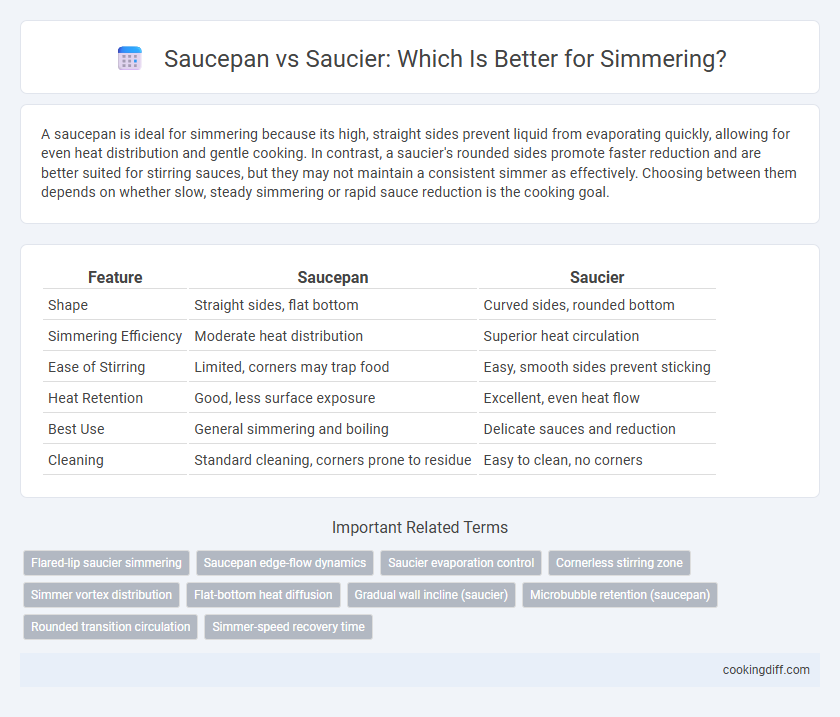
A saucepan is ideal for simmering because its high, straight sides prevent liquid from evaporating quickly, allowing for even heat distribution and gentle cooking. In contrast, a saucier's rounded sides promote faster reduction and are better suited for stirring sauces, but they may not maintain a consistent simmer as effectively. Choosing between them depends on whether slow, steady simmering or rapid sauce reduction is the cooking goal.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Saucepan | Saucier |
|---|---|---|
| Shape | Straight sides, flat bottom | Curved sides, rounded bottom |
| Simmering Efficiency | Moderate heat distribution | Superior heat circulation |
| Ease of Stirring | Limited, corners may trap food | Easy, smooth sides prevent sticking |
| Heat Retention | Good, less surface exposure | Excellent, even heat flow |
| Best Use | General simmering and boiling | Delicate sauces and reduction |
| Cleaning | Standard cleaning, corners prone to residue | Easy to clean, no corners |
Introduction to Simmering: Why Cookware Matters
What distinguishes a saucepan from a saucier when simmering delicate sauces? A saucepan's straight sides offer consistent heat distribution, ideal for simmering soups and stews evenly. The saucier's curved edges facilitate easy stirring and reduce food sticking, enhancing control during prolonged simmering processes.
Saucepan vs Saucier: Key Design Differences
Saucepans feature straight sides and a flat bottom, which promote even heat distribution ideal for simmering liquids consistently. Saucier pans have gently curved sides that allow for easy stirring and reduce the risk of food getting caught in corners, enhancing the simmering process for sauces and reductions.
The narrower base of a saucepan concentrates heat, making it suitable for slow, controlled simmering, while a saucier's wider opening accelerates evaporation, perfect for thickening sauces. Both pans typically have long handles, but the saucier's rounded shape offers better maneuverability for whisking and stirring during simmering tasks.
Heat Distribution: Which Pan Simmer Better?
The saucier's rounded bottom allows for more even heat distribution compared to a saucepan's flat base, promoting consistent simmering without hot spots. Saucepans, with their straight sides, tend to concentrate heat along the edges, which can lead to uneven cooking during prolonged simmering. For recipes requiring gentle, uniform heat, such as sauces or reductions, a saucier typically simmers ingredients more effectively than a standard saucepan.
Control and Precision in Simmering
A saucepan offers greater control over liquid levels and heat distribution, enabling precise simmering for sauces, soups, and reductions. The saucier's rounded bottom promotes even heat circulation, reducing hotspots and preventing scorching during delicate simmering tasks. Choosing between a saucepan and saucier depends on the need for exact temperature management versus gentle fluid motion during simmering.
Ease of Stirring and Reducing Sauces
The saucier's rounded bottom enables easier stirring and prevents ingredients from getting stuck in corners, making it ideal for simmering delicate sauces. In contrast, saucepans with flat bottoms are better suited for even heat distribution but can make stirring and reducing sauces less efficient due to sharp edges.
- Ease of Stirring - The saucier's curved interior allows effortless whisking and blending without scraping corners.
- Reducing Sauces - Rounded sides promote faster reduction by ensuring consistent heat contact and evaporation.
- Heat Distribution - Saucepan's flat base provides stable heat but creates edges that complicate thorough stirring during simmering.
Capacity and Volume Considerations
When choosing between a saucepan and a saucier for simmering, capacity plays a crucial role. Saucepans typically offer higher volume capacity, making them ideal for larger batches of soups or stews.
The saucier's rounded sides facilitate even heat distribution, but they often have smaller volume compared to saucepans. This makes sauciers better suited for sauces or delicate reductions where precise simmering is essential.
Cleaning and Maintenance for Simmering
Simmering in a saucepan often results in food residues that are easier to clean due to the straight sides and wide base. Saucier pans, with their curved sides, can make scrubbing more thorough but help prevent stubborn food buildup during simmering.
- Ease of Cleaning - Saucepans have flat bottoms and straight edges, simplifying the cleaning process after simmering.
- Residue Prevention - The curved interior of sauciers reduces food sticking, minimizing hard-to-clean spots.
- Maintenance Frequency - Saucepans typically require less frequent deep cleaning compared to sauciers due to their shape.
Choosing the right pan based on cleaning efficiency can enhance maintenance while simmering.
Versatility Beyond Simmering
Saucepans offer excellent heat retention and even cooking, making them ideal for simmering soups and stews, but their straight sides can limit stirring and reduction. Sauciers feature rounded bottoms and sloped sides, enhancing their versatility for both gentle simmering and whisking sauces or making reductions.
The rounded design of sauciers promotes even heat distribution, preventing food from sticking and allowing better incorporation of ingredients, which is especially useful beyond simple simmering. Saucepans excel when it comes to boiling or steaming, thanks to their larger capacity and straight sides that maximize volume. The choice between saucepan and saucier depends on the cooking technique, with sauciers preferred for delicate sauces and reductions, while saucepans handle liquid-heavy dishes and reheating effectively.
Professional Chefs’ Preferences: Saucepan vs Saucier
| Cookware Type | Simmering Efficiency | Professional Chefs' Preference |
|---|---|---|
| Saucepan | Offers even heat distribution and retains heat well, ideal for steady simmering of sauces and stocks. | Widely favored for versatility and ability to maintain consistent low temperatures during long simmering processes. |
| Saucier | Features rounded bottom that facilitates stirring and prevents food from sticking, enhancing sauce reduction during simmering. | Preferred for delicate sauces and emulsions that require frequent stirring and precise temperature control. |
Related Important Terms
Flared-lip saucier simmering
Flared-lip saucers enhance simmering by allowing gentle evaporation and easier stirring, preventing scorching and ensuring even heat distribution compared to traditional saucepans. This design optimizes simmering performance, making it ideal for delicate sauces and reductions requiring precise temperature control.
Saucepan edge-flow dynamics
Saucepans offer precise edge-flow dynamics ideal for simmering by facilitating even heat distribution and minimizing hot spots, which ensures consistent temperature control for delicate sauces. Their straight sides help maintain moisture and reduce evaporation, preserving flavor and texture during longer simmering processes.
Saucier evaporation control
A saucier's curved sides and rounded bottom enhance evaporation control during simmering by facilitating even heat distribution and preventing liquid from sticking or burning. This design allows for better reduction and thickening of sauces compared to a traditional saucepan, which has straight sides that can cause uneven heat and faster evaporation.
Cornerless stirring zone
A saucier features a rounded, cornerless stirring zone that allows ingredients to be mixed and stirred evenly during simmering, preventing food from getting trapped in corners. In contrast, a saucepan's sharp corners can hinder thorough stirring and create hotspots, making a saucier more efficient for tasks requiring constant movement and gentle heat distribution.
Simmer vortex distribution
A saucier's rounded bottom promotes superior simmer vortex distribution, ensuring even heat circulation and preventing hot spots during slow cooking. In contrast, a saucepan's flat bottom can lead to uneven simmering, causing inconsistent temperature zones and potential food scorching.
Flat-bottom heat diffusion
A saucepan with a flat bottom provides even heat diffusion, ensuring consistent simmering without hot spots, ideal for delicate sauces and soups. In contrast, a saucier's rounded bottom limits direct surface contact with the heat source, resulting in less efficient heat distribution during simmering.
Gradual wall incline (saucier)
A saucier's gradual wall incline promotes even heat distribution and prevents food from sticking, making it ideal for gentle simmering and reducing sauces, while a saucepan's straight sides may lead to uneven heat and hotter spots. This design difference enhances precise temperature control and efficient stirring during slow simmering processes in a saucier.
Microbubble retention (saucepan)
Saucepans excel in simmering by promoting microbubble retention along their straight sides, which enhances gentle heat distribution and prevents rapid boiling. This property allows sauces and soups to cook evenly at low temperatures, preserving delicate flavors and textures.
Rounded transition circulation
A saucier's rounded transition between the base and sides promotes even heat distribution and fluid motion, ideal for gentle simmering and stirring without food catching in corners. Saucepan edges form sharper angles that can disrupt circulation, making sauciers more efficient for delicate simmering tasks requiring consistent temperature and seamless stirring.
Saucepan vs Saucier for simmering. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com