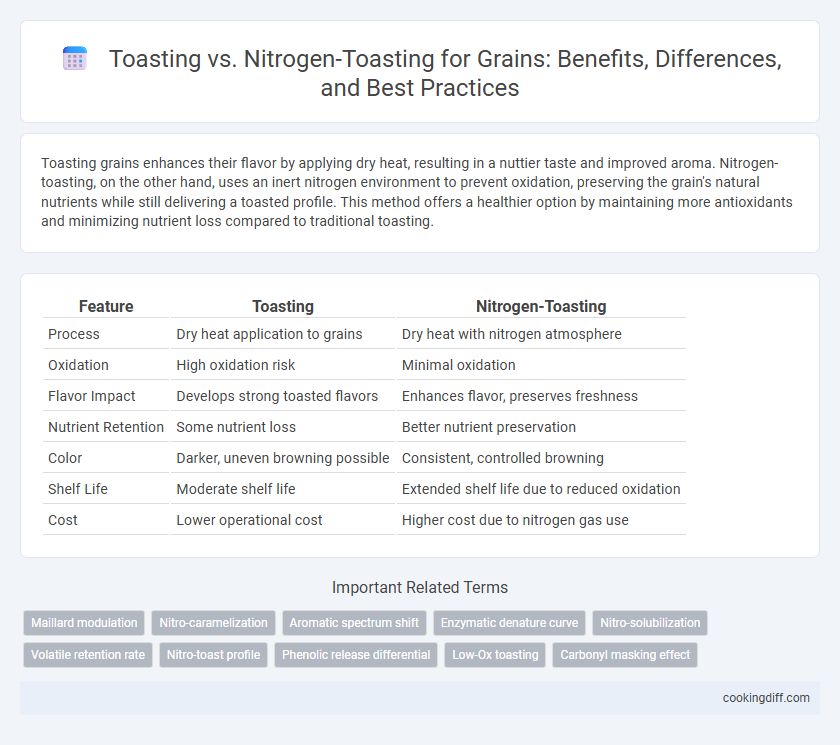
Toasting grains enhances their flavor by applying dry heat, resulting in a nuttier taste and improved aroma. Nitrogen-toasting, on the other hand, uses an inert nitrogen environment to prevent oxidation, preserving the grain's natural nutrients while still delivering a toasted profile. This method offers a healthier option by maintaining more antioxidants and minimizing nutrient loss compared to traditional toasting.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Toasting | Nitrogen-Toasting |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Dry heat application to grains | Dry heat with nitrogen atmosphere |
| Oxidation | High oxidation risk | Minimal oxidation |
| Flavor Impact | Develops strong toasted flavors | Enhances flavor, preserves freshness |
| Nutrient Retention | Some nutrient loss | Better nutrient preservation |
| Color | Darker, uneven browning possible | Consistent, controlled browning |
| Shelf Life | Moderate shelf life | Extended shelf life due to reduced oxidation |
| Cost | Lower operational cost | Higher cost due to nitrogen gas use |
Introduction to Toasting and Nitrogen-Toasting
Toasting is a heat treatment process applied to grains to enhance flavor, aroma, and shelf life by driving off moisture and triggering Maillard reactions. Nitrogen-toasting involves the use of nitrogen gas to create an oxygen-free environment during toasting, reducing oxidation and preserving nutritional quality.
- Toasting - Uses dry heat to alter grain properties, improving taste and texture.
- Nitrogen-toasting - Employs inert nitrogen gas to minimize oxidative damage during heating.
- Benefit comparison - Nitrogen-toasting better preserves antioxidants and extends shelf life compared to traditional toasting.
Understanding Traditional Grain Toasting
Traditional grain toasting involves heating grains to enhance flavor, aroma, and texture by triggering Maillard reactions and caramelization. This method uses direct dry heat, which can bring out nutty and toasted notes while reducing moisture content. Unlike nitrogen-toasting, traditional toasting relies solely on temperature control without inert gas environments, affecting the grain's chemical composition and resulting taste profile.
What is Nitrogen-Toasting?
Nitrogen-toasting is a grain processing technique that uses nitrogen gas to heat and toast grains in an oxygen-free environment, reducing oxidation and preserving nutritional content. This method enhances flavor development while maintaining grain integrity better than traditional toasting.
Compared to conventional toasting, nitrogen-toasting minimizes rancidity by preventing exposure to oxygen, resulting in longer shelf life and improved grain quality. It is commonly used in food industries aiming for high-quality grain products with superior taste and nutritional benefits.
Comparing Chemical Reactions in Both Methods
How do the chemical reactions differ between toasting and nitrogen-toasting in grain processing? Toasting involves Maillard reactions and caramelization, which develop complex flavors through heat-induced browning. Nitrogen-toasting limits oxidation by replacing oxygen with nitrogen, reducing oxidative reactions and preserving grain nutrients while still enhancing texture.
Flavor Profiles: Toasting vs Nitrogen-Toasting
| Method | Flavor Profile |
|---|---|
| Toasting | Develops rich, deep caramelized flavors with robust nutty and smoky notes through direct heat exposure. |
| Nitrogen-Toasting | Preserves the grain's natural sweetness while generating subtle toasted aromas without oxidative bitterness, resulting in a cleaner, smoother taste. |
Impact on Nutritional Value
Toasting grains enhances flavor and aroma by applying dry heat, which may reduce some heat-sensitive vitamins like B-complex but generally preserves mineral content. Nitrogen-toasting, a technique using inert nitrogen gas to prevent oxidation, better retains antioxidants and essential nutrients by minimizing exposure to oxygen and high temperatures. Studies show nitrogen-toasted grains maintain higher levels of polyphenols and vitamins compared to conventional toasting methods.
Efficiency and Energy Use
Toasting grains typically requires higher energy input due to the need for consistent dry heat, whereas nitrogen-toasting employs an inert nitrogen atmosphere that can reduce oxidation and energy consumption. The use of nitrogen in the process can optimize fuel efficiency by lowering the temperature and time needed for effective grain treatment.
- Energy Efficiency - Nitrogen-toasting reduces oxygen exposure, enabling lower temperature settings and conserving energy compared to traditional toasting.
- Process Duration - Nitrogen-toasting can shorten toasting times by enhancing heat transfer and preventing grain degradation.
- Operational Costs - While nitrogen-toasting uses specialized equipment and gas supply, overall energy savings can lead to reduced operational expenses.
Nitrogen-toasting presents an energy-efficient alternative to conventional toasting by minimizing oxidation and optimizing heat usage.
Suitability for Different Types of Grains
Toasting is ideal for grains like barley and oats, enhancing their nutty flavor and aroma through dry heat exposure. Nitrogen-toasting preserves the grain's natural nutrients by reducing oxidation, making it suitable for sensitive grains such as quinoa and millet.
- Toasting enhances flavor - Grains with denser structures, like barley, develop richer, roasted notes when toasted.
- Nitrogen-toasting reduces oxidation - This method protects delicate grains like quinoa from nutrient loss and off-flavors.
- Suitability depends on grain type - Hard, aromatic grains benefit from traditional toasting, while fragile, nutrient-rich grains favor nitrogen-toasting.
Industrial Applications and Scalability
Toasting grains in industrial applications offers a straightforward process focused on enhancing flavor and shelf life through consistent thermal exposure, supporting large-scale production with manageable capital investment. Nitrogen-toasting provides an advanced alternative by utilizing inert nitrogen atmospheres to prevent oxidation, ideal for high-value grains requiring superior quality retention.
Nitrogen-toasting systems demand specialized equipment and higher operational costs but deliver enhanced scalability in ultra-sensitive grain processing environments, reducing spoilage and preserving nutritional content. Industrial scalability for standard toasting is well-established, enabling efficient throughput in bulk grain processing with moderate energy consumption. Selection between toasting and nitrogen-toasting depends on product specifications, economic considerations, and desired grain attributes in large-scale manufacturing.
Related Important Terms
Maillard modulation
Toasting enhances grain flavor through Maillard reaction modulation by applying dry heat, resulting in deeper caramelization and rich, nutty notes. Nitrogen-toasting reduces oxidation and preserves delicate aroma compounds while still promoting Maillard browning, yielding a cleaner, more controlled flavor profile.
Nitro-caramelization
Nitrogen-toasting enhances grains through nitro-caramelization, a process that traps nitrogen gas to create richer, more complex caramel flavors without burning the grain. This technique outperforms traditional toasting by preserving nutritional content while intensifying sweetness and aroma in the final product.
Aromatic spectrum shift
Toasting grains enhances their aromatic spectrum by developing rich, nutty, and caramelized flavors through Maillard reactions and thermal degradation of sugars. Nitrogen-toasting preserves volatile aromatic compounds by reducing oxidation, resulting in a cleaner, more subtly toasted flavor profile with distinct floral and grassy notes.
Enzymatic denature curve
Toasting grains raises temperatures quickly, causing rapid enzymatic denaturation that follows a steep curve, while nitrogen-toasting provides a controlled, oxygen-free environment that slows enzymatic activity reduction with a more gradual denaturation curve. This controlled process preserves grain quality by minimizing oxidation, resulting in enhanced flavor stability and extended shelf life compared to traditional toasting.
Nitro-solubilization
Nitrogen-toasting enhances grain processing by promoting nitro-solubilization, which increases protein and starch digestibility compared to traditional toasting methods. This process reduces nutrient loss and improves bioavailability by minimizing oxidation and preserving grain quality during thermal treatment.
Volatile retention rate
Toasting grains results in a lower volatile retention rate compared to nitrogen-toasting, as exposure to oxygen during traditional toasting promotes the evaporation of aromatic compounds. Nitrogen-toasting preserves a higher concentration of volatiles by creating an oxygen-free environment, enhancing flavor stability and intensity in the final grain product.
Nitro-toast profile
Nitrogen-toasting imparts a distinct, intensified flavor profile to grains by preserving their natural aromas and enhancing nutty, roasted notes through an oxygen-free environment. This method minimizes oxidation, resulting in a cleaner taste and extended shelf life compared to traditional toasting.
Phenolic release differential
Toasting grains enhances phenolic release by breaking down cell walls and increasing antioxidant availability, whereas nitrogen-toasting preserves phenolic compounds by minimizing oxidation during processing. This differential impact on phenolic content significantly affects the nutritional quality and flavor profile of grain-based products.
Low-Ox toasting
Low-oxygen toasting minimizes grain oxidation by using controlled nitrogen atmospheres, preserving flavor profiles and nutritional value better than traditional air-based toasting. This method enhances the grain's shelf life and sensory attributes by reducing rancidity and color degradation during heat treatment.
Toasting vs Nitrogen-Toasting for grains. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com