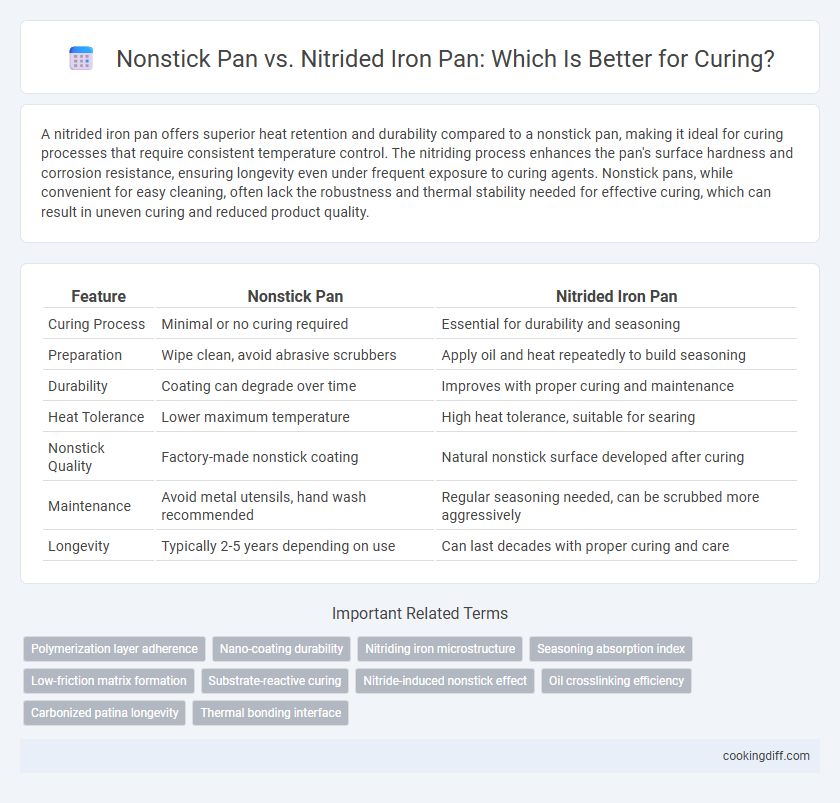
A nitrided iron pan offers superior heat retention and durability compared to a nonstick pan, making it ideal for curing processes that require consistent temperature control. The nitriding process enhances the pan's surface hardness and corrosion resistance, ensuring longevity even under frequent exposure to curing agents. Nonstick pans, while convenient for easy cleaning, often lack the robustness and thermal stability needed for effective curing, which can result in uneven curing and reduced product quality.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Nonstick Pan | Nitrided Iron Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Curing Process | Minimal or no curing required | Essential for durability and seasoning |
| Preparation | Wipe clean, avoid abrasive scrubbers | Apply oil and heat repeatedly to build seasoning |
| Durability | Coating can degrade over time | Improves with proper curing and maintenance |
| Heat Tolerance | Lower maximum temperature | High heat tolerance, suitable for searing |
| Nonstick Quality | Factory-made nonstick coating | Natural nonstick surface developed after curing |
| Maintenance | Avoid metal utensils, hand wash recommended | Regular seasoning needed, can be scrubbed more aggressively |
| Longevity | Typically 2-5 years depending on use | Can last decades with proper curing and care |
Introduction to Pan Curing: Why It Matters
Proper curing enhances the durability and nonstick properties of cooking pans. Comparing nonstick pans and nitrided iron pans highlights key differences in maintenance and performance during curing.
- Nonstick Pan Curing - Requires gentle seasoning to maintain the synthetic coating and prevent damage.
- Nitrided Iron Pan Curing - Involves creating a hardened oxide layer that improves resistance to rust and wear.
- Importance of Curing - Ensures optimal cooking performance and extends the lifespan of both pan types.
What Is a Nonstick Pan? Features and Benefits
A nonstick pan is coated with a layer of polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE) or ceramic, designed to prevent food from sticking during cooking. This coating reduces the need for excessive oil, making it easier to cook delicate foods and clean the pan afterward.
Nonstick pans heat quickly and offer even cooking, but their coating can degrade over time and is sensitive to high temperatures and metal utensils. For curing, the nonstick surface limits seasoning buildup, unlike nitrided iron pans that develop a natural patina enhancing durability and flavor.
Understanding Nitrided Iron Pans
Nitrided iron pans undergo a specialized heat treatment that infuses nitrogen into the surface, enhancing durability and corrosion resistance compared to traditional nonstick pans. This process creates a hard, wear-resistant layer that promotes better seasoning and a natural nonstick effect without synthetic coatings. Understanding the unique curing properties of nitrided iron helps users maintain pan longevity and optimize cooking performance over time.
Curing Process: Nonstick vs Nitrided Iron
| Type of Pan | Curing Process | Durability and Maintenance |
|---|---|---|
| Nonstick Pan | Typically pre-coated, requiring minimal curing; seasoning is not necessary due to the synthetic nonstick layer. | Coating can degrade with high heat or metal utensils, leading to reduced lifespan and potential release of harmful compounds. |
| Nitrided Iron Pan | Requires thorough curing by applying oil and heating to form a natural, durable nonstick layer through nitriding and polymerization. | Highly durable surface improves with regular seasoning, resistant to scratching and corrosion, enhancing pan longevity. |
Heat Resistance and Durability Comparison
Nonstick pans typically feature a PTFE coating that withstands heat up to 260degC, but extended exposure to higher temperatures can degrade the coating and reduce lifespan. In contrast, nitrided iron pans endure temperatures exceeding 400degC due to their hardened surface layer formed through nitrogen diffusion, enhancing heat resistance significantly.
Durability of nitrided iron pans surpasses nonstick pans as the nitriding process creates a corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant surface ideal for high-heat cooking and long-term use. Nonstick coatings are prone to scratching and peeling under heavy use, while nitrided iron pans maintain structural integrity and performance over years with regular seasoning.
Nonstick Coating: Pros and Cons for Curing
Nonstick pans offer easy release and minimal seasoning requirements, making the curing process straightforward and less time-consuming. However, their nonstick coating may degrade under high heat or prolonged curing, potentially releasing harmful chemicals and shortening the pan's lifespan. For optimal curing, maintaining low to medium heat and avoiding abrasive cleaning is essential to preserve the nonstick surface quality.
Nitrided Iron Surface: Advantages in Curing
The nitrided iron pan surface offers superior durability and enhanced seasoning retention compared to nonstick pans, making it ideal for curing. Its porous texture allows better oil absorption, creating a natural, long-lasting nonstick layer that improves with use.
- Improved Heat Retention - Nitrided iron pans maintain consistent heat, essential for effective curing processes.
- Enhanced Surface Hardness - The nitriding process significantly strengthens the pan's surface, reducing wear and prolonging lifespan.
- Superior Flavor Development - The seasoning on nitrided iron enhances the taste of food by building a flavorful, protective coating over time.
Nitrided iron pans provide a robust and evolving seasoning surface unmatched by nonstick alternatives, optimizing the curing experience.
Maintenance and Longevity: Which Pan Lasts Longer?
A nitrided iron pan requires regular seasoning to maintain its corrosion resistance and improve nonstick properties, ensuring long-term durability. Nonstick pans, while easier to clean and maintain, often have a shorter lifespan due to coating wear and potential flaking over time.
- Nitrided Iron Pan longevity - Proper maintenance such as seasoning extends the pan's lifespan by preventing rust and improving surface durability.
- Nonstick Pan maintenance - Avoiding metal utensils and abrasive cleaners helps preserve the nonstick coating, but the surface degrades naturally after several years.
- Durability comparison - Nitrided iron pans generally outlast nonstick pans by multiple years when maintained correctly due to their resilient surface treatment.
Flavor, Texture, and Cooking Results
Nonstick pans provide a consistent, smooth surface that preserves delicate flavors without adding metallic notes, while nitrided iron pans develop a natural seasoning that enhances flavor complexity over time. The seasoned nitrided iron surface uniquely contributes to richer textures, offering a slightly crispy finish favored in high-heat cooking.
Nitrided iron pans excel in heat retention and even cooking, improving Maillard reactions for deeper flavor and better browning. Nonstick pans excel in delivering uniform texture with less oil, making them ideal for delicate foods requiring gentle cooking. Both pan types yield distinct cooking results, with nitrided iron offering durability and flavor development, and nonstick emphasizing ease and cleanliness.
Related Important Terms
Polymerization layer adherence
Nonstick pans typically feature a synthetic polymer coating that may hinder effective polymerization layer adherence during curing, leading to less durable seasoning. In contrast, nitrided iron pans possess a hardened surface that promotes strong polymerization bonding, enhancing the longevity and performance of the curing layer.
Nano-coating durability
Nonstick pans feature a synthetic nano-coating designed to enhance durability and resist wear during curing, but they may degrade faster under high heat compared to nitrided iron pans. Nitrided iron pans develop a naturally durable nano-layer through heat treatment that improves corrosion resistance and strengthens the surface over time, offering superior nano-coating longevity for curing applications.
Nitriding iron microstructure
Nitrided iron pans exhibit a hardened microstructure formed by nitrogen diffusion that enhances surface durability and corrosion resistance during curing processes. This microstructural modification creates a robust iron nitride layer, promoting superior seasoning retention and reducing the likelihood of rusting compared to nonstick pans.
Seasoning absorption index
Nitrided iron pans exhibit a higher seasoning absorption index than nonstick pans, allowing for deeper oil penetration and a more durable curing layer. This enhanced seasoning process improves cooking performance and longevity by creating a robust, nonstick surface that strengthens with use.
Low-friction matrix formation
Nitrided iron pans develop a durable, low-friction matrix through nitrogen diffusion that enhances curing by creating a naturally nonstick surface resistant to wear. In contrast, traditional nonstick pans rely on synthetic coatings that can degrade over time, offering less effective and less durable low-friction surfaces during the curing process.
Substrate-reactive curing
Nonstick pans lack the substrate-reactive properties needed for effective curing, resulting in a less durable seasoning layer prone to peeling. Nitrided iron pans undergo surface modification that enhances substrate reactivity, promoting superior polymerization and a more resilient, long-lasting cured coating.
Nitride-induced nonstick effect
Nitrided iron pans develop a durable nitride layer that enhances the nonstick effect by reducing surface energy and preventing food adhesion without the need for synthetic coatings. This nitride-induced nonstick surface improves heat retention and durability compared to traditional nonstick pans, making it ideal for long-term curing and seasoning.
Oil crosslinking efficiency
Nitrided iron pans exhibit superior oil crosslinking efficiency during curing due to their enhanced surface hardness and reduced porosity, which promotes a more uniform and durable seasoning layer. In contrast, nonstick pans hinder proper oil polymerization, resulting in less effective seasoning and decreased longevity of the cured coating.
Carbonized patina longevity
Nonstick pans generally lack the ability to develop a durable carbonized patina, resulting in inferior longevity compared to nitrided iron pans, which form a hard, corrosion-resistant surface through the nitriding process that enhances carbonized patina retention. The nitrided iron pan's surface enables prolonged seasoning and superior carbonized layer durability, making it ideal for maintaining long-lasting nonstick performance through curing.
Nonstick pan vs nitrided iron pan for curing. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com