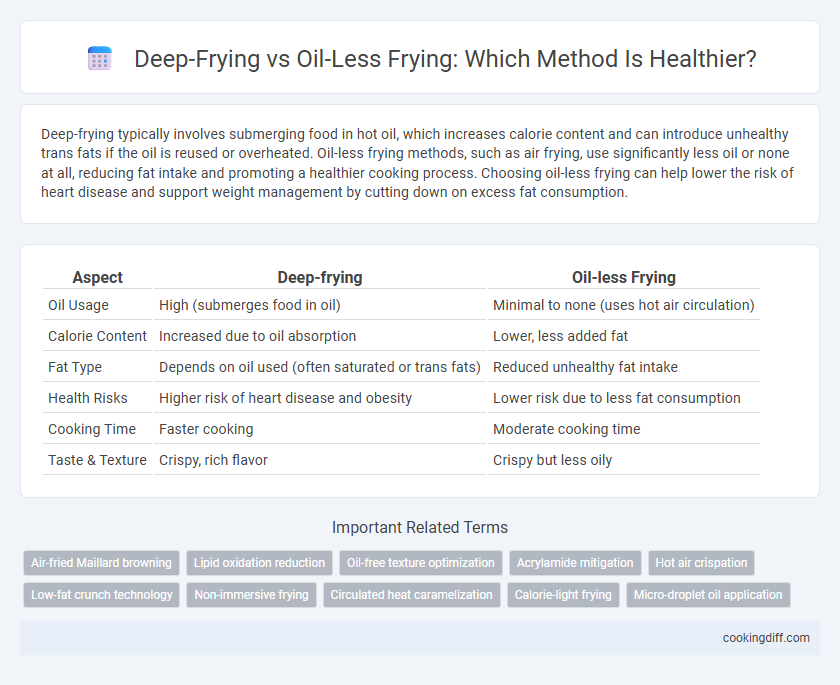
Deep-frying typically involves submerging food in hot oil, which increases calorie content and can introduce unhealthy trans fats if the oil is reused or overheated. Oil-less frying methods, such as air frying, use significantly less oil or none at all, reducing fat intake and promoting a healthier cooking process. Choosing oil-less frying can help lower the risk of heart disease and support weight management by cutting down on excess fat consumption.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Deep-frying | Oil-less Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Oil Usage | High (submerges food in oil) | Minimal to none (uses hot air circulation) |
| Calorie Content | Increased due to oil absorption | Lower, less added fat |
| Fat Type | Depends on oil used (often saturated or trans fats) | Reduced unhealthy fat intake |
| Health Risks | Higher risk of heart disease and obesity | Lower risk due to less fat consumption |
| Cooking Time | Faster cooking | Moderate cooking time |
| Taste & Texture | Crispy, rich flavor | Crispy but less oily |
Understanding Deep-Frying and Oil-less Frying Methods
Deep-frying involves submerging food in hot oil, which can increase calorie and fat content due to oil absorption. Oil-less frying uses technologies like hot air circulation to cook food with minimal or no added oil, resulting in lower fat content and fewer calories.
- Deep-frying - Cooks food by immersing it in hot oil, often leading to higher fat absorption.
- Oil-less frying - Utilizes hot air or infrared heating to cook food with little to no oil, reducing fat intake.
- Health impact - Oil-less frying generally offers a healthier alternative by lowering calorie and fat consumption compared to traditional deep-frying.
Nutritional Differences: Deep-frying vs Oil-less Frying
Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content and calories of foods due to oil absorption, leading to higher levels of unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats. Oil-less frying uses little to no oil, preserving the natural nutrients and reducing overall fat intake.
Deep-fried foods often contain higher concentrations of acrylamide, a potentially harmful compound formed during high-temperature cooking. Oil-less frying methods such as air frying minimize acrylamide formation, making them a healthier alternative. Nutritionally, oil-less frying retains more vitamins and antioxidants, contributing to better overall dietary quality.
How Deep-Frying Affects Fat Content in Food
| Deep-frying significantly increases the fat content of food as it absorbs the cooking oil, often adding 10-15 grams of fat per serving depending on food type and frying duration. |
| Oil-less frying methods, such as air frying, use little to no oil, reducing fat intake by up to 70-80% compared to traditional deep-frying. |
| Excessive fat absorption during deep-frying can raise calorie density and impact cardiovascular health, making oil-less frying a healthier alternative for fat reduction. |
Health Benefits of Oil-less Frying
Oil-less frying significantly reduces calorie intake by eliminating the need for added oils, which lowers fat consumption and supports heart health. This method preserves essential nutrients better than traditional deep-frying, enhancing the overall nutritional value of foods. Reduced exposure to harmful compounds like acrylamide and trans fats makes oil-less frying a healthier alternative for regular meal preparation.
Calorie Comparison Between Deep-fried and Oil-less Foods
Deep-frying significantly increases the calorie content of foods due to oil absorption, while oil-less frying methods like air frying reduce calorie intake by using minimal or no added fat. This calorie difference makes oil-less frying a healthier option for weight management and overall calorie control.
- Calorie Density - Deep-fried foods can contain up to 50% more calories than their oil-less fried counterparts due to oil absorption.
- Fat Content - Oil-less frying methods drastically reduce fat content, lowering the overall calorie count of the food.
- Health Impact - Choosing oil-less frying helps reduce calorie intake, supporting healthier eating habits and weight management.
Impact on Cholesterol and Heart Health
How does deep-frying compare to oil-less frying in terms of cholesterol impact and heart health? Deep-frying typically increases the absorption of unhealthy trans fats and saturated fats, which can raise LDL cholesterol levels and contribute to heart disease. Oil-less frying methods significantly reduce fat intake, promoting better cholesterol management and improved cardiovascular health.
Retention of Nutrients: Which Method Wins?
Deep-frying often leads to nutrient loss due to high temperatures causing degradation of heat-sensitive vitamins like vitamin C and some B vitamins. Oil-less frying methods, such as air frying, preserve more nutrients by using rapid air circulation and lower temperatures, minimizing nutrient breakdown. Studies indicate air frying retains antioxidants and maintains higher levels of minerals compared to traditional deep-frying techniques.
Taste and Texture Variations: Deep-frying vs Oil-less Frying
Deep-frying immerses food in hot oil, creating a crispy, golden exterior and a moist interior due to rapid Maillard reaction and caramelization. This method enhances flavor complexity and provides a rich, satisfying texture unattainable by oil-less frying techniques.
Oil-less frying, such as air frying, uses circulating hot air to cook food, producing a crisp surface with significantly less fat absorption, which can result in a drier interior and milder taste profile. While healthier due to reduced oil content, oil-less frying may lack the depth of flavor and crunch characteristic of traditional deep-fried foods.
Common Myths About Deep-frying and Oil-less Frying
Deep-frying is often criticized for being unhealthy due to high oil absorption, but proper temperature control minimizes oil uptake and preserves nutrient content. Oil-less frying technologies use hot air circulation to mimic frying, reducing fat while potentially compromising texture and flavor.
Common myths claim deep-frying always leads to greasy, calorie-dense food, yet using fresh oil and correct techniques lowers harmful compounds like acrylamide. Conversely, oil-less frying is believed to be completely fat-free, but some models require small amounts of oil for optimal taste and crispiness.
Related Important Terms
Air-fried Maillard browning
Deep-frying achieves Maillard browning through submersion in hot oil at temperatures between 160-190degC, which enhances flavor but increases fat absorption and calorie content. Oil-less frying, such as air frying, uses rapid hot air circulation to replicate Maillard browning while significantly reducing oil usage, resulting in lower fat content and fewer harmful compounds associated with excessive oil exposure.
Lipid oxidation reduction
Deep-frying causes significant lipid oxidation, producing harmful compounds like aldehydes and free radicals, which can increase oxidative stress and inflammation in the body. Oil-less frying methods, such as air frying, substantially reduce lipid oxidation by minimizing oil exposure and high-temperature oil degradation, resulting in healthier cooking with fewer oxidative byproducts.
Oil-free texture optimization
Oil-less frying enhances healthiness by significantly reducing oil absorption while using advanced air circulation technology to achieve a crispy, golden texture similar to traditional deep-frying. This method minimizes calorie intake and unhealthy fats without sacrificing the appealing crunch and flavor expected from fried foods.
Acrylamide mitigation
Deep-frying typically produces higher levels of acrylamide, a potential carcinogen formed from the Maillard reaction at high temperatures, while oil-less frying methods use lower temperatures and reduce acrylamide formation significantly. Choosing oil-less frying techniques can mitigate health risks associated with acrylamide exposure by limiting the compound's development during cooking.
Hot air crispation
Hot air crispation in oil-less frying reduces calorie intake by circulating hot air to achieve a crispy texture without submerging food in oil, lowering fat absorption compared to traditional deep-frying methods. This technique preserves flavor and texture while significantly decreasing the risk of heart disease and obesity linked to excessive oil consumption.
Low-fat crunch technology
Low-fat crunch technology enhances the crispiness of foods in oil-less frying by using rapid hot air circulation and minimal oil spray, significantly reducing fat absorption compared to traditional deep-frying. This method preserves texture and flavor while delivering healthier, lower-fat meals ideal for those seeking to minimize calorie intake without sacrificing taste.
Non-immersive frying
Non-immersive frying methods, such as air frying, significantly reduce oil absorption compared to traditional deep-frying, resulting in lower calorie intake and diminished risk of heart disease. Studies show air frying decreases acrylamide formation and preserves food nutrients better, making it a healthier alternative for crispy texture without excess fat.
Circulated heat caramelization
Deep-frying promotes rapid circulated heat caramelization, enhancing flavor and texture through Maillard reactions, but often results in higher oil absorption and increased fat content. Oil-less frying utilizes circulating hot air to achieve caramelization with significantly reduced oil usage, offering a healthier alternative by minimizing calorie intake and lowering the risk of cardiovascular issues.
Calorie-light frying
Deep-frying typically involves submerging food in hot oil, which significantly increases calorie content due to oil absorption, making it less suitable for calorie-conscious diets. In contrast, oil-less frying methods, such as air frying, use hot air circulation to cook food, drastically reducing added fats and overall calories while maintaining crispiness.
Deep-frying vs Oil-less frying for healthiness. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com