Sous vide cooking offers exceptional precision through vacuum-sealed food cooked in a water bath with stable, evenly distributed temperatures. Ohmic heating provides rapid and uniform temperature control by passing an electrical current directly through the food, allowing real-time monitoring and adjustment. When comparing both, sous vide excels in consistent low-temperature cooking, while ohmic heating is advantageous for faster, energy-efficient heating with precise control.
Table of Comparison
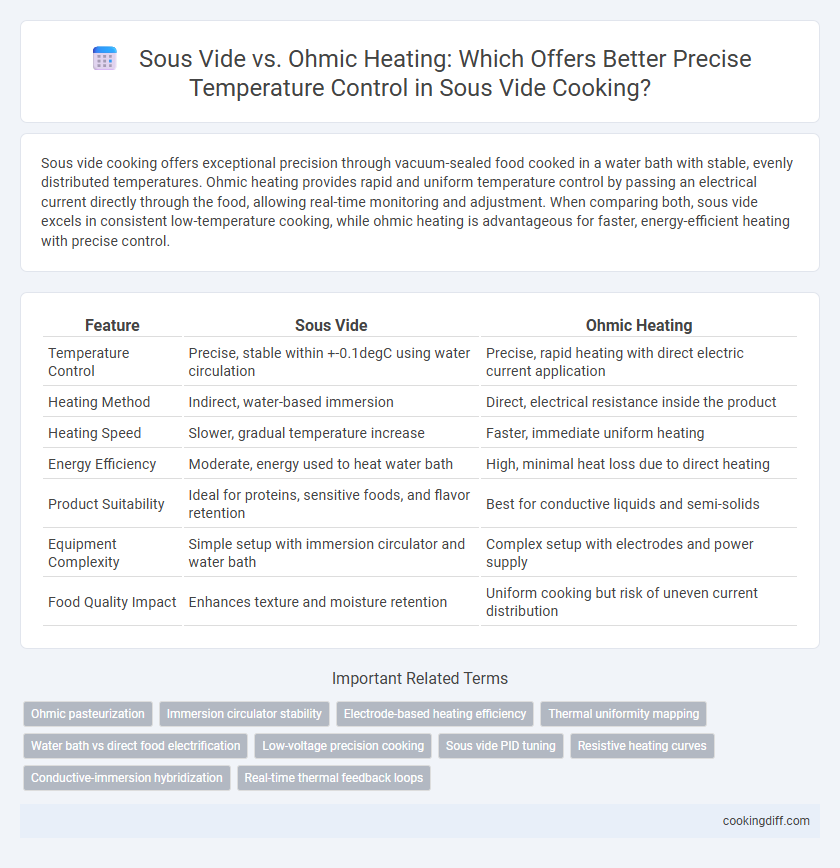
| Feature | Sous Vide | Ohmic Heating |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature Control | Precise, stable within +-0.1degC using water circulation | Precise, rapid heating with direct electric current application |
| Heating Method | Indirect, water-based immersion | Direct, electrical resistance inside the product |
| Heating Speed | Slower, gradual temperature increase | Faster, immediate uniform heating |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate, energy used to heat water bath | High, minimal heat loss due to direct heating |
| Product Suitability | Ideal for proteins, sensitive foods, and flavor retention | Best for conductive liquids and semi-solids |
| Equipment Complexity | Simple setup with immersion circulator and water bath | Complex setup with electrodes and power supply |
| Food Quality Impact | Enhances texture and moisture retention | Uniform cooking but risk of uneven current distribution |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Ohmic Heating
| Sous Vide | A cooking method involving vacuum-sealing food and immersing it in a water bath at precisely controlled temperatures typically ranging from 50degC to 90degC, ensuring even and accurate heat distribution. |
| Ohmic Heating | Technique that uses electric currents passing through food to generate heat internally, enabling rapid and uniform temperature control without relying on external heating elements. |
| Temperature Control Comparison | Sous vide offers highly consistent and gentle temperature regulation with minimal fluctuations, while ohmic heating provides fast, uniform heating ideal for conductive foods but requires precise electrical property management for accuracy. |
Fundamentals of Precise Temperature Control in Cooking
Sous vide cooking utilizes a water bath heated to a precise temperature, maintaining consistent heat through immersion circulation, ensuring uniform doneness. Ohmic heating achieves temperature control by passing electric current directly through the food, generating heat internally and enabling rapid, even heating. Both methods prioritize precise temperature regulation, but sous vide offers superior uniformity and fine-tuned control essential for delicate culinary textures.
How Sous Vide Achieves Temperature Precision
Sous vide achieves precise temperature control by immersing food in a water bath heated to an exact temperature, maintained by a digital immersion circulator. This method relies on water's high heat capacity to evenly distribute temperature, minimizing fluctuations and preventing overcooking.
Ohmic heating controls temperature through electrical resistance heating directly within the food product, allowing for rapid and uniform heating. However, sous vide offers superior precision by continuously circulating water to maintain a stable, consistent temperature typically within +-0.1degC. This level of control ensures even cooking and preservation of texture and flavor in delicate foods.
Ohmic Heating Technology Explained
Ohmic heating technology utilizes electric currents passed directly through food to generate heat uniformly, enabling precise temperature control crucial in sous vide cooking. Unlike traditional sous vide methods relying on water baths and external heat sources, ohmic heating achieves rapid, evenly distributed heating without temperature gradients. This precise control enhances cooking consistency, texture, and safety by maintaining exact temperatures throughout the food matrix.
Accuracy and Consistency: Sous Vide vs. Ohmic Heating
Sous vide cooking offers highly accurate temperature control by circulating water at precise, stable temperatures, ensuring consistent cooking results. Ohmic heating heats food through electrical resistance, which can lead to rapid temperature changes but may lack the uniformity of sous vide immersion.
- Temperature Precision - Sous vide systems maintain water baths within +-0.1degC accuracy for meticulous cooking control.
- Heat Distribution - Ohmic heating can cause uneven temperature zones due to variable electrical conductivity in food.
- Consistency Over Time - Sous vide's continuous water circulation promotes uniform heat transfer, resulting in reproducible taste and texture.
Speed and Efficiency Differences
Sous vide cooking provides precise temperature control by circulating water at a consistent temperature, but it generally requires longer cooking times. Ohmic heating uses electrical currents to heat food rapidly and evenly from within, significantly reducing cooking time while maintaining temperature accuracy.
- Speed Advantage of Ohmic Heating - Ohmic heating reduces cooking duration by directly heating the food, unlike sous vide's indirect water bath method.
- Energy Efficiency - Ohmic heating consumes less energy as it heats food faster and minimizes heat loss compared to the prolonged water circulation in sous vide.
- Temperature Consistency - Sous vide offers stable, uniform temperature control ideal for delicate foods, whereas ohmic heating achieves rapid temperature increases with precise regulation through electrical control.
Impact on Food Quality and Texture
Sous vide offers unparalleled precision in temperature control by immersing food in a water bath heated to a consistent temperature, preserving moisture and enhancing texture. Ohmic heating, which uses electric currents to heat food internally and rapidly, may cause uneven cooking and negatively affect delicate textures compared to sous vide.
- Sous vide maintains uniform heat distribution - This method ensures even cooking, preventing overcooking or drying out of proteins.
- Ohmic heating accelerates cooking time - Rapid internal heating can lead to textural changes, especially in sensitive food items.
- Sous vide enhances flavor retention - The slow, precise temperature prevents volatile compounds from evaporating.
Sous vide's gentle and consistent temperature control results in superior food quality and texture compared to ohmic heating techniques.
Energy Consumption Comparison
Sous vide cooking uses a water bath heated by an immersion circulator, which maintains precise temperature control with minimal energy loss due to water's high heat capacity and insulation. Ohmic heating applies electrical current directly through the food, resulting in faster heating times but often higher energy consumption because of resistance variations and less efficient thermal distribution.
Energy consumption in sous vide is generally lower over longer cooking periods due to sustained low-temperature heat and effective insulation. In contrast, ohmic heating's rapid temperature increase can spike energy usage, making it less efficient for prolonged precise temperature control compared to sous vide systems.
Versatility and Practicality in Home and Commercial Kitchens
Sous vide offers unparalleled versatility for precise temperature control, enabling consistent results in both home and commercial kitchens by immersing food in a water bath maintained at exact temperatures. This method suits a wide range of ingredients, from delicate fish to robust meats, ensuring even cooking without risk of overcooking.
Ohmic heating, relying on electrical resistance to generate heat within the food, provides rapid and uniform temperature control, making it practical for high-volume commercial kitchens focused on efficiency. However, its complexity and equipment costs limit its accessibility and adaptability for everyday home cooking scenarios compared to sous vide machines.
Related Important Terms
Ohmic pasteurization
Ohmic pasteurization utilizes electrical currents passing through food to generate uniform internal heat, enabling precise temperature control critical for sous vide cooking. This method offers faster heat transfer and reduced thermal gradients compared to traditional sous vide water baths, enhancing pasteurization efficiency and maintaining product quality.
Immersion circulator stability
Sous vide immersion circulators offer superior temperature stability by maintaining water bath precision within +-0.1degC, enabling consistent cooking results unlike ohmic heating systems where temperature fluctuations are more common due to electrode interference. The precise control of immersion circulators ensures even heat distribution, critical for achieving desired texture and doneness in sous vide cooking.
Electrode-based heating efficiency
Sous vide and ohmic heating both offer precise temperature control, but ohmic heating relies on electrode-based heating efficiency to uniformly generate heat directly within the food, minimizing heat loss and ensuring rapid temperature response. This electrode-driven method enhances energy efficiency and allows for more consistent thermal gradients compared to the external water bath heating used in traditional sous vide cooking.
Thermal uniformity mapping
Sous vide ensures precise temperature control through consistent thermal uniformity mapping, maintaining water bath temperatures within +-0.1degC to achieve evenly cooked results. Ohmic heating offers rapid, volumetric heating by passing electric current directly through the food, but thermal uniformity can vary depending on food conductivity, requiring careful monitoring to match sous vide's uniform precision.
Water bath vs direct food electrification
Sous vide utilizes a water bath to ensure uniform temperature distribution around the food, providing precise and consistent heat control without direct contact. Ohmic heating employs direct electrification of the food through electrical resistance, enabling rapid and uniform heating but requiring careful monitoring to prevent uneven cooking or overheating.
Low-voltage precision cooking
Sous vide utilizes low-voltage precision cooking by maintaining water temperature within +-0.1degC through continuous circulation and sensor feedback, ensuring consistent heat transfer and food doneness. Ohmic heating achieves precise temperature control by passing electrical current directly through the food, allowing rapid, uniform heating but may require complex calibration to match the stable, gradual heat profile of traditional sous vide methods.
Sous vide PID tuning
Sous vide cooking achieves precise temperature control through advanced PID tuning, which continuously adjusts heat input to maintain water bath temperature within +-0.1degC, ensuring consistent food texture and safety. In contrast, ohmic heating relies on electrical resistance for rapid and uniform heating but generally lacks the fine-tuned PID capabilities integral to sous vide systems for ultra-precise temperature stability.
Resistive heating curves
Sous vide relies on precisely controlled water baths for uniform heat transfer, while ohmic heating uses resistive heating curves characterized by direct electrical current passing through food, enabling rapid and uniform internal temperature rise. The resistive heating curve in ohmic heating offers superior responsiveness and accuracy compared to conventional sous vide temperature maintenance, improving precision in cooking delicate proteins.
Conductive-immersion hybridization
Conductive-immersion hybridization combines sous vide's water bath precision with ohmic heating's rapid, uniform energy transfer, enhancing temperature control accuracy for sensitive food processing. This method leverages ohmic heating's volumetric heat generation to complement sous vide's stable conductive environment, ensuring consistent thermal profiles and minimizing thermal gradients.
Sous vide vs ohmic heating for precise temperature control. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com