Stewing involves cooking food slowly in liquid at a low temperature, allowing flavors to meld and ingredients to tenderize naturally. Sous vide stewing, however, uses precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag to retain moisture and intensify flavors without overcooking. While traditional stewing offers robust, home-cooked comfort, sous vide stewing provides consistent results and enhanced texture through gentle, even heat distribution.
Table of Comparison
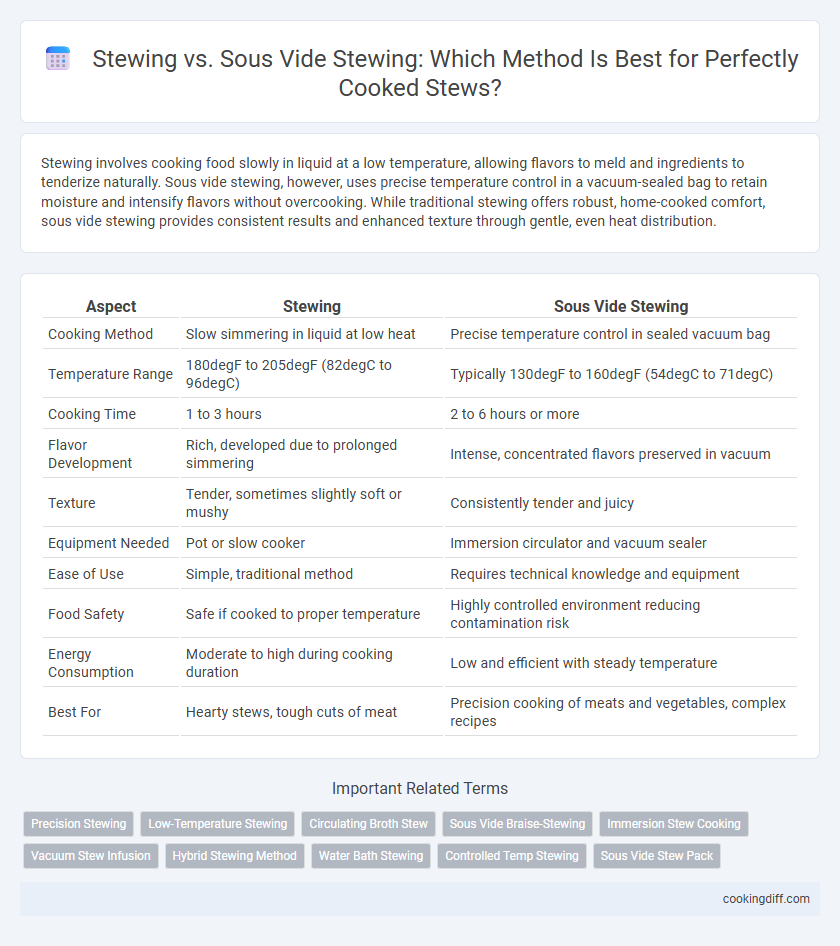
| Aspect | Stewing | Sous Vide Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Slow simmering in liquid at low heat | Precise temperature control in sealed vacuum bag |
| Temperature Range | 180degF to 205degF (82degC to 96degC) | Typically 130degF to 160degF (54degC to 71degC) |
| Cooking Time | 1 to 3 hours | 2 to 6 hours or more |
| Flavor Development | Rich, developed due to prolonged simmering | Intense, concentrated flavors preserved in vacuum |
| Texture | Tender, sometimes slightly soft or mushy | Consistently tender and juicy |
| Equipment Needed | Pot or slow cooker | Immersion circulator and vacuum sealer |
| Ease of Use | Simple, traditional method | Requires technical knowledge and equipment |
| Food Safety | Safe if cooked to proper temperature | Highly controlled environment reducing contamination risk |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate to high during cooking duration | Low and efficient with steady temperature |
| Best For | Hearty stews, tough cuts of meat | Precision cooking of meats and vegetables, complex recipes |
Introduction to Stewing and Sous Vide Stewing
Stewing is a traditional slow-cooking method where ingredients are simmered in liquid at low temperatures to develop deep flavors and tender textures. Sous vide stewing involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath, which ensures even cooking and preserves moisture. Both techniques enhance the taste and tenderness of meats and vegetables, but sous vide stewing offers superior consistency and nutrient retention.
Key Differences Between Stewing and Sous Vide Stewing
Stewing involves slow-cooking food in liquid at a low temperature over an extended period, allowing flavors to meld and meats to tenderize naturally. Sous vide stewing, by contrast, cooks vacuum-sealed food in a precisely controlled water bath, ensuring consistent temperature and even doneness throughout.
The key difference lies in temperature control; stewing subjects food to varying heat levels, while sous vide stewing maintains exact temperatures for hours, preserving texture and moisture. Sous vide stewing also reduces oxidation and nutrient loss compared to traditional stewing methods.
The Science Behind Traditional Stewing
Traditional stewing relies on slow cooking at temperatures just below boiling, allowing collagen in tougher cuts of meat to break down into gelatin, which tenderizes and enriches the dish. The Maillard reaction occurs at the surface of the meat, enhancing flavor complexity through browning before the simmering phase.
Heat transfer in stewing happens through convection, where hot liquid surrounds the ingredients evenly, ensuring thorough cooking and moisture retention. This method contrasts with sous vide stewing, which uses precise temperature control and vacuum sealing to prevent nutrient loss and achieve uniform texture.
Sous Vide Stewing: How It Works
| Method | Sous Vide Stewing |
| Temperature Control | Precise, low-temperature water bath (typically 55degC to 85degC) maintains consistent heat for even cooking. |
| Cooking Time | Extended duration, ranging from 2 to 48 hours, allows tenderizing tough cuts without overcooking. |
| Texture & Flavor | Retains moisture and enhances natural flavors by sealing ingredients in a vacuum pouch, preventing nutrient loss. |
| Equipment | Requires a sous vide immersion circulator and vacuum sealer for airtight cooking environment. |
| Comparison to Traditional Stewing | Offers more consistent results, precise temperature control, and prevents overcooking typical in stovetop methods. |
Flavor and Texture Comparison
Stewing extracts deep, rich flavors by slow cooking ingredients in liquid, creating a tender texture as collagen breaks down. Sous vide stewing gently cooks food at precise temperatures, preserving intense flavors and delivering uniform, melt-in-the-mouth texture.
- Flavor Intensity - Traditional stewing develops complex, caramelized notes from prolonged simmering, while sous vide intensifies natural ingredient flavors without oxidation.
- Texture Consistency - Stewing can result in variable tenderness due to heat fluctuations, whereas sous vide ensures consistent softness throughout the protein or vegetable.
- Culinary Control - Sous vide stewing offers precise temperature control that prevents overcooking, contrasting with traditional stewing's broader heat range and risk of toughening textures.
Nutrient Retention: Stewing vs Sous Vide
Stewing traditionally involves cooking food slowly in liquid over low heat, which can cause some nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to heat and water. Sous vide stewing uses precise temperature control and vacuum sealing, significantly preserving vitamins and minerals by reducing oxidation and nutrient leaching.
- Vitamin Retention - Sous vide stewing maintains higher levels of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex compared to traditional stewing.
- Mineral Preservation - Mineral content remains more stable in sous vide stewing because nutrients are sealed within the vacuum pouch, minimizing loss to cooking liquids.
- Antioxidant Protection - Sous vide reduces nutrient degradation by cooking at consistent low temperatures, preserving antioxidant compounds better than conventional stewing.
Choosing sous vide stewing over traditional methods enhances nutrient retention, leading to more nutritious meals with enriched flavor and texture.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Stewing requires a heavy-bottomed pot or Dutch oven with a tight-fitting lid to maintain low, consistent heat and retain moisture during long cooking times. Sous vide stewing relies on specialized equipment such as an immersion circulator and vacuum-sealed bags, which provide precise temperature control and ensure even cooking. While traditional stewing equipment is commonly found in most kitchens, sous vide stewing demands investment in modern, temperature-regulated devices to achieve optimal results.
Time and Temperature Considerations
Stewing typically requires cooking at a simmering temperature between 85degC to 95degC for 1.5 to 3 hours, allowing collagen to break down and flavors to meld slowly. Sous vide stewing uses precise temperature control, commonly set between 60degC to 70degC, but extends the cooking time to 8 to 24 hours for optimized texture and tenderness.
Time and temperature are crucial variables in both stewing methods, directly influencing meat tenderness and flavor infusion. Conventional stewing uses higher heat to speed up collagen breakdown, but can risk overcooking or drying out meat if not closely monitored. Sous vide stewing relies on lower temperatures and extended cooking durations to maintain juiciness and uniform doneness throughout the protein.
Ideal Foods for Stewing vs Sous Vide Stewing
What types of foods are ideal for traditional stewing compared to sous vide stewing? Traditional stewing is perfect for tougher cuts of meat like beef chuck, pork shoulder, and lamb shanks, as it tenderizes through long, slow cooking in liquid. Sous vide stewing excels with more delicate proteins such as chicken breasts and fish, allowing precise temperature control to retain moisture and texture without overcooking.
Related Important Terms
Precision Stewing
Precision stewing offers consistent temperature control that ensures even cooking and optimal flavor extraction, unlike traditional stewing which relies on variable heat sources. Sous vide stewing further enhances this precision by vacuum-sealing ingredients and cooking them in a water bath, preserving moisture and intensifying textures.
Low-Temperature Stewing
Low-temperature stewing uses a gentle simmer at temperatures between 170degF and 200degF to tenderize tough cuts by breaking down connective tissues while maintaining rich, concentrated flavors. Compared to sous vide stewing, which involves precise temperature control and vacuum sealing, traditional low-temperature stewing offers a more hands-on approach with potential variations in heat distribution and texture.
Circulating Broth Stew
Circulating broth stews enhance flavor infusion by continuously moving liquid around ingredients, creating even heat distribution and tenderizing meat more effectively than traditional stewing. Sous vide stewing maintains precise temperature control within a sealed environment, preserving moisture and intensifying taste while preventing nutrient loss, but lacks the dynamic circulation of broth found in conventional methods.
Sous Vide Braise-Stewing
Sous vide braise-stewing offers precise temperature control that enhances flavor infusion and tenderness compared to traditional stewing methods. This technique maintains consistent heat, preventing overcooking while allowing slow collagen breakdown for succulent, evenly cooked meats.
Immersion Stew Cooking
Immersion stew cooking delivers deep flavor infusion through prolonged heat exposure and liquid immersion, while sous vide stewing enhances precise temperature control and texture consistency by vacuum-sealing ingredients and cooking them in a water bath. Both methods optimize tenderness and moisture retention, but sous vide stewing offers superior nutrient preservation and reduced oxidation compared to traditional immersion stewing.
Vacuum Stew Infusion
Vacuum stew infusion in sous vide stewing enhances flavor penetration and tenderness by cooking sealed ingredients at precise low temperatures, contrasting traditional stewing that relies on prolonged heat and liquid immersion. This method preserves nutrients and intensifies aromatic profiles, offering a controlled cooking environment that maximizes infusion efficiency and texture consistency.
Hybrid Stewing Method
The hybrid stewing method combines traditional slow cooking with sous vide precision, ensuring meat retains maximum juiciness and flavor while achieving perfect tenderness. By controlling temperature with sous vide technology and finishing with classic stewing techniques, this approach enhances texture and intensifies the infusion of herbs and spices.
Water Bath Stewing
Water bath stewing uses consistent, gently heated water to cook food slowly and evenly, preserving moisture and tenderizing tough cuts through prolonged heat exposure. Compared to sous vide stewing, water bath stewing is more accessible without specialized equipment but offers slightly less precise temperature control, resulting in excellent yet less uniform texture and flavor development.
Controlled Temp Stewing
Controlled temperature stewing maintains consistent heat between 160degF and 190degF, ensuring tender, evenly cooked meat with enhanced flavor absorption. Unlike sous vide stewing, which uses precise water bath temperatures, controlled temp stewing utilizes stovetop or slow cookers to balance texture and moisture retention without vacuum sealing.
Stewing vs Sous Vide Stewing for Cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com