Stewing breaks down tough cuts of meat by cooking them slowly in liquid at low temperatures, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes. Sous-vide stewing uses precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag, ensuring even cooking and enhanced moisture retention. Compared to traditional stewing, sous-vide offers consistent tenderness and preserves the natural juices, making meats exceptionally succulent.
Table of Comparison
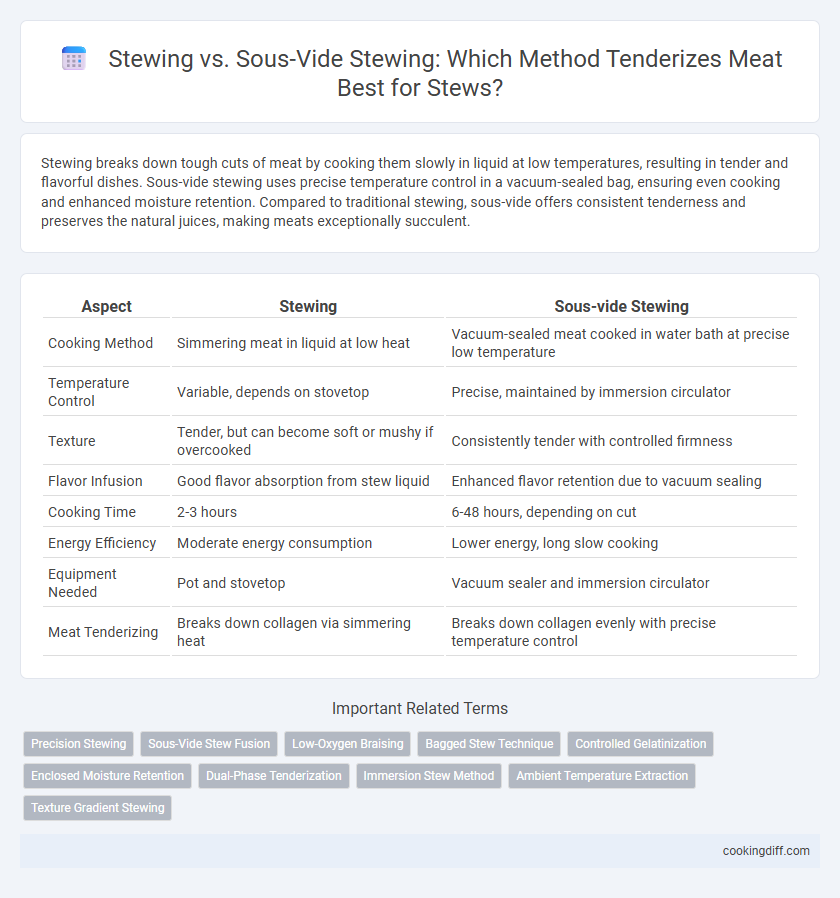
| Aspect | Stewing | Sous-vide Stewing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Simmering meat in liquid at low heat | Vacuum-sealed meat cooked in water bath at precise low temperature |
| Temperature Control | Variable, depends on stovetop | Precise, maintained by immersion circulator |
| Texture | Tender, but can become soft or mushy if overcooked | Consistently tender with controlled firmness |
| Flavor Infusion | Good flavor absorption from stew liquid | Enhanced flavor retention due to vacuum sealing |
| Cooking Time | 2-3 hours | 6-48 hours, depending on cut |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy consumption | Lower energy, long slow cooking |
| Equipment Needed | Pot and stovetop | Vacuum sealer and immersion circulator |
| Meat Tenderizing | Breaks down collagen via simmering heat | Breaks down collagen evenly with precise temperature control |
Introduction to Stewing and Sous-vide Stewing
Stewing is a traditional cooking method that uses low heat and moisture to break down tough meat fibers, resulting in tender and flavorful dishes. Sous-vide stewing involves vacuum-sealing meat and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath, which enhances tenderness by maintaining consistent temperatures over extended periods. Both techniques prioritize slow cooking, but sous-vide stewing offers precise temperature control for optimized texture and juiciness.
What is Traditional Stewing?
Traditional stewing is a slow-cooking method where meat is fully submerged in liquid and cooked at a low temperature for several hours, allowing tough cuts to become tender and flavorful. This technique typically involves simmering ingredients in a pot on the stovetop or in an oven, using broth, wine, or water as the cooking medium.
The long cooking time breaks down connective tissues and collagen in the meat, resulting in a soft, juicy texture and rich taste. Unlike sous-vide, traditional stewing often allows for more evaporation and flavor concentration during the cooking process.
Understanding Sous-vide Stewing
Sous-vide stewing involves cooking meat in vacuum-sealed bags at precise, low temperatures to achieve superior tenderness. This method allows for consistent heat distribution, preventing overcooking and preserving moisture more effectively than traditional stewing.
- Temperature control - Sous-vide stewing maintains exact, low temperatures that break down collagen without drying out the meat.
- Flavor retention - Vacuum-sealing locks in juices and enhances meat flavor during slow cooking.
- Texture improvement - Extended cooking times in sous-vide create exceptionally tender meat with uniform doneness.
Sous-vide stewing offers a scientifically controlled approach that elevates meat tenderness beyond conventional stewing techniques.
Meat Tenderization: How Stewing Works
Stewing tenderizes meat by slowly cooking it in liquid at low temperatures, which breaks down collagen into gelatin, resulting in a soft texture. This method allows connective tissues to dissolve gradually, enhancing flavor and moisture retention. Compared to sous-vide stewing, traditional stewing relies on consistent simmering rather than precise temperature control for tenderization.
Meat Tenderization: How Sous-vide Stewing Works
Stewing uses prolonged cooking in liquid at moderate temperatures to break down collagen and tenderize meat. Sous-vide stewing enhances this process by precisely controlling temperature and time, preserving moisture and texture for superior tenderness.
- Controlled temperature - Sous-vide stewing maintains a consistent low temperature, preventing overcooking and ensuring even collagen breakdown.
- Moisture retention - Vacuum sealing in sous-vide stewing seals in juices, enhancing the meat's tenderness and flavor.
- Extended cooking time - Longer cooking at stable temperatures allows connective tissues to dissolve slowly, resulting in a consistently tender texture.
Texture and Juiciness: Side-by-Side Comparison
Stewing breaks down collagen through prolonged simmering, producing tender meat with a slightly drier texture compared to sous-vide techniques. Sous-vide stewing slowly cooks meat in vacuum-sealed bags at precise low temperatures, retaining more juices and delivering a consistently moist and tender texture.
Stewing typically results in a rich, hearty flavor with a softer but occasionally uneven texture due to variations in heat exposure. Sous-vide stewing ensures uniform doneness and juiciness by cooking meat evenly throughout without moisture loss. This method enhances the natural flavors while maintaining superior tenderness and succulence compared to traditional stewing.
Flavor Development in Stewing vs Sous-vide Stewing
Stewing develops rich, complex flavors through prolonged exposure to direct heat and the Maillard reaction, intensifying the meat's taste. Sous-vide stewing preserves the pure, natural flavors of the meat while infusing subtle seasoning evenly due to precise temperature control.
- Maillard Reaction - Traditional stewing promotes browning, enhancing flavor complexity in meats.
- Flavor Concentration - Slow simmering reduces liquid, concentrating taste and aroma within the stew.
- Even Infusion - Sous-vide stewing maintains consistent temperature, resulting in uniform and delicate flavor penetration.
Time and Temperature: Key Differences
| Method | Temperature Range | Cooking Time | Effect on Meat Tenderness |
|---|---|---|---|
| Traditional Stewing | 160degF to 212degF (71degC to 100degC) | 1 to 3 hours | Breaks down collagen at higher temperatures, producing tender but sometimes stewed-textured meat |
| Sous-vide Stewing | 130degF to 158degF (54degC to 70degC) | 8 to 24 hours | Precise low-temperature cooking retains moisture and evenly tenderizes meat without overcooking |
Equipment and Preparation Requirements
Stewing requires basic kitchen equipment such as a heavy pot or Dutch oven and stovetop heat, making it accessible for most home cooks. Preparation involves cutting meat into smaller pieces and cooking them slowly in liquid over low heat to break down connective tissues.
Sous-vide stewing necessitates a precision immersion circulator and vacuum-sealing bags, allowing for exact temperature control during cooking. This method requires sealing the meat in airtight bags and cooking it in water baths for extended periods, ensuring even tenderness and flavor infusion.
Related Important Terms
Precision Stewing
Precision stewing offers controlled heat and consistent temperature over extended periods, breaking down collagen and connective tissues to tenderize meats more effectively than traditional stewing. Unlike sous-vide stewing, precision stewing combines precise temperature regulation with the infusion of flavorful liquids, enhancing both texture and taste in the final dish.
Sous-Vide Stew Fusion
Sous-vide stew fusion combines precise temperature control and low cooking temperatures to break down collagen in tough cuts of meat, resulting in unparalleled tenderness and enhanced flavor infusion compared to traditional stewing. This method preserves moisture and nutrients while ensuring consistent doneness, making it a superior technique for creating rich, melt-in-the-mouth stews.
Low-Oxygen Braising
Low-oxygen braising in stewing minimizes oxidation and moisture loss, resulting in consistently tender and flavorful meats compared to traditional high-oxygen methods. Sous-vide stewing enhances this process by precisely controlling temperature and oxygen exposure, further preserving meat texture and juiciness for superior tenderness.
Bagged Stew Technique
Bagged stew technique in sous-vide stewing ensures precise temperature control, allowing meat fibers to break down evenly and retain moisture for unparalleled tenderness compared to traditional stewing methods. This method minimizes nutrient loss and enhances flavor infusion by sealing ingredients in a vacuum bag during slow cooking.
Controlled Gelatinization
Stewing relies on prolonged low-temperature cooking to break down collagen into gelatin, but sous-vide stewing offers precise temperature control that optimizes gelatinization without overcooking. This controlled gelatinization in sous-vide stewing enhances meat tenderness and juiciness by maintaining ideal collagen breakdown over extended cooking times.
Enclosed Moisture Retention
Stewing uses a slow cooking process in a closed pot where moisture retention is achieved through simmering meats in liquid, resulting in tender texture as collagen breaks down. Sous-vide stewing enhances enclosed moisture retention by vacuum-sealing the meat, ensuring flavors and juices are locked in during precise low-temperature cooking, further intensifying tenderness.
Dual-Phase Tenderization
Dual-phase tenderization in stewing combines prolonged low-temperature cooking with gradual heat penetration, breaking down collagen and connective tissues effectively for tender meats. Sous-vide stewing enhances this process through precise temperature control and vacuum sealing, preserving moisture and intensifying flavors while ensuring consistent texture throughout the meat.
Immersion Stew Method
Immersion stew method involves cooking meat slowly in a flavorful liquid at a consistent, moderate temperature, allowing collagen to break down and resulting in tender, juicy meat. Unlike sous-vide stewing, immersion stewing offers a more traditional approach with direct heat transfer and rich, concentrated flavors from continuous simmering.
Ambient Temperature Extraction
Stewing relies on slow cooking at simmering temperatures around 85-95degC to gradually break down collagen in meats, resulting in tender texture through prolonged heat exposure and moisture. Sous-vide stewing uses precise, lower ambient temperatures typically between 55-65degC to extract flavors and tenderize meat evenly by controlling denaturation without overcooking, preserving juiciness and enhancing texture through vacuum-sealed, water-bath immersion.
Stewing vs Sous-vide Stewing for tenderizing meats. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com