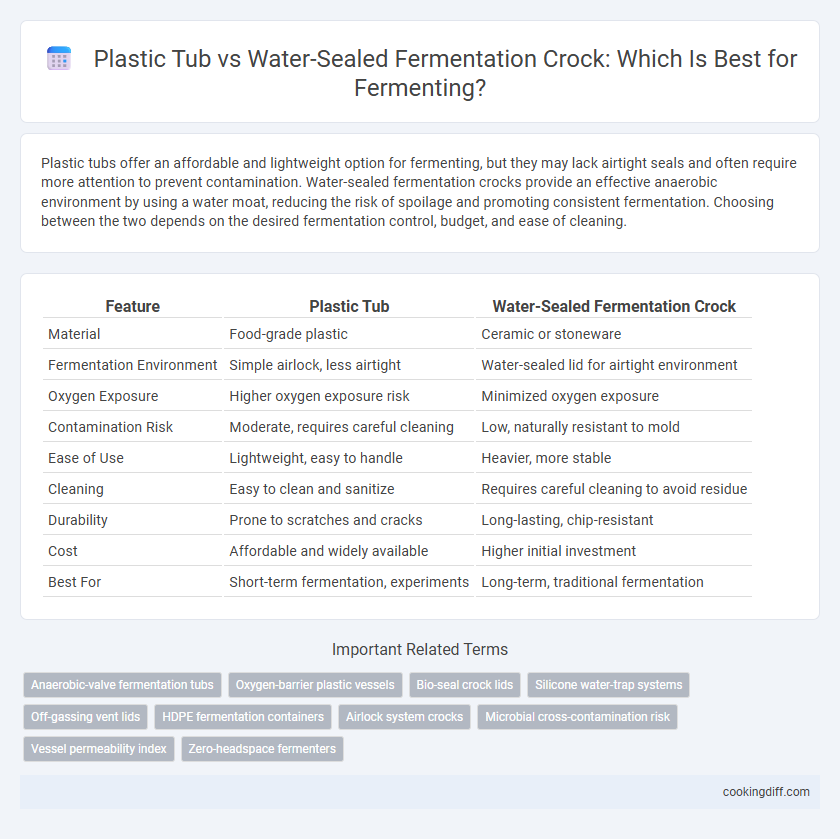
Plastic tubs offer an affordable and lightweight option for fermenting, but they may lack airtight seals and often require more attention to prevent contamination. Water-sealed fermentation crocks provide an effective anaerobic environment by using a water moat, reducing the risk of spoilage and promoting consistent fermentation. Choosing between the two depends on the desired fermentation control, budget, and ease of cleaning.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Plastic Tub | Water-Sealed Fermentation Crock |
|---|---|---|
| Material | Food-grade plastic | Ceramic or stoneware |
| Fermentation Environment | Simple airlock, less airtight | Water-sealed lid for airtight environment |
| Oxygen Exposure | Higher oxygen exposure risk | Minimized oxygen exposure |
| Contamination Risk | Moderate, requires careful cleaning | Low, naturally resistant to mold |
| Ease of Use | Lightweight, easy to handle | Heavier, more stable |
| Cleaning | Easy to clean and sanitize | Requires careful cleaning to avoid residue |
| Durability | Prone to scratches and cracks | Long-lasting, chip-resistant |
| Cost | Affordable and widely available | Higher initial investment |
| Best For | Short-term fermentation, experiments | Long-term, traditional fermentation |
Introduction: Choosing the Right Fermentation Vessel
Choosing the right fermentation vessel is crucial for successful fermenting, as it impacts air exposure, temperature control, and ease of use. Plastic tubs offer affordability and lightweight portability, while water-sealed fermentation crocks provide superior oxygen barriers and traditional craftsmanship.
Plastic tubs are ideal for beginners due to their accessibility and clear material allowing visible fermentation monitoring. Water-sealed crocks maintain an anaerobic environment by trapping gases under a water seal, preventing spoilage and enhancing flavor development. Prioritizing vessel material, size, and sealing method helps achieve consistent, high-quality fermented foods.
Material Matters: Plastic vs Ceramic Construction
Plastic tubs offer lightweight, affordable options for fermentation but can absorb odors and stains over time. Ceramic water-sealed fermentation crocks provide superior durability and a natural barrier against contaminants, enhancing flavor preservation.
- Plastic tubs are porous - They may retain smells and are prone to scratches that harbor bacteria.
- Ceramic crocks maintain temperature - Their thick walls ensure consistent fermentation conditions.
- Water-seal design prevents air exposure - This minimizes mold growth compared to plastic lids.
Airflow and Contamination Risk
Water-sealed fermentation crocks provide a controlled environment that minimizes airflow and reduces contamination risk by creating an anaerobic seal. In contrast, plastic tubs often allow more airflow, which can increase the potential for unwanted bacteria and mold growth during fermentation.
- Water-sealed fermentation crock - Uses a water channel to create an airtight barrier preventing oxygen exposure and limiting contamination.
- Plastic tub fermentation - Typically lacks an airtight seal, allowing more air exchange that could introduce contaminants.
- Contamination risk - Lower in water-sealed crocks due to anaerobic conditions crucial for safe, consistent fermentation.
Water-Sealed Crock: How It Works
The water-sealed fermentation crock uses a unique water lock system to create an anaerobic environment essential for proper fermentation. It prevents oxygen from entering while allowing gases produced during fermentation to escape through the water seal.
- Oxygen Barrier - The water seal blocks oxygen, reducing the risk of mold and spoilage.
- Gas Release - Carbon dioxide generated during fermentation escapes through the water channel to avoid pressure buildup.
- Consistent Environment - The crock maintains stable conditions, promoting optimal fermentation and flavor development.
This design enhances fermentation quality compared to plastic tubs which typically lack effective oxygen barriers and gas release mechanisms.
Pros and Cons of Plastic Tubs for Fermenting
Plastic tubs for fermenting are lightweight and affordable, making them accessible for beginners and easy to handle during the fermentation process. They typically come with lids that help maintain an anaerobic environment, though the seal is not always as reliable as specialized fermentation crocks.
However, plastic tubs can be prone to scratching, which may harbor bacteria and affect the flavor of fermented foods over time. Their non-porous surfaces do not allow for natural carbon dioxide release like water-sealed crocks, sometimes requiring careful monitoring to avoid pressure buildup.
Maintaining Optimal Fermentation Environment
Plastic tubs offer lightweight convenience but may lack consistent airtight sealing required for maintaining an optimal fermentation environment. Water-sealed fermentation crocks create a natural barrier against oxygen and contaminants, preserving anaerobic conditions essential for high-quality fermentation. Ensuring stable temperatures and controlled humidity in water-sealed crocks enhances microbial activity and flavor development during fermentation.
Cleaning and Maintenance: Ease and Safety
Which is easier and safer to clean: a plastic tub or a water-sealed fermentation crock? Plastic tubs are lightweight and dishwasher-safe, making them simple to sanitize quickly but can retain odors over time. Water-sealed crocks require thorough disassembly and hand-washing to prevent mold, but their natural ceramic surface resists scratches and bacterial buildup better than plastic.
Flavor Impact: Do Materials Change the Taste?
Plastic tubs can sometimes impart a slight odor or taste to fermented foods due to chemical leaching, especially if low-quality plastic is used, potentially altering the flavor profile. Water-sealed fermentation crocks, typically made from ceramic, provide a neutral environment that preserves the pure flavors of fermentation without imparting off-notes. The choice of container material directly influences the authenticity and depth of flavor developed during the fermentation process.
Cost, Availability, and Sustainability
Plastic tubs used for fermenting are widely available and generally cost less upfront compared to water-sealed fermentation crocks, making them accessible for beginners and large-batch fermenters. However, plastic may degrade over time and can harbor bacteria if scratched, potentially impacting the quality of fermentation.
Water-sealed fermentation crocks offer a sustainable and reusable option with natural materials like ceramic, promoting eco-friendliness and long-term durability. Their initial cost is higher, and they can be harder to find, but they provide superior fermentation control by preventing oxygen exposure efficiently.
Related Important Terms
Anaerobic-valve fermentation tubs
Anaerobic-valve fermentation tubs provide a controlled environment by allowing gases to escape without letting air in, reducing the risk of contamination compared to traditional plastic tubs. Water-sealed fermentation crocks create an airtight barrier through a water lock, but anaerobic-valve tubs offer easier monitoring and maintenance of optimal anaerobic conditions for consistent fermentation results.
Oxygen-barrier plastic vessels
Plastic tubs designed for fermentation provide an affordable and lightweight option but often lack effective oxygen barriers, which can compromise anaerobic conditions and lead to spoilage. Water-sealed fermentation crocks create a natural airtight seal by submerging ingredients beneath a brine barrier, ensuring optimal anaerobic fermentation and consistent flavor development.
Bio-seal crock lids
Bio-seal crock lids used in water-sealed fermentation crocks create an airtight seal that prevents oxygen and contaminants from entering, promoting safe anaerobic fermentation and preserving beneficial lactobacillus cultures. Plastic tubs lack this water-sealed barrier, increasing the risk of exposure to mold and spoilage, making bio-seal crocks the preferred choice for consistent, high-quality fermentation results.
Silicone water-trap systems
Silicone water-trap systems in water-sealed fermentation crocks create an airtight environment that prevents oxygen and contaminants from entering while allowing gases to escape, significantly reducing the risk of mold and spoilage compared to plastic tubs. Unlike plastic tubs, these crocks maintain consistent fermentation conditions by effectively managing carbon dioxide release through the silicone seal, enhancing flavor development and preserving beneficial probiotic cultures.
Off-gassing vent lids
Plastic tubs with off-gassing vent lids offer a lightweight and affordable option for fermenting, allowing gases to escape while minimizing oxygen exposure to prevent spoilage. Water-sealed fermentation crocks provide a more traditional anaerobic environment through a submerged seal, enhancing flavor development by effectively controlling off-gassing without the risk of leaks.
HDPE fermentation containers
HDPE fermentation containers offer chemical resistance and durability, making them ideal for long-term fermenting without risk of contamination or cracking. Unlike water-sealed crocks, plastic tubs made from HDPE provide a lightweight, affordable option that is easier to clean and less prone to leaks during the fermentation process.
Airlock system crocks
Water-sealed fermentation crocks with airlock systems provide a controlled anaerobic environment that effectively prevents oxygen exposure and contamination, promoting consistent lactic acid fermentation. Plastic tubs often lack built-in airlock mechanisms, increasing the risk of mold growth and uneven fermentation due to variable air exposure.
Microbial cross-contamination risk
Plastic tubs for fermenting pose a higher risk of microbial cross-contamination due to their porous surfaces that can harbor harmful bacteria and are harder to sanitize thoroughly. Water-sealed fermentation crocks provide an airtight environment that minimizes exposure to airborne contaminants and reduces the chance of microbial cross-contamination during the fermentation process.
Vessel permeability index
Plastic tubs for fermenting exhibit higher vessel permeability indexes, allowing more oxygen transfer that may affect anaerobic fermentation stability, while water-sealed fermentation crocks provide a low permeability barrier, maintaining an anaerobic environment crucial for preserving lactic acid bacteria viability. The water seal in fermentation crocks minimizes gas exchange and contamination risks, enhancing flavor development and consistent fermentation outcomes compared to permeable plastic tubs.
Plastic tub vs water-sealed fermentation crock for fermenting. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com