Sauteing uses a small amount of oil to cook food quickly over high heat, enhancing flavor and texture while preserving nutrients. No-oil frying eliminates added fats, reducing calorie intake but may result in less browning and a different taste profile. Choosing between sauteing and no-oil frying depends on balancing health goals with desired flavor and texture in meals.
Table of Comparison
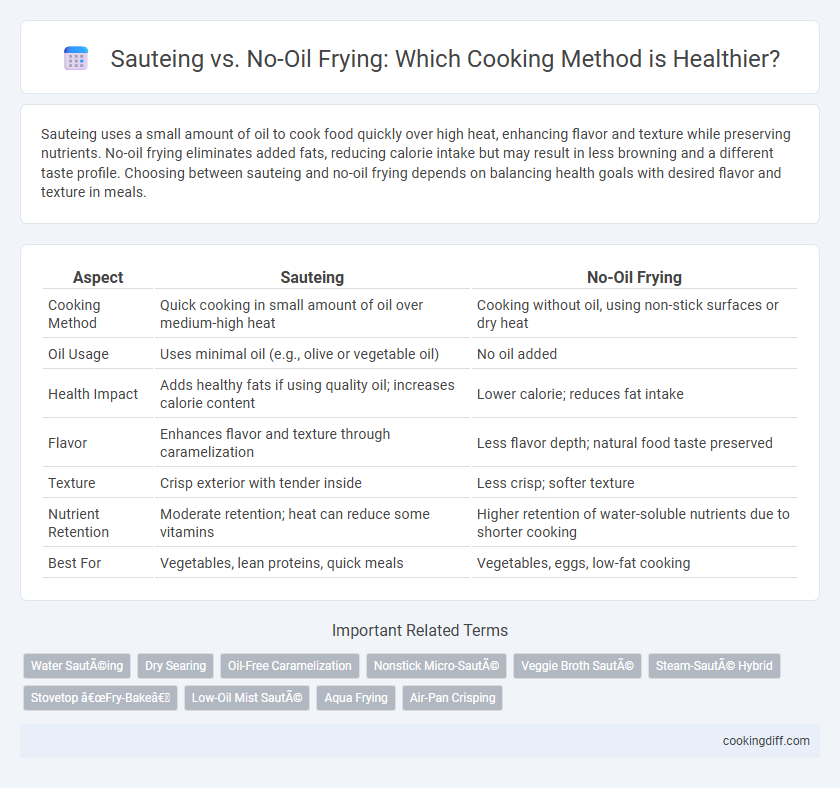
| Aspect | Sauteing | No-Oil Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Quick cooking in small amount of oil over medium-high heat | Cooking without oil, using non-stick surfaces or dry heat |
| Oil Usage | Uses minimal oil (e.g., olive or vegetable oil) | No oil added |
| Health Impact | Adds healthy fats if using quality oil; increases calorie content | Lower calorie; reduces fat intake |
| Flavor | Enhances flavor and texture through caramelization | Less flavor depth; natural food taste preserved |
| Texture | Crisp exterior with tender inside | Less crisp; softer texture |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate retention; heat can reduce some vitamins | Higher retention of water-soluble nutrients due to shorter cooking |
| Best For | Vegetables, lean proteins, quick meals | Vegetables, eggs, low-fat cooking |
Introduction to Healthy Cooking Techniques
Sauteing uses a small amount of oil to cook food quickly at high heat, enhancing flavor and texture while retaining nutrients. No-oil frying, often done with non-stick pans or cooking sprays, reduces calorie intake and fat consumption but may sacrifice some taste and mouthfeel. Both methods support healthy cooking by minimizing added fats compared to deep frying, making them suitable for balanced diets focused on nutrient preservation and weight management.
What is Sautéing?
Sauteing is a cooking technique that involves quickly frying food in a small amount of oil or fat over medium-high heat. This method enhances flavor and texture by creating a caramelized outer layer while preserving the interior's moisture.
No-oil frying, often done using non-stick pans or dry heat methods, avoids added fats and reduces calorie content but may produce less intense flavors and browning. Comparing sauteing and no-oil frying highlights the balance between flavor development and health-conscious cooking choices.
Understanding No-Oil Frying
No-oil frying uses dry heat or minimal liquid to cook food, preserving the natural flavors without added fats. This method reduces calorie intake and avoids the potential health risks associated with excessive oil consumption.
- Heat Transfer - Utilizes direct heat from pans or grills, eliminating the need for oil as a cooking medium.
- Food Texture - Maintains a firmer texture and reduces greasiness compared to sauteing with oil.
- Nutrient Retention - Helps preserve water-soluble vitamins and antioxidants that might degrade with oil frying.
No-oil frying offers a heart-healthy alternative for preparing vegetables and proteins while maintaining essential nutrients.
Nutritional Comparison: Sautéing vs No-Oil Frying
Sauteing with a small amount of oil enhances nutrient absorption, especially fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K, compared to no-oil frying. No-oil frying retains more water-soluble vitamins but may lack the healthy fats essential for optimal nutrient bioavailability.
Studies show sauteing can increase antioxidant levels in vegetables due to oil's heat transfer properties. No-oil frying reduces calorie intake by avoiding added fats but may decrease the retention of certain phytonutrients. Both methods preserve fiber content, contributing to digestive health.
Flavor and Texture Differences
Sauteing uses oil to enhance flavor by promoting caramelization and Maillard reactions, resulting in a richer, more complex taste and a crisp, golden texture. No-oil frying preserves the natural flavors of ingredients but often yields a drier texture and less pronounced browning due to the absence of fat.
In sauteing, the oil creates a barrier that helps retain moisture within vegetables or proteins, contributing to tenderness and juiciness. No-oil frying relies on high heat and frequent stirring to prevent sticking, which may cause uneven cooking and a firmer, sometimes tougher consistency.
Health Benefits of Sautéing
Is sauteing a healthier cooking method compared to no-oil frying? Sauteing allows for minimal use of healthy oils, which helps retain essential nutrients and enhances the absorption of fat-soluble vitamins like A, D, E, and K. This method also promotes better texture and flavor without adding excessive calories, making it a beneficial choice for heart health and weight management.
Health Benefits of No-Oil Frying
No-oil frying significantly reduces calorie intake by eliminating added fats, which supports weight management and heart health. This cooking method preserves essential nutrients like vitamins C and B complex that can degrade at high temperatures in oil-based sauteing. Incorporating no-oil frying enhances antioxidant retention, contributing to reduced inflammation and improved metabolic function.
Best Foods for Each Method
| Cooking Method | Best Foods | Health Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Sauteing | Lean proteins like chicken breast, shrimp, and tofu; firm vegetables such as bell peppers, zucchini, and mushrooms | Enhances flavor and nutrient absorption, preserves texture, and uses healthy fats like olive oil to support heart health |
| No-Oil Frying | Delicate vegetables like spinach, broccoli, and asparagus; low-fat proteins including egg whites and seafood | Reduces calorie intake and fat consumption while retaining vitamins and minerals through gentle cooking methods like steaming or air frying |
Tips for Healthier Sautéing and No-Oil Frying
Sauteing uses a small amount of oil to cook food quickly at high heat, preserving nutrients and flavor. No-oil frying eliminates added fats, relying on non-stick surfaces or water/steam to reduce calorie intake while maintaining texture.
- Choose healthy oils - Use oils rich in unsaturated fats like olive or avocado oil to promote heart health during sauteing.
- Control heat level - Cook at medium-high heat to prevent burning and formation of harmful compounds while retaining nutrients.
- Use non-stick cookware - Enables no-oil frying by reducing food sticking and allowing easy cooking without added fat.
Related Important Terms
Water Sautéing
Water sauteing preserves the nutrients and minimizes fat intake by using water or broth instead of oil, making it an ideal method for healthy cooking. This technique reduces calorie content while maintaining texture and flavor, offering a low-fat alternative to traditional oil-based sauteing.
Dry Searing
Dry searing, a no-oil frying method, uses high heat to cook food quickly, preserving nutrients and reducing calorie intake compared to sauteing with oil. This technique promotes a healthier meal by minimizing added fats while still achieving a flavorful, caramelized exterior.
Oil-Free Caramelization
Oil-free caramelization enhances the natural sweetness and browning of vegetables without added fats, preserving nutrients and reducing calorie intake compared to sauteing with oil. Using techniques like dry pan roasting or water sauteing allows for healthier preparation while maintaining flavor and texture.
Nonstick Micro-Sauté
Nonstick Micro-Saute cookware enables healthier sauteing by requiring minimal to no oil, preserving nutrients while reducing added fats compared to traditional sauteing methods. Its superior nonstick surface ensures even cooking and easy food release, making it an excellent choice for oil-free or low-oil frying techniques that promote heart health.
Veggie Broth Sauté
Veggie broth sauteing uses vegetable broth instead of oil, significantly reducing fat content while maintaining moisture and enhancing the natural flavors of vegetables. This method preserves nutrients better than traditional sauteing and is ideal for low-calorie, heart-healthy meals.
Steam-Sauté Hybrid
Steam-saute hybrid cooking combines the benefits of sauteing and steaming, reducing oil usage while retaining food's texture and nutrients. This method enhances flavor development through sauteing's high heat while maintaining moisture and nutrients with steaming, making it a healthier alternative to traditional no-oil frying.
Stovetop “Fry-Bake”
Sauteing with a small amount of healthy oil enhances nutrient absorption and flavor complexity compared to no-oil frying, which can result in drier, less palatable dishes. Stovetop "fry-bake" techniques combine gentle sauteing and baking, optimizing texture retention while minimizing unhealthy fat usage for balanced, nutritious meals.
Low-Oil Mist Sauté
Low-oil mist sauteing uses minimal oil sprayed directly onto the pan, reducing fat intake compared to traditional sauteing while maintaining food's texture and flavor. This method extracts fewer calories and retains more nutrients than no-oil frying, which often sacrifices taste and browning quality.
Aqua Frying
Aqua frying uses hot water or broth instead of oil, reducing fat intake and calorie content compared to traditional sauteing, which relies on oil for cooking and flavor enhancement. This method retains moisture and nutrients in vegetables and lean proteins while delivering a lighter texture ideal for health-conscious meal preparation.
Sautéing vs No-Oil Frying for healthy preparation Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com