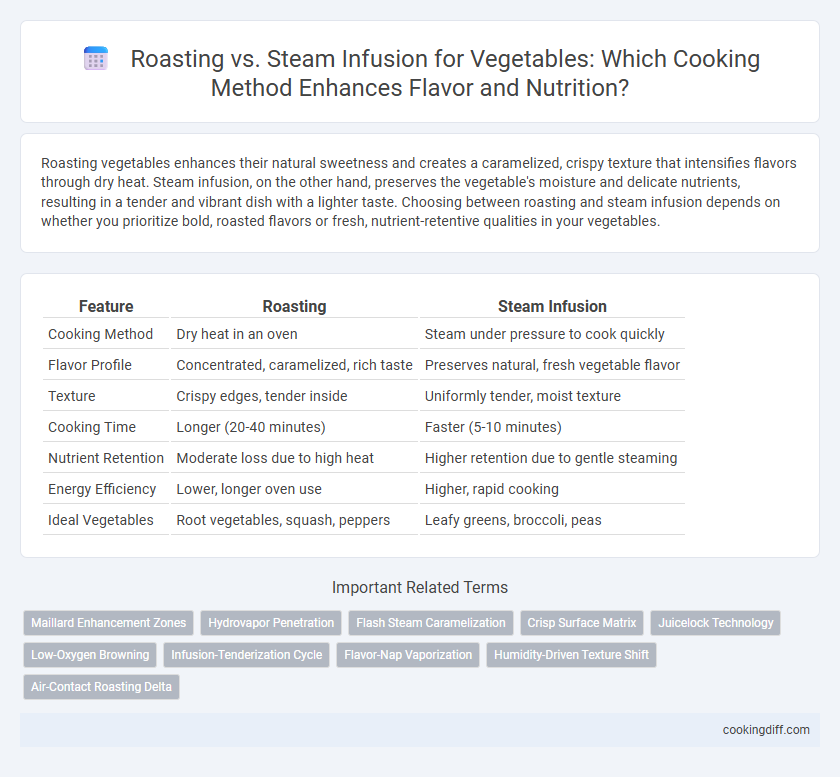
| Feature | Roasting | Steam Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Dry heat in an oven | Steam under pressure to cook quickly |
| Flavor Profile | Concentrated, caramelized, rich taste | Preserves natural, fresh vegetable flavor |
| Texture | Crispy edges, tender inside | Uniformly tender, moist texture |
| Cooking Time | Longer (20-40 minutes) | Faster (5-10 minutes) |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate loss due to high heat | Higher retention due to gentle steaming |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, longer oven use | Higher, rapid cooking |
| Ideal Vegetables | Root vegetables, squash, peppers | Leafy greens, broccoli, peas |
Introduction to Roasting and Steam Infusion
Roasting vegetables involves cooking them with dry heat, typically in an oven, which enhances their natural flavors through caramelization and Maillard browning. This method produces a crisp texture and deep, rich taste by concentrating sugars and reducing moisture content.
Steam infusion uses pressurized steam to cook vegetables quickly while preserving their color, texture, and nutritional content. This technique infuses moisture and heat simultaneously, allowing for even cooking and maintaining freshness without the caramelization effects seen in roasting.
Key Differences Between Roasting and Steam Infusion
Roasting and steam infusion are two distinct methods used to cook vegetables, each affecting texture and flavor differently. Roasting uses dry heat causing caramelization, while steam infusion relies on moist heat to preserve nutrients.
- Heat Source - Roasting employs dry, high-temperature heat from an oven, enhancing Maillard reactions for deeper flavor.
- Moisture Level - Steam infusion uses steam to cook vegetables, maintaining their moisture and resulting in a tender texture.
- Nutrient Retention - Steam infusion better preserves vitamins like vitamin C compared to roasting, which may degrade some nutrients due to higher temperatures.
Flavor Development in Roasting vs Steam Infusion
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor development through caramelization and Maillard reactions, creating complex, rich, and deep flavors. Steam infusion preserves the natural taste and nutrients but results in subtler, less intense flavor profiles.
- Roasting generates complex flavors - High dry heat causes browning that intensifies sweetness and savory notes.
- Steam infusion retains natural flavors - Moist heat softens vegetables without significantly altering their inherent taste.
- Flavor intensity differs - Roasting produces a bold, robust taste while steam infusion offers freshness and mildness.
Texture and Mouthfeel: Crispiness vs Tenderness
Roasting vegetables enhances their texture by creating a crispy exterior while maintaining a tender interior, offering a satisfying mouthfeel that highlights caramelized flavors. Steam infusion, on the other hand, produces uniformly tender vegetables with a softer texture, preserving moisture without any crispiness.
Roasting uses dry heat that evaporates surface moisture, resulting in a crisp, slightly charred crust ideal for vegetables like Brussels sprouts and carrots. Steam infusion employs moist heat, which gently cooks the vegetables, retaining their natural juiciness and delivering a smooth, tender bite perfect for delicate greens or root vegetables. Texture preference depends on the desired culinary experience--roasting emphasizes a robust crunch, while steam infusion ensures gentle tenderness.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Preserves More?
Roasting vegetables typically results in a slight loss of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B vitamins due to high dry heat exposure. Steam infusion preserves more nutrients by cooking vegetables quickly with minimal contact with water, preventing leaching of vitamins and minerals.
- Roasting causes vitamin degradation - High temperatures can reduce heat-sensitive nutrients, especially when vegetables are exposed for prolonged periods.
- Steam infusion limits nutrient loss - The method gently cooks with steam, maintaining higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals.
- Moisture retention affects nutrient preservation - Steam infusion preserves cellular moisture better than roasting, which can dry out vegetables and reduce nutrient content.
Steam infusion is generally superior to roasting in preserving the maximum nutrient content of vegetables.
Cooking Time and Energy Efficiency Comparison
How does roasting compare to steam infusion in terms of cooking time and energy efficiency?
Roasting typically requires longer cooking times, often ranging from 20 to 45 minutes depending on the vegetable, while steam infusion can cook vegetables in as little as 5 to 10 minutes. Steam infusion is generally more energy-efficient due to its shorter cooking duration and lower heat requirements, resulting in reduced energy consumption compared to the extended heating needed for roasting.
Best Vegetables for Roasting vs Steam Infusion
Root vegetables like carrots, potatoes, and beets are ideal for roasting due to their dense texture and ability to caramelize, enhancing their natural sweetness. Leafy greens and delicate vegetables such as spinach and asparagus benefit from steam infusion, which preserves their vibrant color and nutrients while maintaining tenderness. Cruciferous vegetables like broccoli and cauliflower can be prepared effectively by both methods, but roasting brings out a deeper, nuttier flavor compared to the lighter taste achieved through steam infusion.
Culinary Applications: When to Use Each Technique
Roasting vegetables enhances their natural sugars through caramelization, delivering rich, deep flavors and a crispy texture ideal for hearty dishes. Steam infusion preserves vibrant colors and crisp-tender textures by gently cooking vegetables, making it perfect for delicate salads or side dishes. Chefs often choose roasting for robust, savory profiles and steam infusion when freshness and moisture retention are the priorities in culinary applications.
Pros and Cons of Roasting and Steam Infusion
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through caramelization and Maillard reactions, producing a rich, complex taste and crispy texture that many find appealing. However, it can lead to uneven cooking and nutrient loss due to higher temperatures and longer cooking times.
Steam infusion preserves more vitamins and moisture, resulting in tender, nutrient-rich vegetables with a fresher taste. The method may lack the depth of flavor and texture achieved by roasting, often producing a softer and less intensely flavored product.
Related Important Terms
Maillard Enhancement Zones
Roasting vegetables intensifies flavor through the Maillard reaction, which occurs prominently in high-heat zones where amino acids and reducing sugars interact to create complex, savory compounds. Steam infusion, while preserving moisture, limits Maillard enhancement zones due to lower surface temperatures, resulting in less pronounced browning and flavor development compared to roasting.
Hydrovapor Penetration
Roasting enhances vegetable flavor through caramelization but offers limited hydrovapor penetration, resulting in a drier texture compared to steam infusion, which uses steam to evenly penetrate and hydrate vegetables, preserving moisture and nutrients. Steam infusion promotes faster cook times and improved texture by maximizing hydrovapor absorption into vegetable tissues, creating a juicier, more tender result.
Flash Steam Caramelization
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through Maillard reaction and dry heat caramelization, creating a rich, crispy texture that deep steaming cannot achieve. Flash steam caramelization combines high-temperature steam with intense heat, accelerating sugar browning while preserving moisture, offering a unique balance between roast-like flavor and vegetable juiciness.
Crisp Surface Matrix
Roasting creates a crisp surface matrix on vegetables by using dry heat that caramelizes natural sugars and reduces moisture, resulting in a crunchy texture and concentrated flavors. Steam infusion, while preserving moisture and nutrients, typically produces a softer surface without the same level of crispness or Maillard reaction effects found in roasting.
Juicelock Technology
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through caramelization but often leads to moisture loss, whereas Steam Infusion with Juicelock Technology preserves juiciness by locking in natural water content during cooking. Juicelock Technology uses high-pressure steam to penetrate vegetable fibers quickly, maintaining texture and nutrients while delivering consistent tenderness and vibrant color.
Low-Oxygen Browning
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through Maillard reactions, producing rich, caramelized notes via low-oxygen browning that steam infusion cannot replicate. Steam infusion preserves moisture but limits oxygen exposure, resulting in milder flavor development without the deep browning characteristic of roasting.
Infusion-Tenderization Cycle
The Infusion-Tenderization Cycle in steam infusion enhances vegetable texture by rapidly injecting steam, promoting even heat distribution and moisture retention, resulting in tender yet crisp produce. Unlike roasting, which relies on dry, high-heat exposure causing caramelization and surface browning, steam infusion preserves color and nutrients while reducing cooking time and thermal stress.
Flavor-Nap Vaporization
Roasting vegetables enhances flavor through the Maillard reaction, creating complex caramelized notes, whereas steam infusion relies on Flavor-Nap Vaporization to gently infuse vaporized flavors without browning. This process maintains vegetable texture and moisture while intensifying aromatic compounds, offering a distinct taste profile compared to traditional roasting.
Humidity-Driven Texture Shift
Roasting vegetables induces a humidity-driven texture shift by evaporating moisture, resulting in a crispy exterior and concentrated flavors, whereas steam infusion maintains high humidity, yielding tender and evenly cooked vegetables with a moist interior. This contrast in moisture control directly affects the Maillard reaction and cellulose breakdown, creating distinct textures ideal for different culinary applications.
Roasting vs Steam Infusion for vegetables. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com