A blanching pot provides direct heat by boiling vegetables in water, which can cause nutrient loss and water retention in vegetables, leading to longer dehydration times. A steam blancher uses steam to gently heat vegetables, preserving more nutrients and maintaining vegetable texture for faster and more effective dehydration. Choosing a steam blancher enhances the quality and shelf life of dehydrated vegetables compared to traditional blanching pots.
Table of Comparison
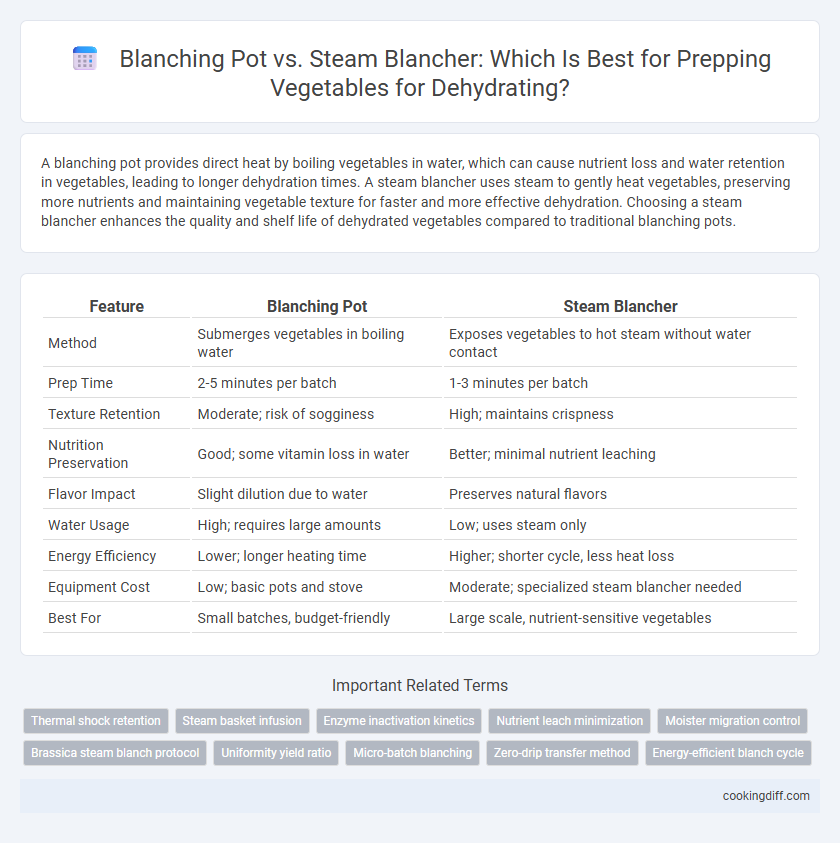
| Feature | Blanching Pot | Steam Blancher |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Submerges vegetables in boiling water | Exposes vegetables to hot steam without water contact |
| Prep Time | 2-5 minutes per batch | 1-3 minutes per batch |
| Texture Retention | Moderate; risk of sogginess | High; maintains crispness |
| Nutrition Preservation | Good; some vitamin loss in water | Better; minimal nutrient leaching |
| Flavor Impact | Slight dilution due to water | Preserves natural flavors |
| Water Usage | High; requires large amounts | Low; uses steam only |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower; longer heating time | Higher; shorter cycle, less heat loss |
| Equipment Cost | Low; basic pots and stove | Moderate; specialized steam blancher needed |
| Best For | Small batches, budget-friendly | Large scale, nutrient-sensitive vegetables |
Introduction to Blanching Methods for Dehydrating Vegetables
Blanching is an essential process in dehydrating vegetables, used to inactivate enzymes and preserve color, texture, and nutritional value. Choosing between a blanching pot and a steam blancher depends on the type of vegetable and desired dehydration quality.
- Blanching Pot - Submerges vegetables in boiling water, ensuring even heat penetration and rapid enzyme inactivation.
- Steam Blancher - Uses steam to gently heat vegetables, reducing nutrient loss and minimizing water absorption.
- Efficiency and Suitability - Steam blanchers are preferred for delicate vegetables, while blanching pots are better for larger, denser produce.
Proper blanching method selection enhances dehydration efficiency and final product quality.
What Is a Blanching Pot?
What is a blanching pot used for in dehydrating vegetables? A blanching pot is a specialized container designed to quickly boil vegetables, softening them and stopping enzymatic reactions that cause spoilage. This method preserves color, texture, and nutritional value before dehydration, ensuring high-quality dried produce.
What Is a Steam Blancher?
A steam blancher uses hot steam to quickly heat vegetables, preserving nutrients and color better than boiling water in a blanching pot. It reduces water absorption, resulting in firmer texture and enhanced flavor retention for dehydrated vegetables.
- Efficient heat transfer - Steam penetrates vegetables rapidly, ensuring even blanching.
- Minimal nutrient loss - Steam blanchers preserve vitamins and antioxidants by avoiding water immersion.
- Reduced waste - Less water usage means lower disposal concerns compared to blanching pots.
How Blanching Pot Works for Dehydration Prep
The blanching pot uses boiling water to quickly heat vegetables, halting enzyme activity and preserving color, texture, and nutrients before dehydration. Immerse vegetables in the pot for a short time, then immediately cool them in ice water to stop cooking and prepare for drying.
This method ensures even heat penetration and softens vegetable fibers, reducing drying time and enhancing shelf life. Temperature control in the blanching pot is critical to avoid overcooking or nutrient loss. Proper blanching improves the final texture and flavor of dehydrated vegetables, making them more appealing and nutritious.
How Steam Blancher Works for Dehydration Prep
A steam blancher uses hot steam to quickly heat vegetables, effectively inactivating enzymes that cause spoilage during dehydration. This method preserves the texture, color, and nutritional value better than boiling in a blanching pot because it minimizes direct water contact. Steam blanching also reduces nutrient leaching and ensures uniform heat distribution, making it ideal for prepping vegetables before dehydration.
Key Differences: Blanching Pot vs Steam Blancher
Blanching pots submerge vegetables in boiling water, ensuring even heat transfer and rapid enzyme deactivation, which is essential for preserving color and texture in dehydrated vegetables. Steam blanchers use hot steam to treat vegetables, reducing nutrient loss and minimizing water absorption compared to water blanching.
Blanching pots require larger water volumes and longer drying times due to moisture retention, while steam blanchers are more energy-efficient and maintain better nutrient profiles. Choosing between these methods depends on the vegetable type and desired dehydration quality, with steam blanchers favored for delicate produce.
Impact on Nutrient Retention in Dehydrated Vegetables
| Blanching Pot | Immerses vegetables in boiling water, causing significant leaching of water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C and B-complex during the blanching process. Nutrient retention in dehydrated vegetables is lower due to water contact. This method may also cause texture softening, affecting final product quality. |
| Steam Blancher | Uses steam to blanch vegetables, minimizing direct water contact and reducing nutrient loss, especially preserving heat-sensitive and water-soluble vitamins. Steam blanching typically results in higher retention of antioxidants and nutrients in dehydrated vegetables. The process maintains firmer texture, enhancing overall vegetable quality post-dehydration. |
Time and Energy Efficiency Comparison
Blanching pots typically require longer heating times and consume more energy due to the need to boil a large volume of water. Steam blanchers heat vegetables faster and more efficiently by directly exposing them to steam, reducing both processing time and energy use.
Steam blanchers maintain nutrient retention better while using less water, making them more sustainable for dehydrating vegetables. The shorter blanching time in steam blanchers enhances overall production speed and lowers operational costs compared to traditional blanching pots.
Best Vegetables for Each Blanching Method
Blanching pots are ideal for vegetables that require full immersion to retain texture, such as green beans and broccoli. Steam blanchers are best suited for delicate or leafy vegetables like spinach and kale, preserving more nutrients.
- Green Beans in Blanching Pot - Submerging green beans in boiling water ensures even heat penetration and crisp texture retention.
- Spinach in Steam Blancher - Gentle steam prevents nutrient loss and reduces waterlogging in delicate spinach leaves.
- Broccoli in Blanching Pot - Full immersion maintains broccoli's vibrant color and firm bite before dehydration.
Related Important Terms
Thermal shock retention
Blanching pots offer direct immersion in boiling water, ensuring rapid heat transfer but risking nutrient leaching, whereas steam blanchers provide gentler heating that minimizes thermal shock, better preserving color and texture in dehydrated vegetables. Steam blanching's controlled temperature environment effectively reduces oxidative enzyme activity while maintaining higher retention of vitamins and antioxidants during dehydration preparation.
Steam basket infusion
Steam blanchers with steam basket infusion preserve nutrients and color better than blanching pots by using gentle, uniform steam exposure that minimizes water contact and nutrient loss. Steam baskets allow for efficient heat distribution and reduce cooking time, enhancing the quality and texture of dehydrated vegetables.
Enzyme inactivation kinetics
Blanching pots use direct hot water immersion, providing uniform heat transfer that rapidly inactivates enzymes but may cause nutrient leaching, whereas steam blanchers apply moist heat with minimal nutrient loss and preserve texture by slowing enzyme inactivation kinetics. Optimizing enzyme inactivation kinetics in steam blanching enhances retention of antioxidants and vitamins critical for quality in dehydrated vegetables.
Nutrient leach minimization
Blanching pots often cause significant nutrient leaching due to prolonged submersion in hot water, leading to loss of water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C and B-complex. Steam blanchers minimize nutrient leach by exposing vegetables to steam rather than boiling water, preserving higher levels of antioxidants and essential minerals during the dehydration prep.
Moister migration control
Steam blanchers offer superior moisture migration control by rapidly heating vegetables with steam, preserving cell structure and minimizing nutrient loss, whereas blanching pots rely on water immersion that can cause excessive moisture absorption and uneven blanching. Efficient moisture control during blanching directly influences drying time and final texture quality in dehydrated vegetables.
Brassica steam blanch protocol
Steam blanchers provide consistent heat application essential for Brassica vegetables, effectively inactivating enzymes and preserving nutrients before dehydration. Unlike blanching pots, steam blanchers minimize water contact, reducing nutrient leaching and improving texture retention in dehydrated Brassica products.
Uniformity yield ratio
A blanching pot often results in uneven heat distribution, causing inconsistent vegetable texture and a lower yield ratio during dehydration. Steam blanchers provide uniform heat and moisture exposure, enhancing vegetable quality and maximizing the yield ratio for dehydrated products.
Micro-batch blanching
Blanching pots offer precise temperature control ideal for micro-batch blanching, preserving nutrient content and color in small vegetable quantities before dehydration. Steam blanchers provide uniform heat distribution with minimal water contact, reducing nutrient leaching and optimizing texture retention in delicate vegetable micro-batches.
Zero-drip transfer method
Blanching pots often require transferring vegetables via zero-drip methods that minimize water retention, preserving texture and nutrient content before dehydration. Steam blanchers inherently use a zero-drip transfer process by steaming vegetables in place, reducing moisture uptake and improving final dehydrated product quality.
Blanching pot vs Steam blancher for prepping dehydrated vegetables Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com