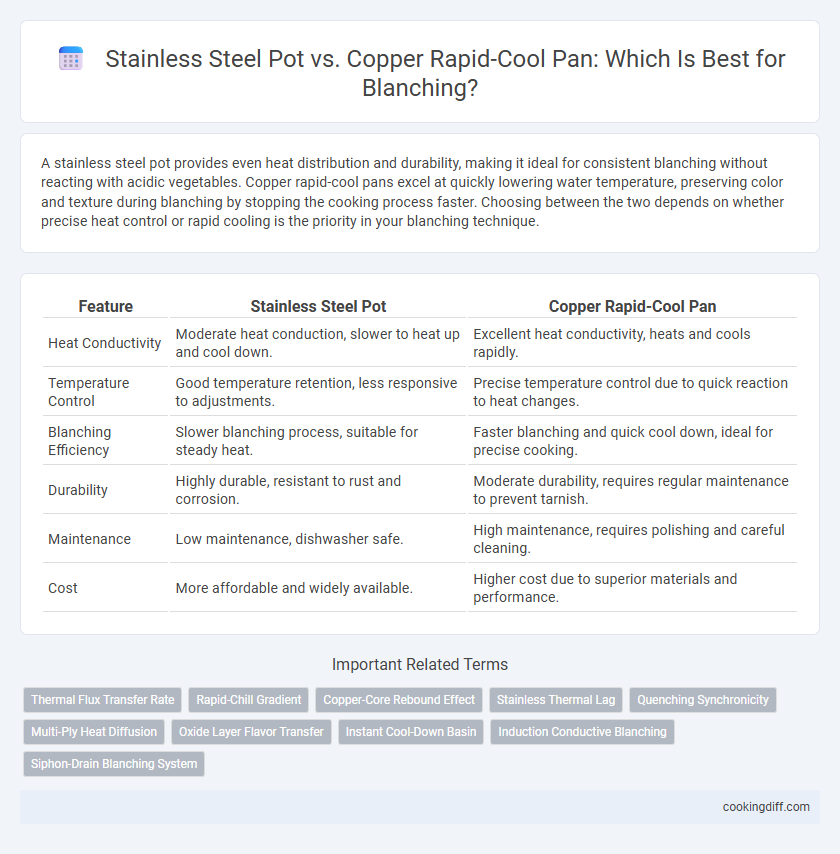
A stainless steel pot provides even heat distribution and durability, making it ideal for consistent blanching without reacting with acidic vegetables. Copper rapid-cool pans excel at quickly lowering water temperature, preserving color and texture during blanching by stopping the cooking process faster. Choosing between the two depends on whether precise heat control or rapid cooling is the priority in your blanching technique.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pot | Copper Rapid-Cool Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Conductivity | Moderate heat conduction, slower to heat up and cool down. | Excellent heat conductivity, heats and cools rapidly. |
| Temperature Control | Good temperature retention, less responsive to adjustments. | Precise temperature control due to quick reaction to heat changes. |
| Blanching Efficiency | Slower blanching process, suitable for steady heat. | Faster blanching and quick cool down, ideal for precise cooking. |
| Durability | Highly durable, resistant to rust and corrosion. | Moderate durability, requires regular maintenance to prevent tarnish. |
| Maintenance | Low maintenance, dishwasher safe. | High maintenance, requires polishing and careful cleaning. |
| Cost | More affordable and widely available. | Higher cost due to superior materials and performance. |
Introduction: Why Pan Choice Matters in Blanching
Which pan offers the best heat control for blanching vegetables effectively? Stainless steel pots provide durable and even heating, preventing hot spots that can cause uneven cooking. Copper rapid-cool pans excel in quickly lowering the temperature, preserving vegetable texture and color during the blanching process.
Stainless Steel Pots: Features and Benefits for Blanching
Stainless steel pots offer excellent durability and resistance to corrosion, making them ideal for frequent blanching tasks. Their even heat distribution ensures consistent blanching, preserving the color, texture, and nutrients of vegetables.
These pots typically feature a heavy bottom that prevents hot spots and reduces the risk of burning. Stainless steel is also non-reactive, ensuring that the taste of food remains pure during the blanching process.
Copper Rapid-Cool Pans: Key Advantages in Blanching
Copper rapid-cool pans offer superior thermal conductivity, allowing for precise temperature control essential in blanching. This rapid heat transfer ensures vegetables are blanched evenly and quickly, preserving texture and nutrients.
The ability of copper pans to cool down swiftly prevents overcooking during the blanching process, maintaining vibrant color and flavor. Stainless steel pots retain heat longer, which can lead to inconsistent blanching results. Copper's responsiveness makes it the preferred choice for chefs aiming for optimal blanching efficiency and quality.
Heat Conductivity: Stainless Steel vs. Copper Performance
Stainless steel pots offer moderate heat conductivity, making them reliable but slower to heat during blanching processes. Copper rapid-cool pans excel with superior thermal conductivity that ensures quick, even heating and faster temperature adjustments.
- Stainless steel heat conductivity - Approximately 16 W/m*K, providing steady but less responsive heat transfer.
- Copper heat conductivity - Around 400 W/m*K, enabling rapid heat distribution and precise temperature control.
- Blanching efficiency - Copper pans reduce cooking time due to fast heat response, improving vegetable texture and color preservation.
Rapid Cooling: The Science Behind Copper Pans
Copper pans excel in rapid cooling due to their exceptional thermal conductivity, approximately 400 W/m*K, which is significantly higher than stainless steel's 16 W/m*K. This efficient heat transfer allows copper pans to quickly lower the temperature of blanched vegetables, preserving color, texture, and nutrients. The rapid-cool feature of copper pans minimizes overcooking risk, making them ideal for precise blanching techniques.
Durability and Maintenance: Comparing Material Longevity
Stainless steel pots offer superior durability and resistance to rust or corrosion, making them ideal for long-term use in blanching processes. Copper rapid-cool pans provide excellent thermal conductivity but require regular polishing and maintenance to prevent tarnishing and maintain material integrity. Comparing material longevity, stainless steel stands out for its low-maintenance, robust performance during repeated exposure to boiling water and rapid cooling cycles.
Ease of Use: Handling and Weight Considerations
Stainless steel pots offer a balanced weight, making them easier to handle during blanching without sacrificing durability. Their sturdy construction provides stability, reducing the risk of spills while maneuvering hot water.
Copper rapid-cool pans are typically lighter, allowing for quick and effortless movement, which is beneficial when rapidly cooling vegetables after blanching. However, their lighter weight can sometimes reduce stability, requiring careful handling to avoid accidents.
Flavor Impact: Does Cookware Material Matter?
Stainless steel pots maintain a neutral flavor during blanching, preventing any metallic taste from altering the vegetable's natural profile. Copper rapid-cool pans conduct heat efficiently, but their reactive surface can subtly impact flavor when blanching acidic vegetables.
- Stainless Steel Neutrality - This material resists flavor transfer, preserving the purity of blanched ingredients.
- Copper Reactivity - Copper may infuse trace metallic notes, especially with high-acidity foods.
- Heat Conductivity Impact - Rapid cooling in copper pans can reduce overcooking, potentially enhancing texture and flavor retention.
Choosing between stainless steel and copper cookware depends on whether flavor neutrality or rapid heat adjustments are prioritized during blanching.
Cost Analysis: Stainless Steel vs. Copper Investment
Stainless steel pots require a lower initial investment compared to copper rapid-cool pans, making them a more budget-friendly option for blanching. The high cost of copper pans is often offset by their superior heat conductivity and energy efficiency over time.
- Initial Cost - Stainless steel pots are significantly cheaper to purchase upfront than copper rapid-cool pans.
- Durability - Stainless steel offers long-lasting resistance to corrosion and wear, reducing replacement frequency.
- Energy Efficiency - Copper pans heat faster and cool rapidly, potentially lowering energy costs despite the higher initial price.
Related Important Terms
Thermal Flux Transfer Rate
Stainless steel pots exhibit lower thermal flux transfer rates compared to copper rapid-cool pans, resulting in slower temperature changes during blanching. Copper pans facilitate quicker heat exchange and rapid cooling, enhancing efficiency and preserving vegetable texture and color more effectively.
Rapid-Chill Gradient
Stainless steel pots offer durability and even heat distribution, but copper rapid-cool pans excel in achieving a rapid-chill gradient critical for blanching, allowing food to cool quickly and stop the cooking process efficiently. The superior thermal conductivity of copper creates a sharper temperature drop, reducing nutrient loss and preserving texture better than stainless steel.
Copper-Core Rebound Effect
Copper rapid-cool pans feature a superior copper-core rebound effect that rapidly dissipates heat, preventing overcooking and preserving the color and texture of vegetables during blanching. Stainless steel pots, lacking this efficient thermal responsiveness, maintain heat longer, increasing the risk of uneven cooking and nutrient loss.
Stainless Thermal Lag
Stainless steel pots exhibit significant thermal lag during blanching, causing slower heat transfer and uneven cooking compared to copper rapid-cool pans, which offer superior thermal conductivity for faster temperature changes. This thermal inefficiency in stainless steel can lead to prolonged blanching times and inconsistent texture in vegetables.
Quenching Synchronicity
Stainless steel pots provide consistent heat retention but may result in slower quenching synchronicity during blanching compared to copper rapid-cool pans, which offer superior thermal conductivity for faster and more uniform temperature drops. Copper pans enhance blanching efficiency by rapidly synchronizing the cooling process, reducing nutrient loss and preserving vegetable texture.
Multi-Ply Heat Diffusion
Multi-ply stainless steel pots offer superior heat diffusion during blanching, ensuring even temperature distribution that prevents hotspots and maintains consistent cooking. Copper rapid-cool pans provide excellent thermal conductivity but may cool unevenly without multi-ply layering, making stainless steel multi-ply cookware more reliable for precise blanching results.
Oxide Layer Flavor Transfer
Stainless steel pots maintain a stable oxide layer that prevents flavor transfer during blanching, ensuring vegetables retain their natural taste. Copper rapid-cool pans develop a thinner oxide layer that may allow slight metallic flavor migration, potentially impacting the purity of blanched produce.
Instant Cool-Down Basin
A copper rapid-cool pan outperforms stainless steel pots in blanching due to its superior thermal conductivity, enabling instant cool-down of vegetables in an ice water basin and preserving texture and color. Stainless steel pots retain heat longer, slowing the cooling process and potentially compromising the crispness and vibrancy of blanched produce.
Induction Conductive Blanching
Stainless steel pots with induction-compatible bases provide even heating and rapid temperature adjustments essential for precise blanching, while copper rapid-cool pans excel in quickly dissipating heat to halt the cooking process effectively. For induction conductive blanching, stainless steel's magnetic properties ensure efficient energy transfer and temperature retention, whereas copper pans require compatible induction bases to leverage their superior thermal conductivity.
Stainless steel pot vs Copper rapid-cool pan for Blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com