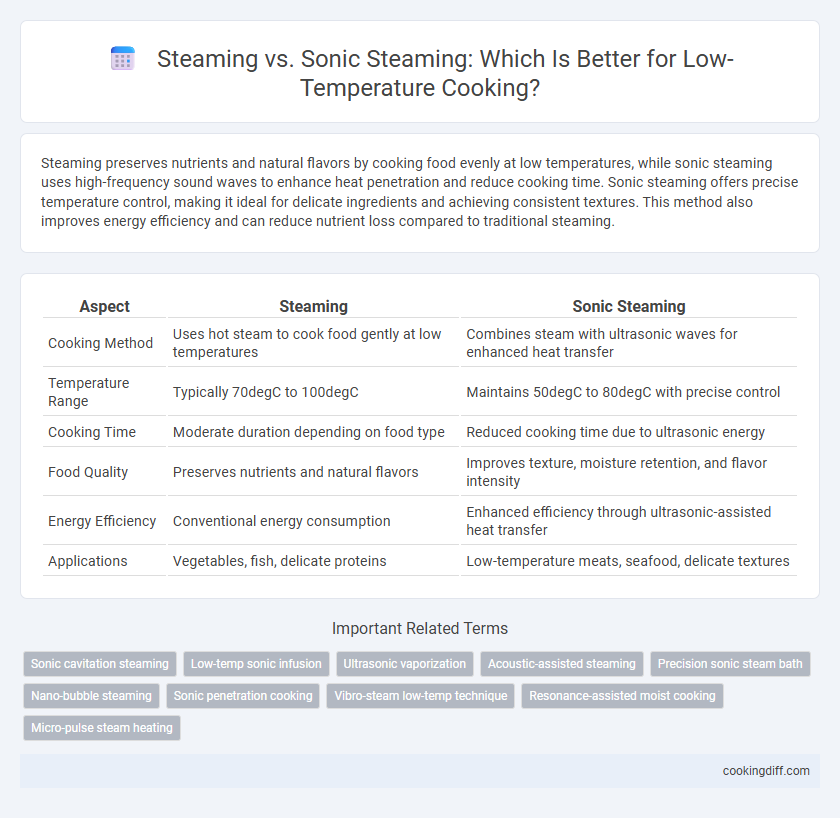
Steaming preserves nutrients and natural flavors by cooking food evenly at low temperatures, while sonic steaming uses high-frequency sound waves to enhance heat penetration and reduce cooking time. Sonic steaming offers precise temperature control, making it ideal for delicate ingredients and achieving consistent textures. This method also improves energy efficiency and can reduce nutrient loss compared to traditional steaming.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Sonic Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses hot steam to cook food gently at low temperatures | Combines steam with ultrasonic waves for enhanced heat transfer |
| Temperature Range | Typically 70degC to 100degC | Maintains 50degC to 80degC with precise control |
| Cooking Time | Moderate duration depending on food type | Reduced cooking time due to ultrasonic energy |
| Food Quality | Preserves nutrients and natural flavors | Improves texture, moisture retention, and flavor intensity |
| Energy Efficiency | Conventional energy consumption | Enhanced efficiency through ultrasonic-assisted heat transfer |
| Applications | Vegetables, fish, delicate proteins | Low-temperature meats, seafood, delicate textures |
Introduction to Low-Temperature Cooking Techniques
Low-temperature cooking techniques, such as steaming and sonic steaming, focus on gently heating food to preserve nutrients and enhance texture. Traditional steaming uses hot vapor to cook food evenly without direct contact with water.
Sonic steaming introduces ultrasonic vibrations to create tiny droplets and improve heat transfer, resulting in faster cooking times and more uniform heat distribution. This method minimizes nutrient loss and maintains food moisture better than conventional steaming. Both techniques suit delicate proteins and vegetables, offering precise temperature control for optimal flavor and texture.
What is Traditional Steaming?
Traditional steaming involves cooking food by exposing it to steam generated from boiling water, typically at temperatures around 100degC (212degF). This gentle cooking method preserves nutrients, texture, and flavor without direct contact with water, making it ideal for vegetables, fish, and delicate foods. It relies on consistent steam circulation within a closed environment, such as a bamboo steamer or metal steaming basket, to evenly cook food at low temperatures.
Understanding Sonic Steaming Technology
Sonic steaming technology uses high-frequency ultrasonic waves to generate steam at lower temperatures compared to traditional steaming methods. This process preserves nutrients and enhances flavors by minimizing heat exposure during cooking.
The ultrasonic vibrations create microbubbles that burst rapidly, producing evenly distributed steam and improving heat penetration. This makes sonic steaming ideal for delicate foods requiring gentle cooking while maintaining texture and moisture.
Temperature Control: Steaming vs Sonic Steaming
Steaming maintains a consistent temperature around 100degC, ideal for gentle cooking that preserves nutrients and texture. Sonic steaming uses ultrasonic waves to generate steam at precise, lower temperatures, enhancing temperature control for delicate ingredients.
- Steaming temperature consistency - Traditional steaming relies on boiling water, limiting temperature control to about 100degC.
- Sonic steaming precision - Ultrasonic technology enables steam generation at variable, lower temperatures, allowing exact thermal regulation.
- Impact on food quality - Enhanced temperature control with sonic steaming prevents overcooking, preserving flavor and nutrients better than conventional steaming.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Wins?
Steaming preserves nutrients by cooking food at lower temperatures and minimizing direct water contact, which reduces nutrient leaching. Sonic steaming uses ultrasonic waves to enhance heat penetration, potentially improving nutrient retention but requires more research to confirm its advantages.
- Traditional steaming retains water-soluble vitamins - Vitamins like B and C are better preserved due to gentler heat exposure.
- Sonic steaming accelerates heat transfer - Ultrasonic waves improve cooking efficiency and may reduce nutrient loss time.
- Research on nutrient retention is ongoing - Limited data suggests sonic steaming could outperform traditional methods but is not yet definitive.
Choosing between steaming and sonic steaming depends on available technology and desired nutrient preservation in low-temperature cooking.
Flavor and Texture Comparisons
Steaming preserves the natural flavor and moisture of ingredients by cooking them gently, maintaining a tender texture. Sonic steaming enhances this process by using ultrasonic waves to create finer steam particles, resulting in a more even heat distribution and improved flavor infusion.
- Flavor Retention - Traditional steaming retains subtle flavors but may dilute intensity due to water vapor.
- Texture Enhancement - Sonic steaming produces tender, uniformly cooked textures by penetrating food more deeply.
- Cooking Efficiency - Sonic steaming reduces cooking time while preserving nutrients better than conventional steaming.
Energy Efficiency and Equipment Needs
Steaming for low-temperature cooking typically requires minimal energy and straightforward equipment such as a conventional steamer or pot with a lid. Sonic steaming, utilizing ultrasonic waves to generate steam, offers enhanced energy efficiency by creating finer steam particles that penetrate food faster, reducing cooking time and energy consumption. However, sonic steaming demands specialized ultrasonic generators and equipment, resulting in higher initial investment compared to traditional steaming methods.
Cooking Times: Standard Steaming vs Sonic Steaming
How does cooking time differ between standard steaming and sonic steaming for low-temperature cooking? Standard steaming typically requires longer periods, often ranging from 20 to 60 minutes depending on the food type. Sonic steaming uses high-frequency sound waves to accelerate heat penetration, reducing cooking times by up to 50% while preserving texture and nutrients.
Safety and Food Quality Considerations
Steaming preserves food quality by gently cooking at low temperatures, retaining nutrients and natural flavors while minimizing oxidation risks. Traditional low-temperature steaming ensures safe food preparation by maintaining internal temperatures that inhibit bacterial growth without overcooking.
Sonic steaming introduces ultrasonic waves to enhance heat transfer, potentially reducing cooking time but raising questions about even temperature distribution and consistent pathogen elimination. Safety protocols must be rigorously maintained in sonic steaming to prevent undercooked areas and ensure optimal food texture and microbiological safety.
Related Important Terms
Sonic cavitation steaming
Sonic cavitation steaming leverages high-frequency sound waves to create microscopic vapor bubbles that implode, producing intense localized heat and pressure ideal for precise low-temperature cooking without nutrient loss. Unlike traditional steaming, this technique enhances heat transfer efficiency and accelerates cooking times while preserving texture and flavor integrity.
Low-temp sonic infusion
Low-temperature sonic infusion enhances traditional steaming by using ultrasonic waves to accelerate heat transfer and flavor penetration without raising the temperature, preserving delicate textures and nutrients. This method achieves precise cooking control and improved ingredient infusion compared to conventional steaming, ideal for sous-vide and low-temp culinary applications.
Ultrasonic vaporization
Ultrasonic vaporization in sonic steaming generates fine vapor particles through high-frequency sound waves, enabling more uniform heat distribution and faster cooking at low temperatures compared to conventional steaming. This method enhances moisture retention and nutrient preservation by reducing thermal damage during the cooking process.
Acoustic-assisted steaming
Acoustic-assisted steaming leverages ultrasonic waves to enhance heat and mass transfer during low-temperature cooking, resulting in faster cooking times and improved nutrient retention compared to conventional steaming. This technique disrupts water molecules and creates microbubbles that increase steam penetration, ensuring even cooking and preserving texture and flavor in delicate foods.
Precision sonic steam bath
Precision sonic steam bath technology enhances low-temperature cooking by using high-frequency sound waves to generate uniform steam, ensuring exact temperature control and even heat distribution. Compared to traditional steaming, this method improves flavor retention and texture while minimizing nutrient loss.
Nano-bubble steaming
Nano-bubble steaming enhances low-temperature cooking by creating ultra-fine steam particles that penetrate food more efficiently than traditional sonic steaming, resulting in improved heat transfer and moisture retention. This advanced method leverages the unique properties of nano-bubbles to accelerate cooking times while preserving texture and nutritional value.
Sonic penetration cooking
Sonic steaming employs high-frequency sound waves to enhance the penetration of steam into food, resulting in faster and more uniform low-temperature cooking compared to traditional steaming methods. This technology improves heat transfer efficiency and helps preserve the texture and nutrients of delicate ingredients.
Vibro-steam low-temp technique
Vibro-steam low-temperature cooking combines gentle steaming with ultrasonic vibrations to enhance heat transfer and moisture retention, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional steaming. This technique operates at controlled low temperatures, ensuring precise cooking and improved flavor development while reducing nutrient loss and cooking time.
Resonance-assisted moist cooking
Resonance-assisted moist cooking in sonic steaming enhances heat transfer efficiency by using ultrasonic waves to generate micro-vibrations, resulting in faster and more uniform cooking at low temperatures compared to traditional steaming. This method preserves food texture and nutrients while reducing cooking time, making it ideal for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Steaming vs Sonic Steaming for Low-Temperature Cooking Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com