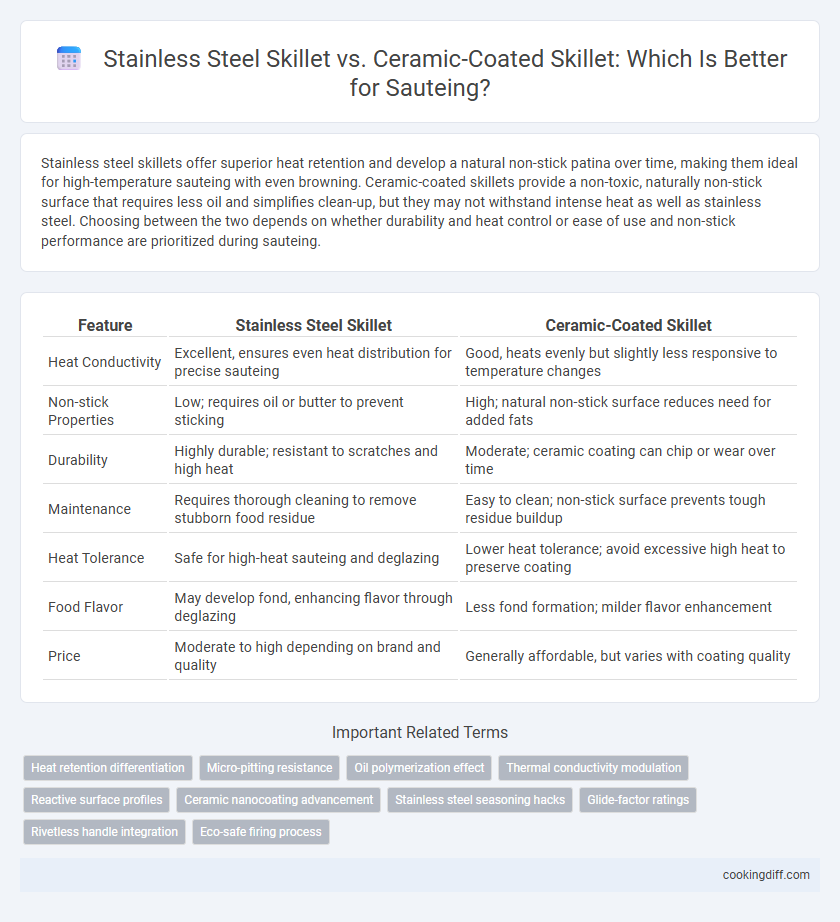
Stainless steel skillets offer superior heat retention and develop a natural non-stick patina over time, making them ideal for high-temperature sauteing with even browning. Ceramic-coated skillets provide a non-toxic, naturally non-stick surface that requires less oil and simplifies clean-up, but they may not withstand intense heat as well as stainless steel. Choosing between the two depends on whether durability and heat control or ease of use and non-stick performance are prioritized during sauteing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Skillet | Ceramic-Coated Skillet |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | Excellent, ensures even heat distribution for precise sauteing | Good, heats evenly but slightly less responsive to temperature changes |
| Non-stick Properties | Low; requires oil or butter to prevent sticking | High; natural non-stick surface reduces need for added fats |
| Durability | Highly durable; resistant to scratches and high heat | Moderate; ceramic coating can chip or wear over time |
| Maintenance | Requires thorough cleaning to remove stubborn food residue | Easy to clean; non-stick surface prevents tough residue buildup |
| Heat Tolerance | Safe for high-heat sauteing and deglazing | Lower heat tolerance; avoid excessive high heat to preserve coating |
| Food Flavor | May develop fond, enhancing flavor through deglazing | Less fond formation; milder flavor enhancement |
| Price | Moderate to high depending on brand and quality | Generally affordable, but varies with coating quality |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Skillet for Sautéing
Stainless steel skillets offer excellent heat conduction and durability, making them ideal for achieving a perfect sear during sauteing. Their non-reactive surface ensures flavors remain pure without imparting any metallic taste to the food.
Ceramic-coated skillets provide a non-stick cooking surface that requires less oil, promoting healthier sauteing. They heat evenly but may wear faster than stainless steel, needing more careful maintenance to preserve their coating.
Stainless Steel Skillets: Key Features and Benefits
Stainless steel skillets provide superior heat retention and even heating, making them ideal for precise sauteing techniques. Their durability and resistance to scratches ensure long-lasting performance in high-temperature cooking environments.
- Heat Conductivity - Stainless steel skillets distribute heat evenly, preventing hot spots during sauteing.
- Durability - The robust nature of stainless steel resists warping and corrosion over time.
- Flavor Development - These skillets allow for superior browning and development of complex flavors when sauteing.
Ceramic-Coated Skillets: Features and Performance
Ceramic-coated skillets offer a non-stick surface that requires less oil, making them ideal for healthy sauteing. Their even heat distribution ensures consistent cooking without hot spots, enhancing the flavor and texture of sauteed foods.
- Non-stick surface - Facilitates easy food release and quick cleanup.
- Even heat distribution - Prevents burning and promotes uniform cooking.
- Chemical-free coating - Provides a safer alternative to traditional non-stick pans.
These features make ceramic-coated skillets a great choice for both novice and experienced cooks focusing on sauteing techniques.
Heat Distribution: Stainless Steel vs Ceramic-Coated
Stainless steel skillets offer superior heat distribution due to their dense metal construction, ensuring even cooking and browning during sauteing. The high thermal conductivity of stainless steel allows for quick temperature adjustments and consistent heat across the cooking surface.
Ceramic-coated skillets provide a more non-stick surface but often have less efficient heat distribution compared to stainless steel. The ceramic layer can create hotspots and slower heat conduction, which may affect uniform cooking when sauteing delicate ingredients.
Searing and Browning Capabilities
Stainless steel skillets excel in searing and browning due to their high heat tolerance and even heat distribution, allowing food to develop a deep, flavorful crust. Ceramic-coated skillets offer non-stick properties but may lack the same intensity in browning, as they generally cannot withstand as high temperatures without damage.
- Stainless steel skillet - Provides superior searing performance by maintaining consistent, high heat essential for Maillard reaction.
- Ceramic-coated skillet - Offers easier food release but requires moderate heat, limiting the browning depth achievable.
- Heat tolerance - Stainless steel withstands higher temperatures, enhancing browning, whereas ceramic coatings degrade under excessive heat.
Ease of Cleaning and Maintenance
Which skillet offers easier cleaning and lower maintenance for sauteing, stainless steel or ceramic-coated? Stainless steel skillets often require thorough scrubbing to remove stuck-on food but can withstand abrasive cleaning tools without damage. Ceramic-coated skillets provide a non-stick surface that simplifies cleaning, although their coatings may degrade over time with improper care.
Durability and Longevity Comparison
Stainless steel skillets offer superior durability due to their resistance to scratching, warping, and high heat, maintaining performance over many years. Ceramic-coated skillets provide a non-stick surface but tend to degrade faster, with coatings wearing off after prolonged use.
The robust construction of stainless steel skillets ensures longevity even under frequent sauteing at high temperatures, making them ideal for heavy-duty cooking. Ceramic-coated skillets require gentler use and careful maintenance to avoid chipping and coating deterioration. Over time, stainless steel skillets typically outperform ceramic-coated ones in durability and consistent cooking results.
Safety and Non-Toxicity Concerns
Stainless steel skillets are highly regarded for their non-reactive properties, ensuring no harmful chemicals leach into food during sauteing, making them a safe choice for health-conscious cooks. Ceramic-coated skillets offer a non-toxic alternative free from PTFE and PFOA, reducing concerns about toxic fumes at high temperatures while providing a naturally non-stick surface. Both options prioritize user safety, but ceramic coatings require careful use to avoid chipping and potential exposure to underlying metals.
Price and Value Considerations
Stainless steel skillets typically offer greater durability and higher heat tolerance, often priced moderately to high depending on the brand. Ceramic-coated skillets are generally more affordable initially but may require replacement sooner due to coating wear. Evaluating the balance between upfront cost and long-term value is crucial when choosing the ideal skillet for sauteing.
Related Important Terms
Heat retention differentiation
Stainless steel skillets exhibit superior heat retention due to their dense metal construction, allowing for consistent and even sauteing at high temperatures without rapid cooling when food is added. Ceramic-coated skillets heat up quickly but tend to lose heat faster, resulting in less stable cooking temperatures ideal for delicate foods requiring lower heat.
Micro-pitting resistance
Stainless steel skillets offer superior micro-pitting resistance compared to ceramic-coated skillets, ensuring long-term durability and maintaining a smooth cooking surface under high heat conditions. Ceramic-coated skillets may develop micro-pits over time due to surface wear, which can affect sauteing performance and reduce non-stick efficiency.
Oil polymerization effect
Stainless steel skillets promote better oil polymerization due to their higher heat retention and even temperature distribution, creating a natural non-stick layer that enhances sauteing performance. Ceramic-coated skillets tend to have lower heat tolerance, which can limit oil polymerization and reduce the development of a durable, non-stick surface during cooking.
Thermal conductivity modulation
Stainless steel skillets offer superior thermal conductivity modulation, allowing precise temperature control essential for perfect sauteing by evenly distributing heat and preventing hot spots. Ceramic-coated skillets provide moderate heat retention with slower responsiveness, which can limit the ability to quickly adjust cooking temperatures during high-heat sauteing tasks.
Reactive surface profiles
Stainless steel skillets exhibit a reactive surface that can withstand high heat and develop a natural non-stick patina over time, making them ideal for achieving a perfect sear during sauteing. Ceramic-coated skillets feature a non-reactive, smooth surface that prevents sticking and avoids flavor transfer but may degrade faster under high heat compared to stainless steel.
Ceramic nanocoating advancement
Ceramic-coated skillets enhanced with advanced ceramic nanocoating offer superior non-stick properties and higher heat resistance compared to traditional stainless steel skillets, enabling precise sauteing with minimal oil and effortless food release. This nanotechnology innovation improves durability and scratch resistance, maintaining the skillet's performance and safety over prolonged cooking sessions.
Stainless steel seasoning hacks
Seasoning a stainless steel skillet for sauteing involves heating oil until it smokes, then coating the pan evenly to create a natural non-stick surface that enhances food browning and prevents sticking. Regular seasoning with high-smoke-point oils like flaxseed or grapeseed improves the skillet's durability and performance compared to ceramic-coated skillets, which may degrade over time and lose their non-stick properties.
Glide-factor ratings
Stainless steel skillets offer a moderate glide-factor rating, providing good control over food movement but sometimes causing sticking with delicate ingredients during sauteing. Ceramic-coated skillets typically feature a higher glide-factor rating, reducing food adhesion and enabling smoother flipping and stirring, which enhances the overall sauteing experience.
Rivetless handle integration
Stainless steel skillets with rivetless handle integration offer a seamless cooking surface that prevents food buildup and simplifies cleaning during sauteing, while ceramic-coated skillets provide a non-stick experience but may have rivet attachments that can trap residue. Rivetless handles enhance durability and hygiene in stainless steel pans, making them ideal for precise sauteing techniques requiring steady, unhindered stirring.
Stainless steel skillet vs Ceramic-coated skillet for sautéing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com