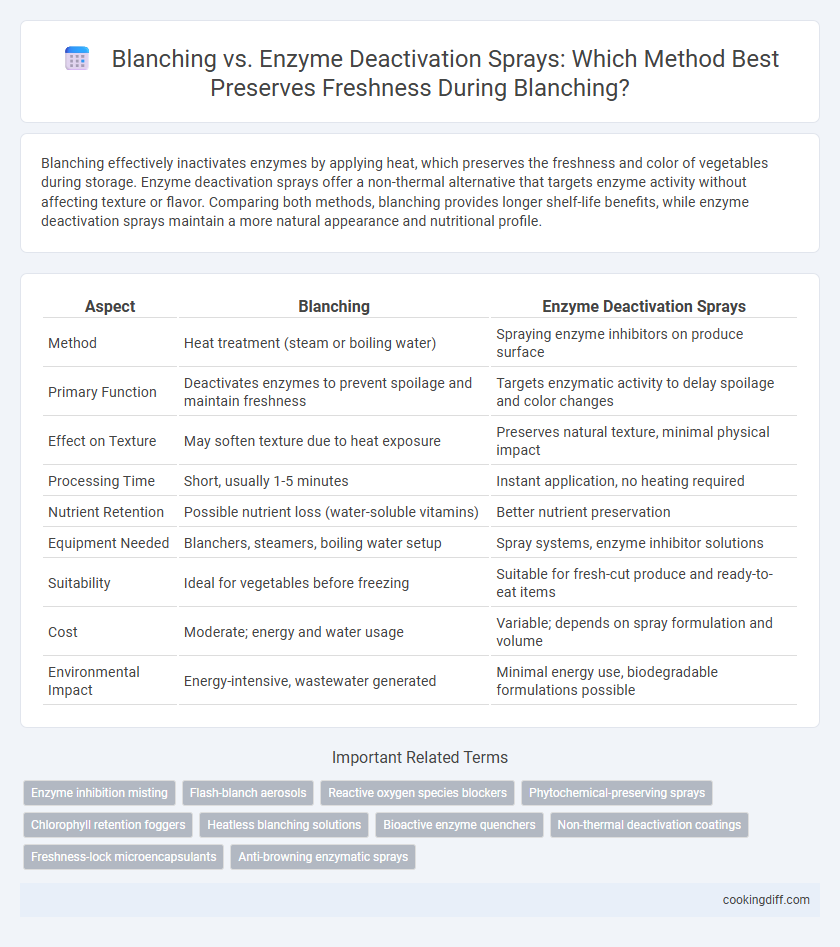
Blanching effectively inactivates enzymes by applying heat, which preserves the freshness and color of vegetables during storage. Enzyme deactivation sprays offer a non-thermal alternative that targets enzyme activity without affecting texture or flavor. Comparing both methods, blanching provides longer shelf-life benefits, while enzyme deactivation sprays maintain a more natural appearance and nutritional profile.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blanching | Enzyme Deactivation Sprays |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Heat treatment (steam or boiling water) | Spraying enzyme inhibitors on produce surface |
| Primary Function | Deactivates enzymes to prevent spoilage and maintain freshness | Targets enzymatic activity to delay spoilage and color changes |
| Effect on Texture | May soften texture due to heat exposure | Preserves natural texture, minimal physical impact |
| Processing Time | Short, usually 1-5 minutes | Instant application, no heating required |
| Nutrient Retention | Possible nutrient loss (water-soluble vitamins) | Better nutrient preservation |
| Equipment Needed | Blanchers, steamers, boiling water setup | Spray systems, enzyme inhibitor solutions |
| Suitability | Ideal for vegetables before freezing | Suitable for fresh-cut produce and ready-to-eat items |
| Cost | Moderate; energy and water usage | Variable; depends on spray formulation and volume |
| Environmental Impact | Energy-intensive, wastewater generated | Minimal energy use, biodegradable formulations possible |
Understanding Blanching: The Traditional Freshness Preserver
Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables or fruits followed by rapid cooling to halt enzyme activity and preserve freshness, texture, and color effectively. This traditional method deactivates enzymes responsible for spoilage, ensuring extended shelf life without the use of chemical preservatives. Unlike enzyme deactivation sprays, blanching maintains natural flavor and nutrient content while offering a reliable, time-tested freshness preservation technique.
What Are Enzyme Deactivation Sprays?
| Enzyme Deactivation Sprays | Specialized formulations that inhibit enzymatic activity responsible for food spoilage and browning. |
| Function | They preserve freshness by targeting enzymes like polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase, preventing oxidation reactions in fruits and vegetables. |
| Advantages over Blanching | Offer on-demand application without heat exposure, maintaining texture, nutrients, and color more effectively than traditional blanching methods. |
Mechanisms: How Blanching and Sprays Work
Blanching uses high-temperature steam or hot water to rapidly inactivate enzymes, halting biochemical reactions that cause spoilage. Enzyme deactivation sprays apply chemical inhibitors directly to the produce surface to suppress enzymatic activity without heat exposure.
- Thermal Inactivation - Blanching denatures enzymes through brief exposure to high heat, effectively stopping enzymatic browning and spoilage.
- Chemical Inhibition - Enzyme deactivation sprays use agents like calcium chloride or antioxidants to chemically block enzyme active sites, preventing degradation.
- Application Method - Blanching requires immersion or steaming, whereas sprays are applied topically, offering different impacts on texture and nutrient retention.
Comparing Effectiveness: Freshness Retention
Blanching effectively halts enzymatic activity by exposing vegetables to high heat, preserving their color, texture, and nutritional value for longer storage periods. This process rapidly deactivates enzymes responsible for spoilage, making it a reliable method for freshness retention in produce.
Enzyme deactivation sprays work by applying chemical inhibitors directly to the surface, offering a less invasive alternative to heat treatment. However, their effectiveness in maintaining freshness varies depending on the type of produce and the specific enzymes targeted, often making blanching more consistent for long-term quality preservation.
Nutrient Preservation: Pros and Cons
Blanching involves briefly heating vegetables to deactivate enzymes, which can lead to some nutrient loss, particularly water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Enzyme deactivation sprays offer a gentler alternative by targeting enzymatic activity with minimal heat, thus better preserving heat-sensitive nutrients.
- Vitamin Retention - Enzyme deactivation sprays maintain higher levels of vitamin C compared to blanching due to reduced heat exposure.
- Antioxidant Preservation - Blanching can reduce antioxidant content, whereas sprays help retain these compounds by avoiding thermal degradation.
- Bioavailability - Blanching sometimes increases bioavailability of certain nutrients, a benefit less pronounced with enzyme sprays.
Choosing between blanching and enzyme deactivation sprays depends on the balance between nutrient preservation and desired texture and flavor retention.
Texture and Color: Which Method Wins?
Which method better preserves texture and color: blanching or enzyme deactivation sprays? Blanching uses heat to inactivate enzymes, often resulting in a firmer texture and vibrant color retention by halting enzymatic browning. Enzyme deactivation sprays protect freshness with minimal heat exposure, maintaining a more delicate texture but sometimes less intense color stabilization compared to blanching.
Safety and Chemical Residues: Evaluating Risks
Blanching uses high temperatures to deactivate enzymes, effectively reducing microbial load and minimizing chemical residues, making it a safer option for maintaining food freshness. Enzyme deactivation sprays often contain chemical agents that may leave residues, raising concerns about food safety and potential health risks.
Blanching ensures a thorough enzyme inactivation with minimal risk of chemical contamination, preserving both nutritional quality and consumer safety. Evaluating the risks associated with enzyme deactivation sprays is essential to avoid exposure to harmful chemicals and ensure compliance with food safety standards.
Application Ease and Suitability for Home Cooks
Blanching requires boiling water and precise timing, which can be challenging for home cooks but effectively inactivates enzymes to maintain freshness. Enzyme deactivation sprays offer a simple, quick application without heat, making them more accessible for everyday kitchen use.
- Blanching's complexity - Requires boiling water and accurate timing, demanding more effort and attention from home cooks.
- Sprays' convenience - Easy to apply directly on produce, eliminating the need for heat and reducing preparation time significantly.
- Suitability - Enzyme deactivation sprays are better suited for home cooks seeking quick preservation without specialized equipment.
Environmental and Cost Considerations
Blanching requires significant energy input due to high-temperature water or steam usage, leading to increased utility costs and environmental footprint from water consumption and wastewater generation. Enzyme deactivation sprays use less water and lower energy, reducing operational costs and environmental impact.
Blanching produces wastewater that must be treated to avoid environmental contamination, thus raising disposal costs. Enzyme deactivation sprays generate minimal wastewater, minimizing treatment expenses and environmental risks. Choosing enzyme sprays also reduces greenhouse gas emissions associated with heating processes.
Related Important Terms
Enzyme inhibition misting
Enzyme inhibition misting delivers rapid, uniform enzyme deactivation by forming a fine, protective layer that preserves color, texture, and nutritional quality without heat application. This method improves freshness retention and extends shelf life more effectively than traditional blanching, which relies on thermal processing that can degrade product quality.
Flash-blanch aerosols
Flash-blanch aerosols provide rapid enzyme deactivation by instantly raising surface temperatures, preserving color, texture, and nutrient content without prolonged exposure to heat, unlike traditional blanching methods. This targeted approach minimizes water usage and processing time, maintaining freshness in fruits and vegetables more efficiently than enzyme deactivation sprays that rely on chemical agents.
Reactive oxygen species blockers
Blanching effectively inactivates enzymes by applying high heat, while enzyme deactivation sprays use reactive oxygen species blockers to prevent oxidative damage and maintain freshness without heat exposure. Reactive oxygen species blockers target free radicals, reducing enzymatic browning and preserving color and texture in fresh produce more gently than traditional blanching.
Phytochemical-preserving sprays
Phytochemical-preserving sprays offer a targeted approach to enzyme deactivation, maintaining freshness by minimizing nutrient loss compared to traditional blanching methods. These sprays retain higher levels of antioxidants, vitamins, and phenolic compounds, enhancing both the nutritional quality and shelf-life of fresh produce.
Chlorophyll retention foggers
Blanching effectively deactivates enzymes by applying high heat, but often leads to significant chlorophyll loss, resulting in duller color and reduced freshness. Enzyme deactivation sprays, especially chlorophyll retention foggers, preserve vibrant green pigments while inhibiting enzymatic activity, maintaining both freshness and aesthetic appeal in vegetables longer than traditional blanching methods.
Heatless blanching solutions
Heatless blanching solutions use enzyme deactivation sprays that preserve freshness by inhibiting enzymatic activity without applying heat, maintaining texture, color, and nutritional value better than traditional blanching. These sprays enhance shelf life and reduce nutrient loss, offering a more efficient alternative for fresh produce preservation.
Bioactive enzyme quenchers
Blanching effectively inactivates enzymes by applying heat, ensuring long-lasting freshness, while enzyme deactivation sprays utilize bioactive enzyme quenchers to target specific enzymatic activities without compromising texture. Bioactive enzyme quenchers in deactivation sprays provide a precision approach to preserve nutritional and sensory qualities by selectively inhibiting polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase enzymes.
Non-thermal deactivation coatings
Non-thermal deactivation coatings provide an innovative alternative to traditional blanching by inhibiting enzymatic activity without heat, preserving the freshness and texture of produce more effectively. These enzyme deactivation sprays form protective barriers that maintain nutritional quality and extend shelf life while minimizing nutrient loss and color degradation commonly associated with thermal blanching.
Freshness-lock microencapsulants
Freshness-lock microencapsulants provide a targeted enzyme deactivation spray option that preserves nutritional quality and texture more effectively than traditional blanching by minimizing heat exposure and nutrient loss. This innovative technology encapsulates active compounds to selectively inhibit enzymatic activity, thereby extending shelf life while maintaining the fresh appearance and flavor of produce.
Blanching vs Enzyme Deactivation Sprays for maintaining freshness. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com