Boiling vegetables involves immersing them in rapidly heated water until they reach the desired tenderness, which can lead to some nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to water and heat. Flash infusion, on the other hand, uses brief, high-pressure steam or hot water exposure, dramatically preserving the vegetable's flavor, texture, and nutritional content. Choosing between boiling and flash infusion depends on the desired balance between cooking speed, nutrient retention, and sensory quality.
Table of Comparison
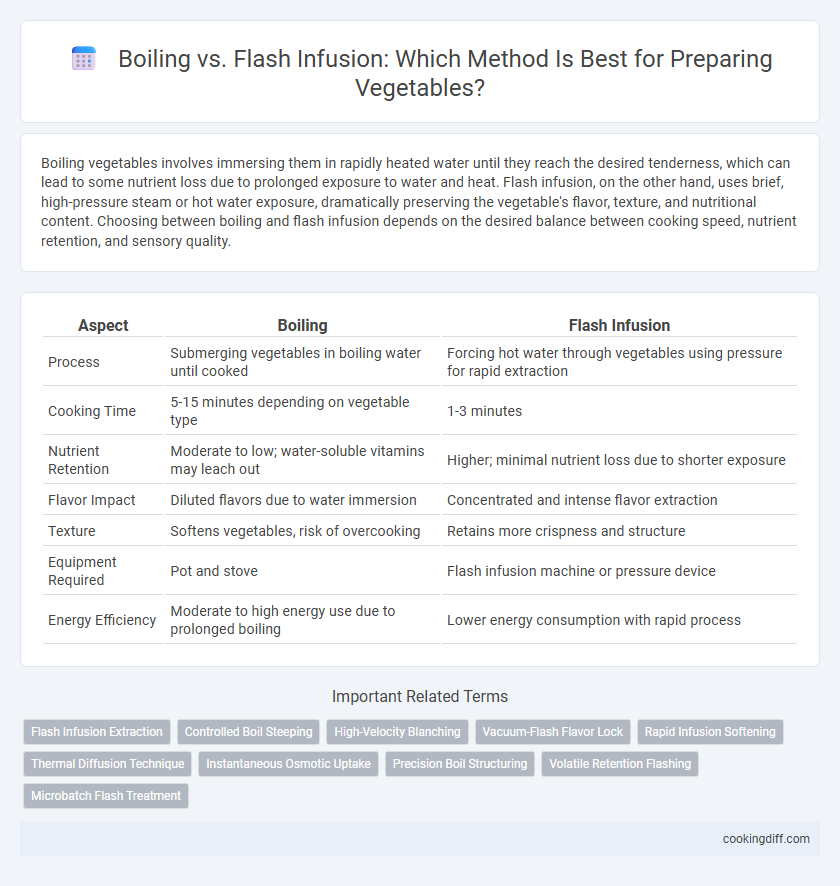
| Aspect | Boiling | Flash Infusion |
|---|---|---|
| Process | Submerging vegetables in boiling water until cooked | Forcing hot water through vegetables using pressure for rapid extraction |
| Cooking Time | 5-15 minutes depending on vegetable type | 1-3 minutes |
| Nutrient Retention | Moderate to low; water-soluble vitamins may leach out | Higher; minimal nutrient loss due to shorter exposure |
| Flavor Impact | Diluted flavors due to water immersion | Concentrated and intense flavor extraction |
| Texture | Softens vegetables, risk of overcooking | Retains more crispness and structure |
| Equipment Required | Pot and stove | Flash infusion machine or pressure device |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate to high energy use due to prolonged boiling | Lower energy consumption with rapid process |
Understanding Boiling: Traditional Vegetable Preparation
Boiling is a traditional cooking method that involves immersing vegetables in boiling water to soften their texture and enhance flavor. This technique facilitates the breakdown of cell walls, making nutrients more accessible, though some water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C may leach out. Compared to flash infusion, boiling requires longer cooking times and higher water volumes, potentially leading to nutrient loss but ensuring even heat distribution and thorough cooking.
What Is Flash Infusion? A Modern Cooking Technique
Flash infusion is a cutting-edge cooking technique that uses rapid pressure changes to extract flavors and nutrients from vegetables almost instantly. Unlike traditional boiling, which relies on prolonged heat exposure, flash infusion preserves texture and enhances taste through controlled rapid infusion.
- Rapid pressure changes - Utilize quick shifts in pressure to infuse vegetables efficiently.
- Preserves texture - Maintains vegetable firmness better than prolonged boiling.
- Enhances flavor extraction - Intensifies vegetable taste by accelerating nutrient release.
Flash infusion offers a modern, efficient alternative to conventional boiling for superior vegetable preparation.
Comparing Cooking Times: Boiling vs Flash Infusion
Boiling vegetables typically requires 5 to 15 minutes, depending on the type and size, to achieve desired tenderness through heat transfer by water. Flash infusion, utilizing high-pressure steam or microwave pulses, reduces cooking times to under 3 minutes by rapidly breaking down cell walls while preserving nutrients.
Boiling's extended cooking time can lead to nutrient leaching and texture softening, whereas flash infusion minimizes nutrient loss and retains vibrant color due to shorter exposure to heat. The efficiency of flash infusion offers significant time-saving benefits in commercial kitchens without sacrificing vegetable quality.
Nutrient Retention: Which Method Preserves More?
Boiling vegetables often leads to significant nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex, due to prolonged exposure to high temperatures and water. Flash infusion, a rapid technique involving high pressure and vacuum, preserves more nutrients by drastically reducing cooking time and limiting water exposure.
- Higher retention of water-soluble vitamins - Flash infusion minimizes leaching of vitamins like vitamin C by reducing cooking duration and water contact.
- Reduced heat degradation - The shorter processing time in flash infusion limits the breakdown of heat-sensitive nutrients compared to boiling.
- Preservation of antioxidants - Flash infusion better maintains antioxidants such as flavonoids, which degrade quickly during conventional boiling.
Flavor Impact: Does Boiling or Flash Infusion Enhance Taste?
| Boiling | Boiling vegetables results in leaching of water-soluble nutrients and flavor compounds, often diluting taste. High heat over extended time can cause loss of volatile aromatic compounds, leading to a milder flavor profile. Texture softens significantly, which may reduce crispness but enhances certain earthy flavors. |
| Flash Infusion | Flash infusion rapidly extracts flavor using pressurized hot water, preserving vibrant and fresh vegetable taste. The brief exposure prevents nutrient and aroma loss, intensifying natural flavors and maintaining texture crispness. It enhances flavor complexity by retaining volatile oils that boiling typically dissipates. |
Texture Differences: How Each Method Affects Vegetables
Boiling softens vegetables uniformly by breaking down cell walls through prolonged exposure to high temperatures, resulting in a tender texture. Flash infusion, using rapid hot water application under pressure, preserves more structure, yielding a crisper bite.
Texture differences between boiling and flash infusion significantly impact culinary outcomes; boiling often causes vegetables like carrots and green beans to become mushy while flash infusion retains firmness and vibrant color. Flash infusion minimizes nutrient loss and maintains the vegetables' natural snap due to shorter cooking times and pressure control. Selecting between these methods depends on the desired texture, with boiling suited for purees and flash infusion ideal for salads or garnishes needing crunch.
Energy Efficiency: Boiling vs Flash Infusion
Boiling requires sustained heat over a prolonged period, leading to higher energy consumption when preparing vegetables. Flash infusion rapidly heats vegetables using pressure, significantly reducing cooking time and energy usage.
- Energy consumption - Boiling uses more energy due to extended heating duration.
- Cooking time - Flash infusion drastically cuts cooking time by applying high-pressure steam quickly.
- Heat transfer efficiency - Flash infusion maximizes heat transfer efficiency with pressurized steam, lowering overall energy demand.
Equipment and Preparation Needs for Both Methods
Boiling requires basic kitchen equipment such as a pot and stove, with water heated to 100degC to cook vegetables evenly. Flash infusion demands specialized apparatus like vacuum chambers and infusion machines to rapidly extract flavors while preserving texture.
Preparation for boiling includes cutting vegetables uniformly to ensure consistent cooking times, often taking 5-15 minutes depending on the vegetable. Flash infusion preparation involves placing vegetables in a vacuum-sealed container, enabling intense flavor absorption in under a minute.
Ideal Vegetables for Boiling and Flash Infusion
Which vegetables are ideally suited for boiling compared to flash infusion? Root vegetables like carrots and potatoes benefit from boiling due to their dense texture that requires longer cooking times. Leafy greens and delicate herbs are better prepared with flash infusion, preserving nutrients and vibrant color through rapid, high-temperature exposure.
Related Important Terms
Flash Infusion Extraction
Flash infusion extraction rapidly extracts nutrients and flavors from vegetables by using high-pressure steam, preserving color and texture better than traditional boiling methods. This technique significantly reduces cooking time while enhancing the retention of vitamins and antioxidants compared to prolonged boiling.
Controlled Boil Steeping
Controlled boil steeping maintains a precise temperature just below boiling to gently soften vegetables while preserving nutrients and texture. Unlike flash infusion, which uses rapid temperature spikes for quick extraction, controlled boil steeping allows gradual flavor development and enhanced nutrient retention in vegetable preparation.
High-Velocity Blanching
High-velocity blanching uses rapid water circulation at boiling temperatures to quickly cook and preserve the texture, color, and nutrients of vegetables, outperforming traditional boiling by reducing cooking time and nutrient loss. Compared to flash infusion, it provides more consistent heat transfer and retains more structural integrity in vegetables due to controlled high-speed water flow.
Vacuum-Flash Flavor Lock
Boiling extracts nutrients and flavors slowly by submerging vegetables in hot water, while Vacuum-Flash Infusion uses vacuum pressure to rapidly infuse liquids and flavors into vegetable cells, preserving vibrant taste and texture. Vacuum-Flash Flavor Lock technology enhances flavor retention by creating a controlled vacuum environment that prevents oxidation and nutrient loss common in boiling.
Rapid Infusion Softening
Flash infusion rapidly softens vegetables by using high-pressure steam, preserving nutrients and texture more effectively than traditional boiling, which heats food slower and risks nutrient loss. This method ensures quicker infusion of flavors while maintaining optimal vegetable firmness and color compared to prolonged boiling times.
Thermal Diffusion Technique
Boiling utilizes prolonged thermal diffusion to evenly cook vegetables by maintaining water at 100degC, allowing heat to penetrate cell walls and soften the texture. Flash infusion, in contrast, employs rapid pressure changes to enhance thermal diffusion, accelerating nutrient extraction and flavor infusion without extended cooking times.
Instantaneous Osmotic Uptake
Boiling induces gradual water absorption in vegetables through traditional heat transfer, whereas flash infusion leverages rapid pressure changes to achieve instantaneous osmotic uptake, significantly enhancing nutrient retention and flavor intensity. This immediate osmotic infusion method preserves cellular integrity better and accelerates hydration compared to conventional boiling techniques.
Precision Boil Structuring
Precision Boil Structuring enables controlled temperature regulation during boiling, preserving vegetable texture and nutrient content more effectively than flash infusion. This method ensures uniform heat penetration, minimizing nutrient loss and enhancing flavor retention in vegetable preparation.
Volatile Retention Flashing
Flash infusion preserves volatile compounds in vegetables by rapidly exposing them to steam, minimizing flavor loss compared to traditional boiling, which often causes significant evaporation of aromatic molecules. This rapid steaming technique enhances the retention of essential oils and nutrients, resulting in more vibrant flavors and improved vegetable texture.
Boiling vs Flash Infusion for vegetable preparation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com