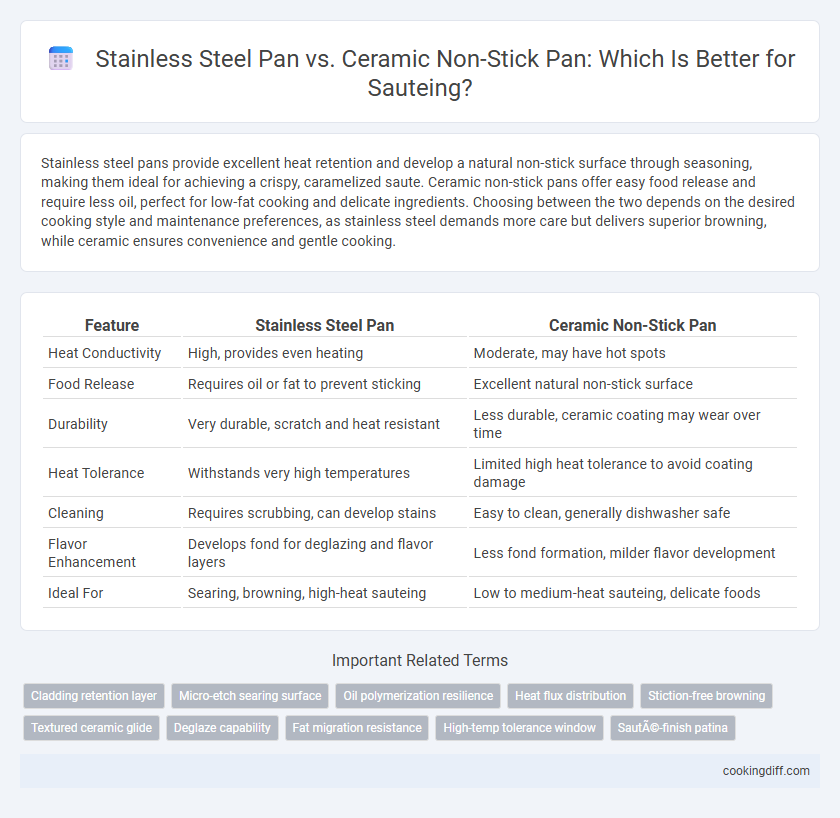
Stainless steel pans provide excellent heat retention and develop a natural non-stick surface through seasoning, making them ideal for achieving a crispy, caramelized saute. Ceramic non-stick pans offer easy food release and require less oil, perfect for low-fat cooking and delicate ingredients. Choosing between the two depends on the desired cooking style and maintenance preferences, as stainless steel demands more care but delivers superior browning, while ceramic ensures convenience and gentle cooking.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pan | Ceramic Non-Stick Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | High, provides even heating | Moderate, may have hot spots |
| Food Release | Requires oil or fat to prevent sticking | Excellent natural non-stick surface |
| Durability | Very durable, scratch and heat resistant | Less durable, ceramic coating may wear over time |
| Heat Tolerance | Withstands very high temperatures | Limited high heat tolerance to avoid coating damage |
| Cleaning | Requires scrubbing, can develop stains | Easy to clean, generally dishwasher safe |
| Flavor Enhancement | Develops fond for deglazing and flavor layers | Less fond formation, milder flavor development |
| Ideal For | Searing, browning, high-heat sauteing | Low to medium-heat sauteing, delicate foods |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Pan for Sautéing
Selecting the ideal pan for sauteing can significantly impact cooking results and ease of use. Stainless steel pans offer durability and excellent heat retention, while ceramic non-stick pans provide effortless food release and easier cleaning.
- Stainless Steel Heat Conductivity - Stainless steel pans distribute heat evenly, allowing precise temperature control for browning.
- Ceramic Non-Stick Surface - Ceramic coatings prevent food from sticking, reducing the need for excess oil during sauteing.
- Durability Comparison - Stainless steel pans resist scratches and high heat better than ceramic non-stick alternatives.
Choosing between stainless steel and ceramic non-stick pans depends on your cooking style and maintenance preferences.
Heat Conductivity: Stainless Steel vs Ceramic Non-Stick
| Pan Type | Heat Conductivity | Effect on Sauteing |
|---|---|---|
| Stainless Steel | High thermal conductivity with efficient heat distribution | Allows precise temperature control and even browning of ingredients |
| Ceramic Non-Stick | Lower heat conductivity compared to stainless steel | Heats up more slowly and may produce less consistent searing results |
Non-Stick Performance and Food Release
Stainless steel pans require proper preheating and use of oil to prevent food from sticking, offering excellent browning and caramelization during sauteing. Their lack of a non-stick coating can make food release more difficult without adequate technique.
Ceramic non-stick pans provide superior food release due to their smooth, coated surfaces, making sauteing delicate ingredients like fish or eggs easier. These pans typically require less oil, promoting healthier cooking and effortless cleanup.
Browning and Flavor Development
Stainless steel pans excel at browning due to their ability to reach high temperatures and develop fond, enhancing flavor depth. Ceramic non-stick pans provide easier food release but limit the Maillard reaction, resulting in less pronounced browning and flavor complexity.
- Heat retention - Stainless steel pans maintain higher heat needed for effective browning and crust formation.
- Fond development - Stainless steel allows residue buildup that intensifies flavor through deglazing.
- Non-stick coating limitations - Ceramic coatings prevent fond formation, reducing flavor layers during sauteing.
Ease of Use for Sautéing Techniques
Which pan offers greater ease of use for sauteing techniques, stainless steel or ceramic non-stick? Stainless steel pans require careful temperature control and preheating to prevent sticking but provide superior browning and deglazing capabilities. Ceramic non-stick pans heat evenly and allow effortless food release, making them ideal for quick, low-fat sauteing without the risk of food sticking.
Durability and Longevity of Each Pan
Stainless steel pans offer superior durability, resisting scratches, warping, and high heat damage, making them ideal for long-term use in sauteing. Ceramic non-stick pans, while providing excellent food release and easy cleaning, tend to degrade faster due to coating wear and sensitivity to metal utensils. Investing in a high-quality stainless steel pan ensures sustained performance and longevity for frequent sauteing tasks.
Maintenance and Cleaning Tips
Stainless steel pans require thorough cleaning to prevent food residue buildup, often needing abrasive scrubbers and specialized stainless steel cleaners. Ceramic non-stick pans demand gentle washing with non-abrasive sponges to preserve the coating and avoid scratching, extending the pan's lifespan. Both types benefit from immediate cleaning after use to maintain surface quality and ensure optimal sauteing performance.
Health and Safety Considerations
Stainless steel pans are praised for their durability and non-reactive surface, which do not leach harmful chemicals into food when sauteing. Ceramic non-stick pans offer a chemical-free coating but may degrade faster, potentially releasing particles if overheated.
Choosing stainless steel reduces health risks associated with synthetic coatings, making it safer for high-heat cooking methods like sauteing. Ceramic pans require careful temperature control to prevent damage to the coating and maintain safety. Both types avoid the use of PTFE and PFOA, chemicals commonly found in traditional non-stick pans linked to health concerns.
Price Comparison and Value
Stainless steel pans typically cost more upfront than ceramic non-stick pans but offer greater durability and long-term value. Ceramic non-stick pans are more affordable initially but may require more frequent replacement due to coating wear.
- Upfront Cost - Stainless steel pans usually have a higher price point compared to ceramic non-stick options.
- Durability - Stainless steel's resistance to scratches and heat warping provides lasting value despite the initial cost.
- Replacement Frequency - Ceramic non-stick pans often need to be replaced every 1-3 years due to coating degradation.
Related Important Terms
Cladding retention layer
Stainless steel pans with a cladding retention layer offer superior heat distribution and durability for sauteing, preventing warping and ensuring consistent cooking temperatures. Ceramic non-stick pans lack this robust layer, which can lead to uneven heating and faster degradation, affecting the sauteing quality over time.
Micro-etch searing surface
Stainless steel pans with a micro-etch searing surface provide superior heat retention and a robust, textured layer that enhances browning and caramelization during sauteing, creating complex flavors and a desirable crust. Ceramic non-stick pans offer easy food release and low-fat cooking but lack the micro-etch surface's ability to develop the intense Maillard reactions essential for optimum sauteed texture and flavor.
Oil polymerization resilience
Stainless steel pans offer superior oil polymerization resilience due to their ability to withstand high heat without damaging the cooking surface, making them ideal for achieving a perfect saute. Ceramic non-stick pans, while providing easy food release, generally have lower tolerance to high temperatures, causing quicker degradation of the non-stick coating when exposed to oil polymerization during intense sauteing.
Heat flux distribution
Stainless steel pans provide superior heat flux distribution due to their high thermal conductivity and even heat retention, ensuring consistent browning and searing during sauteing. Ceramic non-stick pans tend to have less efficient heat distribution, which can result in uneven cooking and hotspots that affect the overall texture and flavor of sauteed ingredients.
Stiction-free browning
Stainless steel pans offer superior stiction-free browning due to their ability to develop a natural fond that enhances flavor and allows precise temperature control, whereas ceramic non-stick pans provide easy food release but may lack the high-heat tolerance necessary for optimal browning. For sauteing, stainless steel's durability and heat responsiveness create a caramelized crust without sticking, making it ideal for searing and flavor development.
Textured ceramic glide
Textured ceramic glide surfaces in ceramic non-stick pans enhance sauteing by providing superior food release and even heat distribution, reducing the need for excess oil. Stainless steel pans, while excellent for browning, often require more skill and oil to prevent sticking, making textured ceramic coatings a more user-friendly option for efficient sauteing.
Deglaze capability
Stainless steel pans excel in deglazing due to their ability to form flavorful brown fond on the surface, which dissolves into sauces, enhancing taste and texture. Ceramic non-stick pans prevent fond formation, resulting in limited deglaze capability and less intense sauce flavors.
Fat migration resistance
Stainless steel pans offer superior fat migration resistance due to their non-porous surface, preventing oils from embedding and promoting even browning during sauteing. Ceramic non-stick pans, while providing a smooth cooking surface, tend to absorb more oils over time, which can impact cooking performance and flavor consistency.
High-temp tolerance window
Stainless steel pans offer a high-temperature tolerance typically up to 500degF (260degC), ideal for achieving optimal searing and caramelization during sauteing without damaging the pan. Ceramic non-stick pans generally withstand lower temperatures around 350degF to 450degF (175degC to 230degC), requiring more careful heat control to prevent coating degradation and maintain non-stick performance.
Stainless steel pan vs ceramic non-stick pan for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com