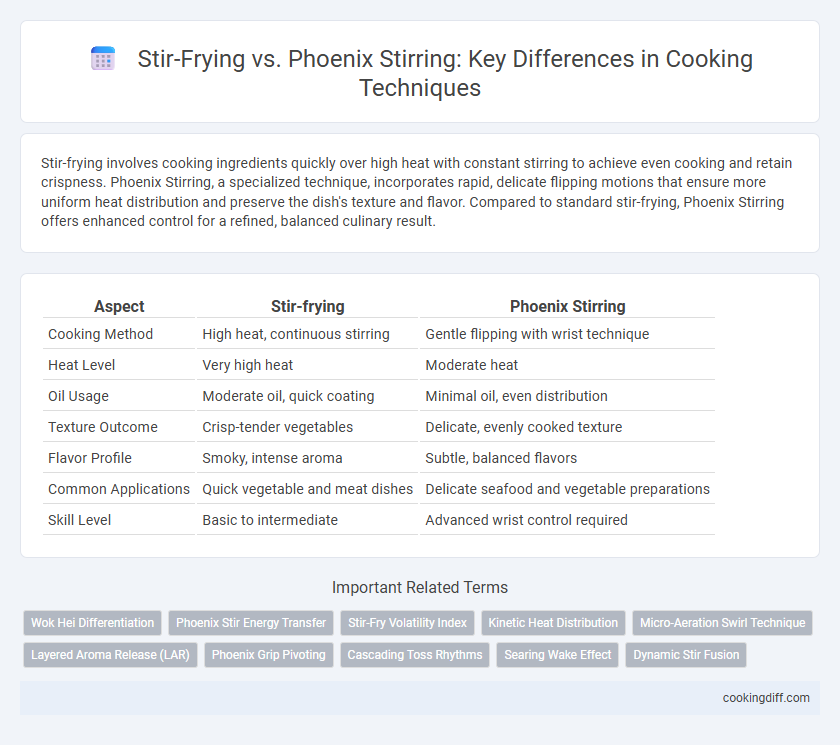
Stir-frying involves cooking ingredients quickly over high heat with constant stirring to achieve even cooking and retain crispness. Phoenix Stirring, a specialized technique, incorporates rapid, delicate flipping motions that ensure more uniform heat distribution and preserve the dish's texture and flavor. Compared to standard stir-frying, Phoenix Stirring offers enhanced control for a refined, balanced culinary result.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stir-frying | Phoenix Stirring |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High heat, continuous stirring | Gentle flipping with wrist technique |
| Heat Level | Very high heat | Moderate heat |
| Oil Usage | Moderate oil, quick coating | Minimal oil, even distribution |
| Texture Outcome | Crisp-tender vegetables | Delicate, evenly cooked texture |
| Flavor Profile | Smoky, intense aroma | Subtle, balanced flavors |
| Common Applications | Quick vegetable and meat dishes | Delicate seafood and vegetable preparations |
| Skill Level | Basic to intermediate | Advanced wrist control required |
Understanding Stir-Frying: A Classic Technique
Stir-frying is a high-heat cooking technique that involves quickly tossing ingredients in a wok with a small amount of oil to preserve texture and flavor. This method ensures even cooking while maintaining the nutritional value of vegetables and proteins.
Phoenix Stirring is a variation of stir-frying characterized by gentle, circular motions that carefully combine ingredients without breaking their structure. Understanding the classic stir-frying technique highlights the balance between heat, speed, and motion essential for achieving vibrant, evenly cooked dishes.
What is Phoenix Stirring? Origins and Overview
Phoenix Stirring, a traditional Chinese cooking technique, involves a delicate and rhythmic motion that mimics a phoenix's graceful flight. This method contrasts with conventional stir-frying by emphasizing gentle turning and lifting of ingredients to preserve texture and flavor.
- Origins - Phoenix Stirring originated in Jiangsu province, known for its refined cooking styles.
- Technique - The process uses precise wrist movements to gently toss ingredients without breaking them.
- Purpose - It aims to maintain the integrity of ingredients while evenly distributing heat and seasoning.
Key Equipment Needed: Wok vs Phoenix Pan
Stir-frying traditionally requires a wok, a deep, round-bottomed pan that distributes heat evenly and allows for rapid tossing of ingredients at high temperatures. In contrast, Phoenix Stirring utilizes a Phoenix pan, which has a flatter base and slightly higher sides, designed for more controlled heating and even cooking.
The wok excels in quick cooking and high heat retention, making it ideal for crisp-tender vegetables and meats. The Phoenix pan offers better heat distribution on flat cooking surfaces and prevents ingredients from spilling during stirring. Choosing between wok and Phoenix pan depends on the cooking style and heat source compatibility in the kitchen.
Ingredients Preparation: Differences in Cutting and Marinating
Stir-frying typically involves cutting ingredients into uniform, bite-sized pieces for quick cooking, while Phoenix Stirring requires more intricate slicing techniques to enhance texture and presentation. Marination in stir-frying is often brief and simple, whereas Phoenix Stirring uses longer marinating times with complex spice blends to deepen flavor.
- Cutting Precision - Stir-frying emphasizes even, small cuts to ensure rapid and uniform cooking of ingredients.
- Intricate Slicing - Phoenix Stirring demands delicate, artistic cuts that contribute to the dish's visual appeal and textural contrast.
- Marination Time - Stir-frying uses short marination periods, while Phoenix Stirring applies extended marinating for richer flavor infusion.
Heat Control: Stir-Frying vs Phoenix Stirring Methods
Stir-frying involves high heat and continuous tossing to quickly cook ingredients while maintaining their texture and flavor. Phoenix Stirring uses a gentler, controlled heat with a specific wrist motion to evenly distribute heat and prevent burning. Effective heat control in Stir-frying maximizes speed, whereas Phoenix Stirring prioritizes even cooking and delicate temperature management.
Oil Usage and Flavor Development
| Oil Usage | Stir-frying typically requires a moderate amount of oil to evenly coat ingredients and prevent sticking, while Phoenix Stirring uses less oil, relying on rapid, high-heat tossing to maintain ingredient moisture without excess fat. |
| Flavor Development | Stir-frying enhances flavor through Maillard reactions by allowing ingredients to sear briefly, creating deeper caramelization, whereas Phoenix Stirring emphasizes quick heat exposure that preserves the natural freshness and crispness of ingredients, resulting in lighter, more vibrant flavors. |
Movement Techniques: Stirring, Tossing, and Phoenix Motions
Stir-frying primarily involves rapid stirring and tossing motions to cook ingredients evenly over high heat, ensuring quick caramelization and flavor development. Phoenix Stirring incorporates a distinctive sweeping and circular movement, mimicking a phoenix's graceful motions to enhance heat distribution and prevent food from sticking to the wok. Both techniques emphasize continuous motion, but Phoenix Stirring offers a more fluid and rhythmic approach, improving texture and preserving ingredient integrity.
Cooking Times and Texture Outcomes
Stir-frying typically requires a higher heat and faster cooking time, usually around 2 to 5 minutes, which results in crisp-tender vegetables and evenly cooked proteins. Phoenix Stirring, a traditional Chinese technique, uses slightly lower heat and gentle, continuous stirring, extending cooking time to 5 to 7 minutes for a more tender, well-marinated texture.
Stir-frying creates a seared, slightly caramelized exterior with a quick moisture lock-in, promoting a vibrant texture contrast. Phoenix Stirring emphasizes even heat distribution and slow absorption of sauces, producing a softer, more harmonious mouthfeel throughout the dish.
Nutritional Impact: Comparing Both Methods
Stir-frying preserves more vitamins and antioxidants due to its quick cooking time and high heat application. Phoenix Stirring, a gentler technique, minimizes nutrient degradation but may retain slightly less heat-sensitive compounds compared to traditional stir-frying.
- Vitamin Retention - Stir-frying generally maintains higher levels of vitamin C and B vitamins due to rapid cooking.
- Mineral Stability - Phoenix Stirring better preserves minerals like potassium and magnesium by avoiding intense heat exposure.
- Antioxidant Preservation - Stir-frying enhances antioxidant availability through Maillard reaction compounds while Phoenix Stirring avoids nutrient loss from oxidation.
Choosing between these methods depends on the desired balance of nutrient retention and flavor development in cooked foods.
Related Important Terms
Wok Hei Differentiation
Stir-frying emphasizes high heat and rapid tossing to develop the characteristic smoky aroma known as wok hei, while Phoenix Stirring utilizes a more controlled, repetitive folding technique to infuse ingredients with heat evenly, resulting in a subtler wok hei expression. The distinctive wok hei imparted by traditional stir-frying produces a complex, charred flavor profile unattainable through the gentler, rhythmic motions of Phoenix Stirring.
Phoenix Stir Energy Transfer
Phoenix Stirring enhances energy transfer by utilizing precise, circular wrist movements that maximize heat distribution across ingredients, resulting in faster and more even cooking compared to traditional stir-frying. This technique reduces nutrient loss and preserves texture by maintaining constant, controlled contact between the wok surface and food, optimizing thermal conductivity for superior culinary outcomes.
Stir-Fry Volatility Index
Stir-frying involves rapid, high-heat cooking with constant movement of food in a wok, characterized by a high Stir-Fry Volatility Index reflecting intense heat and quick flavor development. Phoenix Stirring, a gentler technique, results in a lower volatility index, prioritizing ingredient integrity and gradual flavor infusion over the aggressive searing typical of stir-frying.
Kinetic Heat Distribution
Stir-frying uses continuous, rapid stirring to evenly distribute kinetic heat, ensuring quick cooking at high temperatures. Phoenix Stirring enhances kinetic heat distribution by incorporating precise, rhythmic movements that maximize heat transfer and maintain ingredient integrity during cooking.
Micro-Aeration Swirl Technique
Stir-frying uses high heat and rapid stirring to quickly cook ingredients, preserving their texture and flavor through efficient heat transfer. Phoenix Stirring employs the Micro-Aeration Swirl Technique, integrating controlled air pockets and circular motions to enhance oxidation and flavor infusion, resulting in a more aromatic and evenly cooked dish.
Layered Aroma Release (LAR)
Stir-frying rapidly cooks ingredients over high heat, preserving freshness while creating a balanced blend of flavors; Phoenix Stirring, a technique emphasizing rhythmic, multi-directional stirring, enhances Layered Aroma Release (LAR) by evenly distributing heat and aromatics, resulting in a more complex, intensified fragrance profile. The controlled agitation in Phoenix Stirring promotes gradual volatilization of essential oils from spices and vegetables, amplifying the depth and richness of the dish's aroma compared to standard stir-frying methods.
Phoenix Grip Pivoting
Phoenix Stirring emphasizes the Phoenix Grip Pivoting technique, where the wok is held at a precise angle to maximize heat distribution and ingredient contact, contrasting with traditional stir-frying's constant tossing motion. This method enhances flavor development and texture by carefully controlling the wok's tilt and pivot for even cooking and caramelization.
Cascading Toss Rhythms
Stir-frying relies on a high-heat tossing technique to evenly cook ingredients while preserving texture and flavor, whereas Phoenix Stirring emphasizes Cascading Toss Rhythms, creating a visually dynamic motion that enhances ingredient mixing and heat distribution. The Cascading Toss Rhythms produce a continuous flow, elevating the cooking process by intensifying flavor integration and achieving a superior sear on proteins and vegetables.
Searing Wake Effect
Stir-frying leverages high heat and rapid tossing to sear ingredients evenly, creating the Searing Wake Effect that caramelizes surface proteins and locks in moisture. Phoenix Stirring, contrastingly, emphasizes gentle, swirling motions that enhance heat distribution without aggressive searing, yielding a more tender texture but less pronounced caramelization.
Stir-frying vs Phoenix Stirring for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com