Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature to achieve desired doneness while maintaining texture and flavor, but it does not inherently guarantee safety from pathogens. Sous vide pasteurization extends this method by applying specific time-temperature combinations designed to destroy harmful bacteria and ensure food safety. Understanding the difference is crucial for safely preparing vacuum-sealed foods that require both tenderness and pathogen reduction.
Table of Comparison
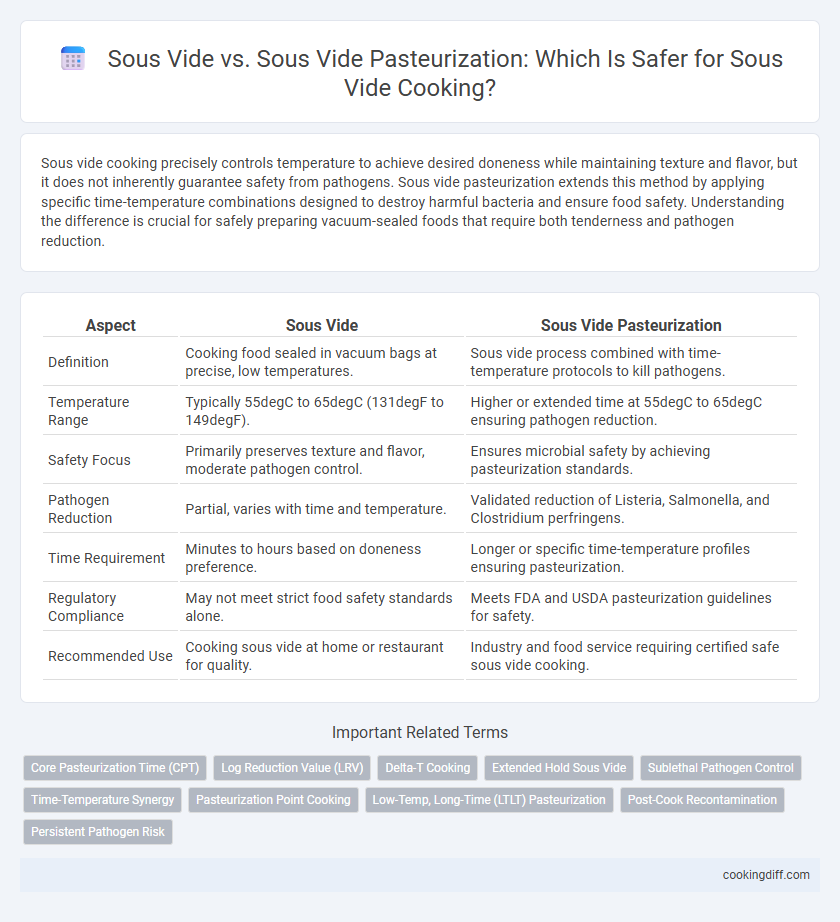
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Sous Vide Pasteurization |
|---|---|---|
| Definition | Cooking food sealed in vacuum bags at precise, low temperatures. | Sous vide process combined with time-temperature protocols to kill pathogens. |
| Temperature Range | Typically 55degC to 65degC (131degF to 149degF). | Higher or extended time at 55degC to 65degC ensuring pathogen reduction. |
| Safety Focus | Primarily preserves texture and flavor, moderate pathogen control. | Ensures microbial safety by achieving pasteurization standards. |
| Pathogen Reduction | Partial, varies with time and temperature. | Validated reduction of Listeria, Salmonella, and Clostridium perfringens. |
| Time Requirement | Minutes to hours based on doneness preference. | Longer or specific time-temperature profiles ensuring pasteurization. |
| Regulatory Compliance | May not meet strict food safety standards alone. | Meets FDA and USDA pasteurization guidelines for safety. |
| Recommended Use | Cooking sous vide at home or restaurant for quality. | Industry and food service requiring certified safe sous vide cooking. |
Understanding Sous Vide: Basics and Benefits
Sous vide cooking involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it at precise, low temperatures to retain moisture and enhance flavor. This method ensures even cooking and preserves nutritional quality by controlling heat exposure effectively.
Sous vide pasteurization specifically targets food safety by holding food at temperatures that eliminate harmful pathogens without overcooking. Understanding the temperature and time parameters for pasteurization is crucial for preventing foodborne illnesses while maintaining sous vide benefits.
What is Sous Vide Pasteurization?
Sous vide pasteurization is a precise cooking technique that combines controlled temperature and time to eliminate harmful pathogens in food, ensuring safety without compromising texture or flavor. This process typically involves cooking vacuum-sealed food at lower temperatures for longer periods compared to traditional sous vide methods.
By maintaining temperatures high enough to destroy bacteria yet low enough to preserve food quality, sous vide pasteurization achieves both pasteurization and cooking simultaneously. This method is especially important in commercial kitchens to comply with food safety standards and prevent foodborne illnesses.
Cooking Temperatures: Sous Vide vs Pasteurization
Sous vide cooking typically uses temperatures between 129degF and 140degF to achieve precise doneness, while sous vide pasteurization requires higher temperatures, usually above 140degF, to ensure food safety by eliminating harmful pathogens. Pasteurization time and temperature combinations are scientifically validated to reduce bacterial load, making sous vide pasteurization critical for meat and seafood safety. Understanding the specific thermal thresholds and required hold times is essential to balance both food quality and microbiological safety in sous vide cooking.
Time and Temperature: Key Safety Differences
Sous vide cooking typically involves lower temperatures ranging from 120degF to 185degF, focusing on precise doneness and texture, whereas sous vide pasteurization requires specific combinations of time and temperature, such as holding food at 131degF for at least 12 minutes, to effectively eliminate pathogens for safety. The critical difference is that sous vide pasteurization follows scientifically validated time-temperature parameters to ensure microbial safety, while regular sous vide cooking may not guarantee the same level of pathogen reduction. Understanding these distinctions helps prevent foodborne illnesses by applying appropriate heat treatments during cooking.
Food Safety Risks in Traditional Sous Vide
| Traditional sous vide cooking at temperatures below 54degC (130degF) increases the risk of bacterial growth, particularly Clostridium botulinum, due to anaerobic vacuum-sealed environments. Sous vide pasteurization employs higher temperatures (typically 55-65degC) and longer cooking times to effectively eliminate pathogens without compromising texture. Ensuring precise temperature control and time adjustments is critical to maintaining food safety and preventing foodborne illnesses in sous vide preparations. |
How Pasteurization Enhances Food Safety
Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature to cook food evenly and retain moisture, but sous vide pasteurization specifically targets pathogens by maintaining food at exact temperatures long enough to kill harmful bacteria. Pasteurization enhances food safety by combining heat and time to reduce microbial load without overcooking.
- Microbial Reduction - Pasteurization ensures that harmful bacteria such as Salmonella and Listeria are effectively reduced to safe levels through controlled heat exposure.
- Consistent Temperature Control - Strict temperature regulation during sous vide pasteurization prevents undercooked zones, minimizing the risk of foodborne illness.
- Extended Shelf Life - By lowering microbial counts, sous vide pasteurization extends refrigerated storage time while maintaining food quality.
Impact on Food Texture and Flavor
Sous vide cooking preserves the natural texture and enhances the flavor of food by cooking it at precise low temperatures over extended periods. Sous vide pasteurization combines these benefits with a food safety process that effectively reduces pathogens without significantly altering taste or tenderness.
- Enhanced Texture - Sous vide maintains moisture and tenderness by preventing overcooking through precise temperature control.
- Flavor Retention - Low-temperature cooking preserves delicate flavors and prevents the loss of volatile compounds.
- Safety without Quality Loss - Pasteurization via sous vide eliminates harmful bacteria while maintaining texture and flavor integrity better than traditional high-heat treatments.
Practical Applications: Home vs Commercial Use
How do sous vide and sous vide pasteurization differ in safety for home versus commercial use? Sous vide at home primarily focuses on temperature control to ensure food is cooked evenly and safely, while sous vide pasteurization applies specific time-temperature combinations to eliminate pathogens, meeting commercial safety standards. Commercial kitchens rely on pasteurization protocols to comply with regulatory requirements and extend shelf life, whereas home cooks prioritize ease of use and consistent results.
Guidelines for Safe Sous Vide Cooking
Sous vide cooking requires precise temperature control to ensure food safety by eliminating harmful bacteria effectively. Sous vide pasteurization involves maintaining specific temperatures over time to achieve a safe reduction of pathogens while preserving food quality.
- Maintain proper temperature - The internal temperature must reach and be held at a level that destroys pathogens, typically between 130degF and 140degF for meats.
- Time control - Sufficient time at temperature is critical; extended cooking durations ensure pasteurization and bacteria elimination.
- Use vacuum-sealed bags - Vacuum sealing prevents contamination and promotes even heat transfer during sous vide cooking.
Following established guidelines for temperature and time is essential for safe sous vide preparation and pasteurization effectiveness.
Related Important Terms
Core Pasteurization Time (CPT)
Core Pasteurization Time (CPT) determines the minimum duration required at a specific temperature to achieve safe microbial reduction during sous vide cooking, ensuring food safety. Sous vide pasteurization specifically targets precise CPT values to inactivate pathogens without compromising texture, unlike traditional sous vide which may prioritize cooking consistency over strict safety thresholds.
Log Reduction Value (LRV)
Sous vide cooking typically achieves a moderate Log Reduction Value (LRV) in microbial populations by precise temperature control, whereas sous vide pasteurization targets higher LRV levels, often exceeding 6-log reductions, to ensure enhanced food safety. Pasteurization sous vide protocols rely on time-temperature combinations validated to inactivate pathogens like Listeria monocytogenes and Salmonella spp., providing a scientifically proven microbial lethality benchmark beyond standard sous vide cooking.
Delta-T Cooking
Sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control to achieve even pasteurization by gradually raising food to target temperatures, ensuring microbial safety without overcooking. Delta-T cooking, a technique that monitors the temperature difference between the core and environment, enhances safety by preventing thermal shock and optimizing pasteurization times in sous vide processes.
Extended Hold Sous Vide
Extended Hold Sous Vide offers enhanced safety by maintaining precise low temperatures for longer durations, effectively pasteurizing food without compromising texture or flavor compared to standard Sous Vide techniques. This method ensures pathogen reduction through sustained heat exposure, aligning with FDA guidelines for safe cooking practices.
Sublethal Pathogen Control
Sous vide cooking controls sublethal pathogens by maintaining precise temperature and time combinations that inhibit microbial growth without compromising food quality. Sous vide pasteurization further enhances safety by applying validated heat treatments to achieve specific log reductions in pathogens like Salmonella and Listeria, ensuring effective microbial inactivation within sealed vacuum environments.
Time-Temperature Synergy
Sous vide leverages precise time-temperature synergy to cook food evenly and safely by maintaining temperatures that inhibit bacterial growth, while sous vide pasteurization specifically targets pathogen reduction by applying controlled heat for extended durations to achieve food safety standards. The critical balance between temperature and exposure time ensures both methods effectively minimize microbial risks without compromising quality.
Pasteurization Point Cooking
Sous vide pasteurization ensures food safety by cooking at precise temperatures long enough to eliminate harmful pathogens, unlike standard sous vide that may focus more on texture and doneness. Pasteurization point cooking balances safety and quality by maintaining target temperatures verified through time-temperature combinations proven to reduce microbial risks effectively.
Low-Temp, Long-Time (LTLT) Pasteurization
Sous vide Low-Temp, Long-Time (LTLT) pasteurization ensures food safety by maintaining precise temperatures typically between 55degC and 65degC for extended periods, effectively eliminating pathogens without compromising texture or flavor. This method differs from standard sous vide cooking by specifically targeting microbial reduction through validated time-temperature combinations, providing both safety and quality in vacuum-sealed foods.
Post-Cook Recontamination
Sous vide cooking maintains food safety by vacuum-sealing and cooking at controlled temperatures, minimizing bacterial growth during cooking, but the risk of post-cook recontamination exists if sealed bags are compromised or handled improperly. Sous vide pasteurization combines precise temperature and time parameters to achieve microbial inactivation, yet preventing post-cook contamination requires strict hygiene and intact packaging to ensure lasting safety.
Sous vide vs Sous vide pasteurization for safety. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com