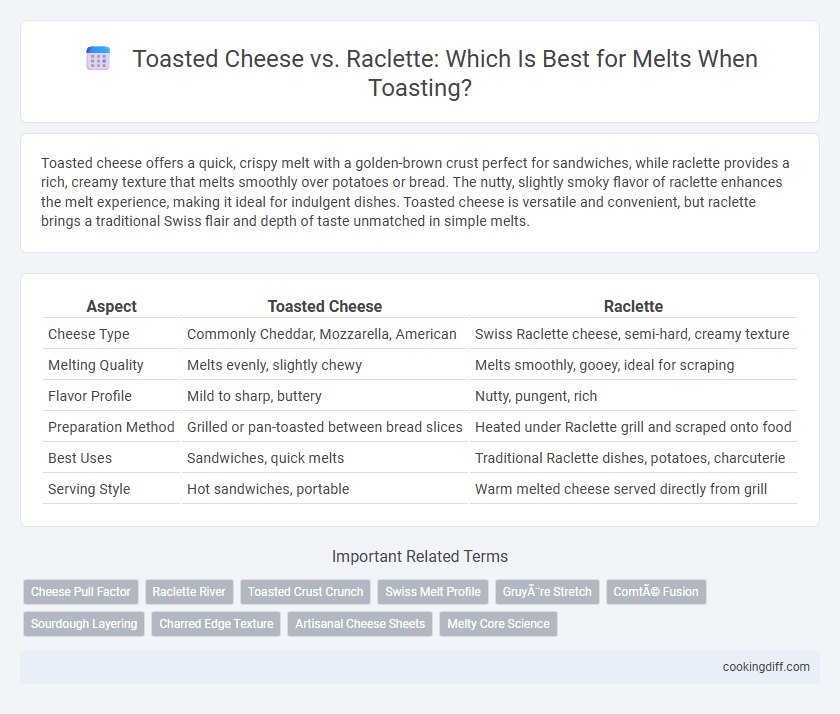
Toasted cheese offers a quick, crispy melt with a golden-brown crust perfect for sandwiches, while raclette provides a rich, creamy texture that melts smoothly over potatoes or bread. The nutty, slightly smoky flavor of raclette enhances the melt experience, making it ideal for indulgent dishes. Toasted cheese is versatile and convenient, but raclette brings a traditional Swiss flair and depth of taste unmatched in simple melts.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Toasted Cheese | Raclette |
|---|---|---|
| Cheese Type | Commonly Cheddar, Mozzarella, American | Swiss Raclette cheese, semi-hard, creamy texture |
| Melting Quality | Melts evenly, slightly chewy | Melts smoothly, gooey, ideal for scraping |
| Flavor Profile | Mild to sharp, buttery | Nutty, pungent, rich |
| Preparation Method | Grilled or pan-toasted between bread slices | Heated under Raclette grill and scraped onto food |
| Best Uses | Sandwiches, quick melts | Traditional Raclette dishes, potatoes, charcuterie |
| Serving Style | Hot sandwiches, portable | Warm melted cheese served directly from grill |
Introduction to Toasted Cheese and Raclette
Toasted cheese is a popular comfort food featuring melted cheese often sandwiched between slices of bread, creating a crispy and gooey texture. Raclette, originating from Swiss Alpine regions, is a semi-hard cheese specifically designed to be melted and scraped over various accompaniments like potatoes and vegetables. Both toasted cheese and raclette showcase unique melting properties that enhance their rich, creamy flavors in distinct culinary experiences.
History and Origins: Toasted Cheese vs Raclette
Toasted cheese sandwiches trace back to early 20th-century Western cuisine, popularized as a simple, comforting meal. Raclette originates from the Swiss Alps, where melting cheese over a fire was a practical method for mountain farmers to enjoy dairy during harsh winters.
- Toasted Cheese History - Emerged in American and British households as an easy, grilled sandwich featuring melted cheese.
- Raclette Origins - Rooted in Swiss tradition, involving heating a wheel of cheese and scraping the melted layer onto foods.
- Melting Techniques - Toasted cheese uses direct heat via a sandwich press, while raclette relies on a specialized grill or open flame for gradual melting.
Types of Cheese Ideal for Toasted Melts
| Cheese Type | Ideal Use | Flavor Profile | Melting Quality |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheddar | Toasted melts | Sharp, tangy | Firm melt with slight stretch |
| Raclette | Traditional melts and toasts | Nutty, creamy | Rich and smooth melt with excellent stretch |
| Gruyere | Toasted sandwiches | Complex, slightly sweet | Velvety and consistent melt |
| Mozzarella | Simple toasted melts | Mild, milky | High meltability with stretchy texture |
| Fontina | Rich toasted melts | Buttery, earthy | Smooth and creamy melt |
Raclette Cheese: Characteristics and Melting Qualities
Raclette cheese, originating from the Swiss Alps, is renowned for its creamy texture and excellent melting qualities, making it ideal for toasting. Unlike standard toasted cheese, Raclette melts smoothly without becoming greasy, providing a rich and velvety flavor profile.
The cheese's high-fat content and semi-hard consistency allow it to soften evenly, creating a perfect melt for dishes like raclette grills and toasted sandwiches. Its distinctive aroma and nutty taste enhance the overall sensory experience, distinguishing it from typical toasted cheese varieties. Raclette is often preferred for melts due to its ability to maintain structure and flavor, even under direct heat.
Preparation Methods: Toasted Cheese vs Raclette
Toasted cheese sandwiches are typically prepared by placing cheese between slices of bread and cooking them on a griddle or in a sandwich press until the bread is golden brown and the cheese melts evenly. Raclette involves heating a wheel of cheese near a heat source, often an open flame or specialized Raclette grill, allowing the surface to melt before scraping the cheese onto potatoes or bread. While toasted cheese relies on direct heat and pressure to achieve uniform melting, Raclette emphasizes slow, radiant heat that produces a creamy, bubbly melt with a slightly caramelized crust.
Flavor Profiles: Comparing Toasted Cheese and Raclette
Toasted cheese delivers a rich, creamy flavor with a subtle nuttiness, while raclette offers a more robust, tangy taste complemented by a smoky aroma. Both cheeses melt smoothly, but raclette's complexity enhances savory dishes with a distinctive alpine character.
- Creaminess vs. Tanginess - Toasted cheese emphasizes a smooth, milky texture, whereas raclette provides a sharper, tangier flavor due to its fermentation process.
- Smoky Notes - Raclette's traditional smoking adds depth and complexity absent in most toasted cheese varieties.
- Melting Behavior - Both cheeses melt evenly, but raclette forms a slightly stringier consistency ideal for melts and fondues.
Serving Suggestions for Melts
Toasted cheese offers a crispy texture perfect for sandwiches, while raclette provides a creamy melt ideal for drizzling over potatoes and vegetables. Both cheeses enhance melts but suit different serving styles based on their melting qualities and flavor profiles.
- Toasted Cheese Sandwiches - Ideal for handheld melts with a crunchy exterior and gooey center, enhancing flavor contrasts.
- Raclette over Vegetables - Best served by scraping melted raclette onto steamed or roasted veggies, creating a rich, savory dish.
- Layered Melt Dishes - Combining toasted cheese for texture and raclette for creaminess elevates melt complexity in casseroles or gratins.
Choosing between toasted cheese and raclette depends on desired texture and presentation in your melt recipes.
Equipment Needed for Toasted Cheese and Raclette
What equipment is essential for making toasted cheese compared to raclette melts? Toasted cheese requires a simple sandwich press or a stovetop pan to evenly melt the cheese and toast the bread, making it accessible for everyday use. Raclette demands a specialized raclette grill or melter with individual trays to melt the cheese perfectly while allowing guests to customize their melts.
Health and Nutritional Differences
Toasted cheese typically contains fewer calories and saturated fats compared to raclette, making it a lighter option for melts. Raclette cheese, known for its rich and creamy texture, is higher in fat content and calories, which can impact heart health if consumed excessively.
Both cheeses provide essential nutrients like calcium and protein, but toasted cheese often has lower sodium levels. Choosing toasted cheese can support better weight management, while raclette offers a more indulgent taste experience at the cost of higher fat intake.
Related Important Terms
Cheese Pull Factor
Toasted cheese varieties like mozzarella or cheddar often deliver a superior cheese pull due to their higher moisture content and elasticity compared to Raclette, which melts smoothly but tends to be creamier and less stringy. The distinct texture of Raclette provides a rich, velvety melt ideal for scooping, while toasted cheese excels in creating that visually appealing, stretchy cheese pull cherished in classic melts.
Raclette River
Raclette River cheese delivers a rich, creamy texture and robust flavor that melts smoothly, making it a superior choice compared to traditional toasted cheese for savory melts. Its high-fat content and distinctive nutty notes enhance the toasting experience, providing a gourmet twist to classic melted cheese dishes.
Toasted Crust Crunch
Toasted cheese offers a satisfying toasted crust crunch that enhances the overall melt experience by providing a crispy, golden exterior, while Raclette typically delivers a creamier, gooey texture with less emphasis on crust crispiness. The toasted crust in toasted cheese melts creates a delightful contrast to the melted cheese, making each bite more texturally complex and enjoyable compared to the softer, less crunchy Raclette melts.
Swiss Melt Profile
Toasted cheese melts like Gruyere deliver a rich, nutty flavor with a smooth, creamy texture that perfectly complements the Swiss melt profile, prized for its balanced sharpness and meltability. Raclette offers a distinctive fruity aroma and slightly pungent taste, melting into a velvety consistency ideal for traditional Swiss toasting, enhancing the overall depth and authenticity of the cheese experience.
Gruyère Stretch
Gruyere used in toasted cheese melts offers a perfect balance of nutty flavor and exceptional stretchiness, creating a gooey, elastic texture that enhances the sensory experience. In contrast, Raclette provides a creamier melt with a slightly less elastic pull, ideal for smooth, rich coatings rather than the pronounced cheese stretch found in Gruyere.
Comté Fusion
Comte cheese, known for its nutty and creamy profile, offers a superior melt compared to traditional toasted cheese or raclette, delivering a smooth and flavorful fusion ideal for gourmet melts. Its natural melting properties enhance texture and taste, making it a preferred choice for artisanal toasted cheese dishes and raclette-style preparations.
Sourdough Layering
Toasted cheese on sourdough offers a crispy, tangy base that enhances the creamy melt, while raclette's rich, nutty flavor complements the bread's chewy texture, creating a balanced, savory experience. Layering sourdough with raclette allows the cheese to melt evenly, soaking into the porous bread and maximizing flavor infusion for a gourmet toastie.
Charred Edge Texture
Toasted cheese delivers a crispy, charred edge that enhances the melt with a satisfying crunch and rich, caramelized flavor, while raclette offers a creamier consistency with a softer, slightly browned crust. The distinct textures influence the melt experience, as toasted cheese provides a contrast between gooey interior and crisp exterior, whereas raclette emphasizes smoothness with subtle charred notes.
Artisanal Cheese Sheets
Artisanal cheese sheets offer a unique texture and melt quality that distinguishes toasted cheese from traditional Raclette melts, providing a smoother, creamier consistency perfect for gourmet sandwiches. Unlike Raclette, which melts in a more rustic, uneven way, these cheese sheets deliver a controlled melt ideal for layered, visually appealing toasted creations.
Toasted Cheese vs Raclette for melts Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com