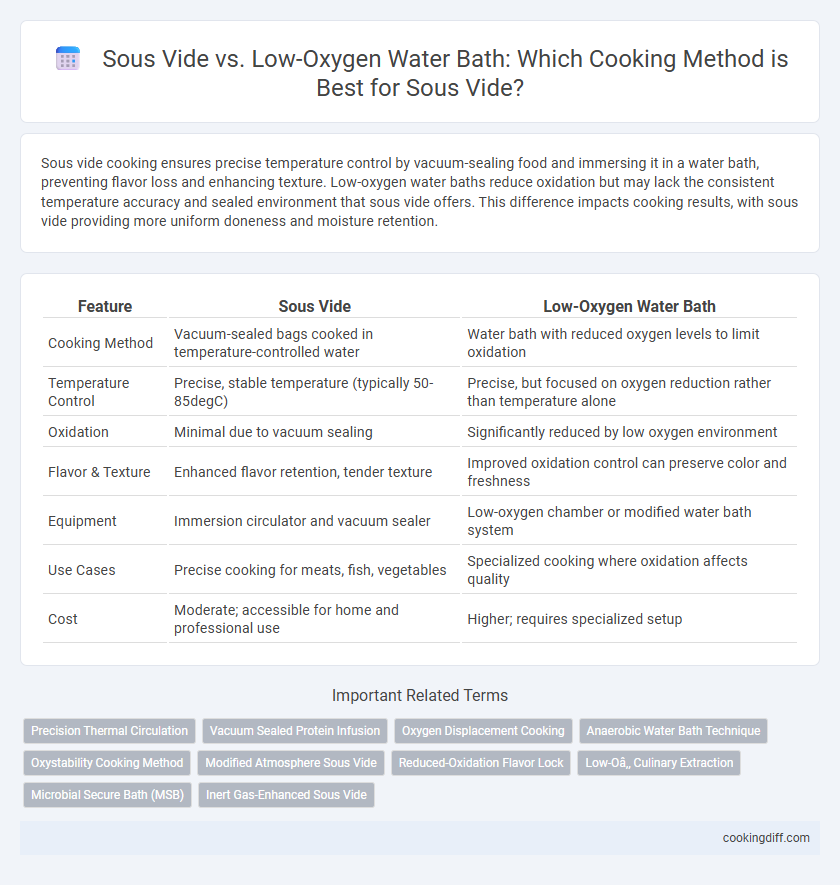
Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control by vacuum-sealing food and immersing it in a water bath, preventing flavor loss and enhancing texture. Low-oxygen water baths reduce oxidation but may lack the consistent temperature accuracy and sealed environment that sous vide offers. This difference impacts cooking results, with sous vide providing more uniform doneness and moisture retention.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Sous Vide | Low-Oxygen Water Bath |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Vacuum-sealed bags cooked in temperature-controlled water | Water bath with reduced oxygen levels to limit oxidation |
| Temperature Control | Precise, stable temperature (typically 50-85degC) | Precise, but focused on oxygen reduction rather than temperature alone |
| Oxidation | Minimal due to vacuum sealing | Significantly reduced by low oxygen environment |
| Flavor & Texture | Enhanced flavor retention, tender texture | Improved oxidation control can preserve color and freshness |
| Equipment | Immersion circulator and vacuum sealer | Low-oxygen chamber or modified water bath system |
| Use Cases | Precise cooking for meats, fish, vegetables | Specialized cooking where oxidation affects quality |
| Cost | Moderate; accessible for home and professional use | Higher; requires specialized setup |
Understanding Sous Vide: Definition and Process
Sous vide is a precision cooking method where food is vacuum-sealed in a bag and cooked in a water bath at a controlled, low temperature for an extended time. This process ensures even cooking, moisture retention, and enhanced flavor development.
Low-oxygen water baths also involve sealed cooking but focus more on reducing oxygen exposure to prevent oxidation, which can affect texture and taste. While both methods use water immersion, sous vide emphasizes temperature precision for consistent results across proteins and vegetables.
What Is Low-Oxygen Water Bath Cooking?
Low-oxygen water bath cooking is a technique that reduces oxygen levels in the cooking water to slow oxidation and preserve food quality. Unlike traditional sous vide, which relies on precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag, low-oxygen water baths enhance shelf life and texture by minimizing microbial growth. This method is especially effective for delicate proteins, maintaining flavor and tenderness during extended cooking periods.
Key Differences: Sous Vide vs Low-Oxygen Water Bath
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and immersing it in a precisely temperature-controlled water bath, ensuring even cooking and retention of moisture. Low-oxygen water bath cooking reduces oxygen content in the water to minimize oxidation and enhance food preservation during the process.
Temperature accuracy in sous vide typically ranges from 0.1degC to 0.5degC, providing consistent results, while low-oxygen water baths primarily focus on the water's oxygen level rather than exact temperature control. Sous vide chambers rely on immersion circulators for uniform heat distribution, whereas low-oxygen environments often require specialized equipment to deoxygenate the water. These differences impact flavor, texture, and shelf life, making sous vide ideal for delicate meats and vegetables, while low-oxygen baths benefit longer storage and reduced spoilage.
Precision and Temperature Control Comparison
Sous vide cooking offers precise temperature control, maintaining water bath temperature within +-0.1degC, ensuring consistent results. Low-oxygen water baths provide stable conditions but often lack the advanced temperature regulation technology found in sous vide devices, leading to slightly less exact heat management.
- Sous vide precision - Utilizes digital thermostats and circulators for ultra-accurate temperature control.
- Low-oxygen water bath stability - Maintains consistent temperature but with less refined regulation.
- Impact on cooking results - Sous vide's tighter controls yield more consistent texture and doneness.
Impact on Food Flavor and Texture
Sous vide cooking maintains a consistent low temperature that enhances food flavor by evenly breaking down proteins and preserving moisture, resulting in tender, juicy dishes. The precise control prevents overcooking and ensures uniform texture throughout the food.
Low-oxygen water baths reduce oxidation, which helps retain the natural colors and fresh flavors of ingredients, especially delicate proteins like fish and seafood. However, without precise temperature regulation, texture may be uneven, leading to less predictable cooking results compared to sous vide methods.
Equipment and Setup Requirements
Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature control equipment like immersion circulators to maintain water at exact cooking temperatures. Low-oxygen water baths need specialized systems to reduce oxygen levels, which often demand more complex and costly setup compared to basic sous vide devices.
- Immersion Circulator - Essential for sous vide, it maintains a consistent temperature within a narrow range for even cooking.
- Oxygen Scavenging System - Used in low-oxygen water baths to remove dissolved oxygen, preventing oxidation and enhancing food texture.
- Cost and Complexity - Sous vide devices are widely available and affordable, whereas low-oxygen setups require advanced equipment and higher investment.
Overall, sous vide offers straightforward, affordable equipment, while low-oxygen water baths demand specialized and more complex setups.
Food Safety Considerations
| Cooking Method | Food Safety Considerations |
| Sous Vide | Maintains precise temperature control between 130degF and 195degF, minimizing bacterial growth and ensuring pasteurization. Vacuum sealing reduces oxygen exposure, limiting aerobic bacteria but requires strict monitoring to prevent anaerobic pathogen proliferation. Proper time-temperature combinations are critical to neutralize pathogens like Clostridium botulinum. |
| Low-Oxygen Water Bath | Reduces dissolved oxygen but lacks precise temperature regulation, increasing the risk of uneven cooking and bacterial survival. The reduced oxygen environment can encourage anaerobic pathogen growth without proper heat levels. Ensuring consistent and adequate temperatures is essential for safe pathogen control in this method. |
Versatility for Home Cooks
How does sous vide compare to a low-oxygen water bath in terms of versatility for home cooks? Sous vide offers precise temperature control suitable for a wide range of proteins, vegetables, and even desserts, making it highly adaptable for various culinary techniques. Low-oxygen water baths primarily focus on reducing oxidation and are less flexible for diverse cooking styles, limiting their practicality in everyday home kitchens.
Energy Efficiency and Cost Analysis
Sous vide cooking typically uses less energy than low-oxygen water baths due to its precise temperature control and insulation, reducing heat loss. Cost analysis shows sous vide devices have lower operational expenses, whereas low-oxygen systems demand higher maintenance and energy input.
- Energy Consumption - Sous vide machines maintain stable temperatures efficiently, minimizing power usage compared to continuous aeration in low-oxygen baths.
- Equipment Costs - Initial investment for sous vide circulators is generally lower and more accessible than specialized low-oxygen systems.
- Operational Expenses - Sous vide setups incur reduced electricity costs and minimal maintenance, resulting in lower long-term expenditure.
Related Important Terms
Precision Thermal Circulation
Sous vide cooking utilizes precision thermal circulation to maintain a consistent temperature within +-0.1degC, ensuring even and controlled heat distribution for perfect food doneness. In contrast, low-oxygen water baths lack advanced temperature regulation, resulting in less precise cooking outcomes and variability in texture and flavor.
Vacuum Sealed Protein Infusion
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise temperature control through vacuum-sealed bags to enhance protein infusion, ensuring even flavor penetration and moisture retention. In contrast, low-oxygen water baths reduce oxidation but lack the airtight seal necessary for optimal nutrient and flavor infusion into proteins.
Oxygen Displacement Cooking
Sous vide cooking relies on vacuum-sealing food to create a low-oxygen environment that preserves flavor and texture by preventing oxidation during precise temperature control. Low-oxygen water baths achieve similar oxidation prevention through oxygen displacement techniques without vacuum sealing, but sous vide offers superior consistency and food safety by tightly controlling the sealed atmosphere around the food.
Anaerobic Water Bath Technique
The Anaerobic Water Bath Technique in sous vide cooking uses a low-oxygen environment to inhibit bacterial growth and enhance flavor development while maintaining precise temperature control. This method contrasts with traditional sous vide, offering improved food safety and extended shelf life by limiting oxidative reactions during the cooking process.
Oxystability Cooking Method
Sous vide cooking relies on precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag, preserving flavors and nutrients through low-oxygen environments that prevent oxidation. Compared to low-oxygen water baths, the oxystability cooking method enhances food texture and shelf life by minimizing oxidative deterioration during prolonged cooking.
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide (MASV) enhances traditional sous vide cooking by using a low-oxygen environment to slow oxidation and microbial growth, resulting in superior preservation of texture, flavor, and color. This method extends shelf life and improves food safety more effectively than conventional sous vide water baths, making it ideal for delicate proteins and high-value ingredients.
Reduced-Oxidation Flavor Lock
Sous vide cooking employs a vacuum-sealed bag that minimizes oxygen exposure, preserving the food's natural flavors and enhancing tenderness through reduced-oxidation flavor lock. In contrast, low-oxygen water baths may lower oxidation but often lack the airtight seal of sous vide, making sous vide superior for maintaining optimal taste and texture.
Low-O₂ Culinary Extraction
Low-O2 Culinary Extraction in sous vide cooking enhances flavor and nutrient retention by minimizing oxidation during the low-oxygen water bath process. This method outperforms traditional sous vide by preserving delicate compounds and improving texture through controlled oxygen levels.
Microbial Secure Bath (MSB)
Sous vide cooking utilizes precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed environment, ensuring consistent heat distribution that effectively reduces microbial growth, whereas low-oxygen water baths like the Microbial Secure Bath (MSB) specifically minimize oxygen presence to inhibit aerobic pathogens and extend food safety. MSB technology enhances microbial control by combining oxygen exclusion with controlled temperature settings, providing an advanced method for safe, high-quality cooking and shelf-life extension.
Sous vide vs low-oxygen water bath for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com