Blanching involves briefly heating vegetables in boiling water or steam to inactivate enzymes, but it can cause significant nutrient loss, especially of water-soluble vitamins. Cryo-blanching, which uses freezing temperatures prior to blanching, better preserves nutrients by reducing thermal degradation and enzyme activity more efficiently. This method ensures higher retention of vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional blanching techniques.
Table of Comparison
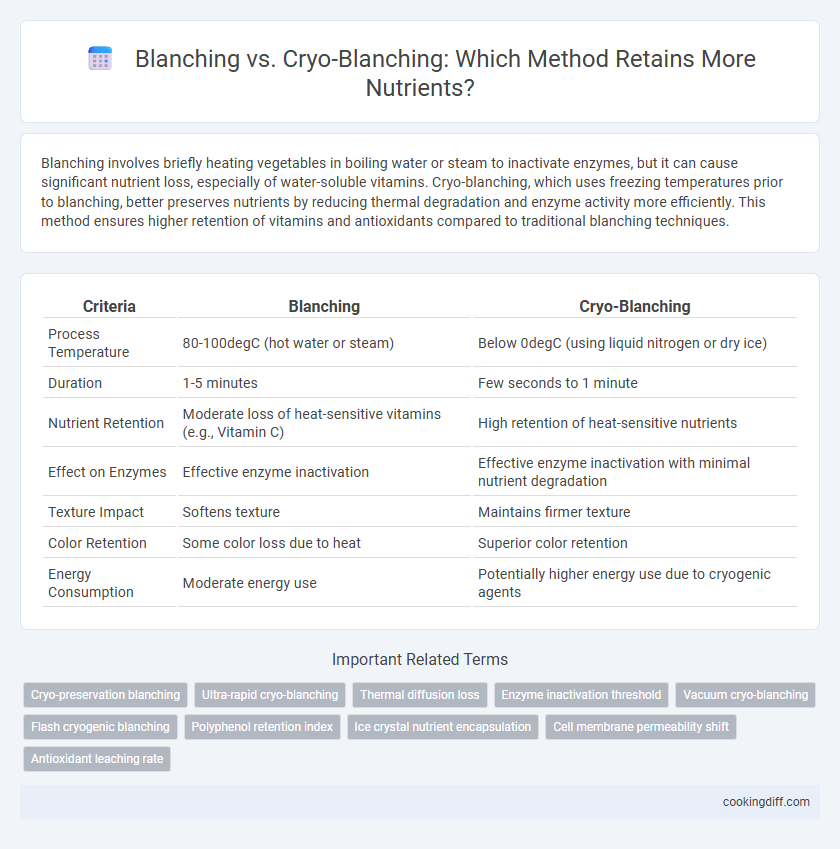
| Criteria | Blanching | Cryo-Blanching |
|---|---|---|
| Process Temperature | 80-100degC (hot water or steam) | Below 0degC (using liquid nitrogen or dry ice) |
| Duration | 1-5 minutes | Few seconds to 1 minute |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate loss of heat-sensitive vitamins (e.g., Vitamin C) | High retention of heat-sensitive nutrients |
| Effect on Enzymes | Effective enzyme inactivation | Effective enzyme inactivation with minimal nutrient degradation |
| Texture Impact | Softens texture | Maintains firmer texture |
| Color Retention | Some color loss due to heat | Superior color retention |
| Energy Consumption | Moderate energy use | Potentially higher energy use due to cryogenic agents |
Introduction to Blanching and Cryo-Blanching
Blanching is a heat treatment process used to inactivate enzymes in vegetables, preserving color, texture, and nutritional value before freezing or drying. Cryo-blanching employs ultra-low temperatures using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to rapidly cool and halt enzymatic activity, minimizing nutrient loss and maintaining freshness. Compared to traditional blanching, cryo-blanching offers superior preservation of vitamins, antioxidants, and phytochemicals due to reduced thermal exposure time.
How Traditional Blanching Works
| Traditional blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables in water or steam to inactivate enzymes that cause spoilage and nutrient loss. This heat treatment leads to partial depletion of water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and certain B vitamins. While effective for microbial control and enzyme inactivation, traditional blanching results in significant nutrient leaching compared to cryo-blanching methods. |
The Science Behind Cryo-Blanching
Cryo-blanching utilizes ultra-low temperatures, typically involving liquid nitrogen, to rapidly halt enzymatic activity in vegetables, preserving essential nutrients like vitamin C and antioxidants more effectively than traditional blanching. This rapid cooling minimizes heat exposure, reducing nutrient degradation and enhancing retention.
Studies show cryo-blanching maintains higher levels of chlorophyll and phenolic compounds due to its ability to prevent thermal damage and oxidative stress. The science behind cryo-blanching lies in its preservation of cellular integrity, which traditional hot water blanching often compromises, resulting in superior nutritional quality.
Nutrient Retention: Blanching vs Cryo-Blanching
Blanching is a traditional heat-based process used to inactivate enzymes in vegetables, while cryo-blanching employs ultra-low temperatures to achieve similar effects. Cryo-blanching generally preserves higher levels of heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C and antioxidants compared to conventional blanching.
- Vitamin C retention - Cryo-blanching minimizes vitamin C loss by reducing thermal degradation.
- Antioxidant preservation - Lower temperatures in cryo-blanching better maintain antioxidant levels in produce.
- Enzyme inactivation - Both methods effectively inactivate enzymes, but cryo-blanching does so with less nutrient damage.
Cryo-blanching stands out as an effective technique for maintaining the nutritional quality of vegetables during processing.
Effects on Vitamin C and Antioxidants
How do blanching and cryo-blanching compare in preserving Vitamin C and antioxidants in vegetables? Cryo-blanching significantly reduces nutrient loss by rapidly cooling the vegetables, which helps retain higher levels of Vitamin C and antioxidants compared to traditional blanching. Studies show that cryo-blanched vegetables maintain up to 30% more Vitamin C and exhibit stronger antioxidant activity due to minimized thermal degradation.
Impact on Flavor, Color, and Texture
Blanching often causes slight flavor loss and color fading due to heat exposure, while cryo-blanching preserves more vibrant color and fresher taste by rapidly cooling with liquid nitrogen. Texture in cryo-blanched vegetables remains crisper compared to the softer texture typically observed after traditional blanching.
Cryo-blanching improves nutrient retention by minimizing thermal degradation, maintaining higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants. The rapid freezing process helps lock in natural pigments, resulting in brighter color and enhanced visual appeal. This method also retains cellular integrity better, preserving the original texture and reducing mushiness commonly found in heat-blanched foods.
Energy Efficiency and Environmental Considerations
Cryo-blanching utilizes extremely low temperatures, significantly reducing energy consumption compared to traditional hot water blanching methods. This process not only enhances nutrient retention in vegetables but also lowers environmental impact by minimizing water usage and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Traditional blanching often involves high energy input due to prolonged heating and water boiling, leading to greater carbon footprints. Cryo-blanching's efficiency in preserving nutrients while consuming less energy presents a sustainable alternative for the food processing industry.
Suitability for Different Fruits and Vegetables
Blanching is widely suitable for a broad range of fruits and vegetables, effectively inactivating enzymes but may cause some nutrient loss due to heat exposure. Cryo-blanching preserves more nutrients by using liquid nitrogen or dry ice, making it ideal for delicate fruits and vegetables sensitive to heat.
- Blanching versatility - Suitable for dense vegetables like green beans and carrots that tolerate brief heat treatment without quality loss.
- Cryo-blanching precision - Best for soft fruits such as berries and leafy greens that require minimal temperature impact to retain vitamins.
- Nutrient retention variance - Cryo-blanching maintains higher levels of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C compared to traditional blanching.
Recent Research and Findings
Recent research indicates that cryo-blanching preserves higher levels of vitamin C and phenolic compounds compared to traditional blanching due to lower exposure to heat. Studies demonstrate that cryo-blanching minimizes enzymatic activity and maintains antioxidant capacity more effectively in vegetables like broccoli and spinach. These findings suggest that cryo-blanching is a superior method for nutrient retention during food processing.
Related Important Terms
Cryo-preservation blanching
Cryo-blanching enhances nutrient retention by rapidly cooling vegetables, minimizing thermal degradation of vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional blanching. This advanced cryo-preservation blanching technique preserves the structural integrity and reduces enzymatic activity, leading to superior preservation of nutritional quality.
Ultra-rapid cryo-blanching
Ultra-rapid cryo-blanching significantly enhances nutrient retention in vegetables by minimizing thermal degradation and enzyme activity compared to traditional blanching methods. This technique uses extremely low temperatures applied swiftly, preserving vitamins such as vitamin C and folate more effectively while maintaining texture and color.
Thermal diffusion loss
Blanching involves thermal exposure that causes significant nutrient loss through thermal diffusion, especially affecting heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Cryo-blanching minimizes thermal diffusion by using ultra-low temperatures, preserving higher nutrient retention and maintaining quality in fruits and vegetables.
Enzyme inactivation threshold
Blanching typically involves heating vegetables to temperatures between 70degC and 100degC, effectively inactivating enzymes such as peroxidase and polyphenol oxidase, which are responsible for nutrient degradation. Cryo-blanching, conducted at sub-zero temperatures using liquid nitrogen, achieves enzyme inactivation by rapidly freezing cellular structures, preserving heat-sensitive nutrients better by avoiding thermal degradation.
Vacuum cryo-blanching
Vacuum cryo-blanching significantly enhances nutrient retention by rapidly cooling vegetables under reduced pressure, minimizing thermal degradation of vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional blanching methods. This technique preserves chlorophyll and ascorbic acid more effectively, extending shelf life while maintaining sensory quality and nutritional value.
Flash cryogenic blanching
Flash cryogenic blanching preserves significantly higher levels of vitamins and antioxidants compared to traditional hot water blanching due to rapid freezing with liquid nitrogen, minimizing nutrient loss and enzymatic degradation. This method not only enhances the retention of heat-sensitive nutrients such as vitamin C and carotenoids but also improves texture and color stability in various fruits and vegetables.
Polyphenol retention index
Cryo-blanching demonstrates a significantly higher polyphenol retention index compared to traditional blanching methods, preserving up to 85-90% of polyphenolic compounds versus 60-70% in conventional blanching. This enhanced nutrient retention is attributed to the lower processing temperatures and reduced thermal degradation during cryo-blanching.
Ice crystal nutrient encapsulation
Cryo-blanching enhances nutrient retention by forming fine ice crystals that encapsulate vitamins and minerals, preventing leaching during processing. Traditional blanching often causes nutrient loss through heat-induced cell damage and water solubilization, whereas ice crystal formation in cryo-blanching acts as a protective barrier maintaining higher nutrient integrity.
Cell membrane permeability shift
Blanching causes a significant increase in cell membrane permeability, leading to nutrient leaching and loss, while cryo-blanching minimizes this permeability shift by using low temperatures to preserve cell structure and enhance nutrient retention. Studies show that cryo-blanching better preserves vitamins such as vitamin C and antioxidants by maintaining membrane integrity compared to conventional blanching methods.
Blanching vs Cryo-blanching for nutrient retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com