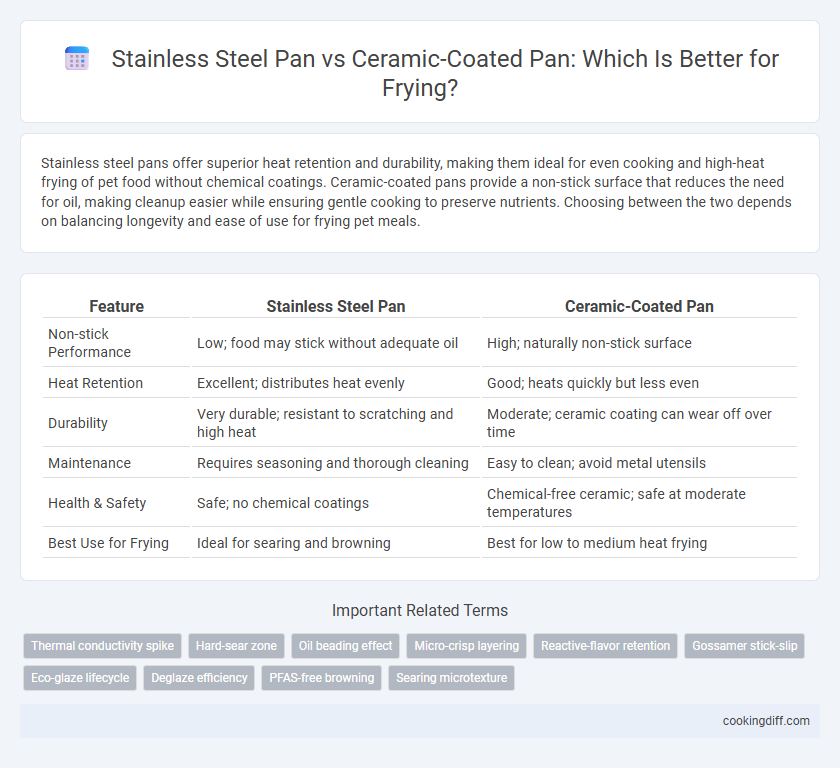
Stainless steel pans offer superior heat retention and durability, making them ideal for even cooking and high-heat frying of pet food without chemical coatings. Ceramic-coated pans provide a non-stick surface that reduces the need for oil, making cleanup easier while ensuring gentle cooking to preserve nutrients. Choosing between the two depends on balancing longevity and ease of use for frying pet meals.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Stainless Steel Pan | Ceramic-Coated Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Non-stick Performance | Low; food may stick without adequate oil | High; naturally non-stick surface |
| Heat Retention | Excellent; distributes heat evenly | Good; heats quickly but less even |
| Durability | Very durable; resistant to scratching and high heat | Moderate; ceramic coating can wear off over time |
| Maintenance | Requires seasoning and thorough cleaning | Easy to clean; avoid metal utensils |
| Health & Safety | Safe; no chemical coatings | Chemical-free ceramic; safe at moderate temperatures |
| Best Use for Frying | Ideal for searing and browning | Best for low to medium heat frying |
Introduction: Comparing Stainless Steel and Ceramic-Coated Pans for Frying
Stainless steel pans offer excellent heat retention and durability, making them ideal for searing and frying at high temperatures. Ceramic-coated pans provide a non-stick surface with easy cleanup but may wear out faster under intense heat.
When frying, stainless steel pans allow for better browning and fond development, which enhances flavor in dishes like steak or vegetables. Ceramic-coated pans require less oil and reduce the risk of food sticking, making them suitable for delicate items like fish or eggs. Choosing between the two depends on cooking style, maintenance preferences, and desired cooking results.
Heat Distribution and Retention in Frying
Stainless steel pans offer superior heat retention due to their dense metal construction, allowing for consistent temperature during frying. The even heat distribution prevents hot spots, ensuring food cooks uniformly and develops a balanced crust.
Ceramic-coated pans excel in quick heat conduction but generally have lower heat retention compared to stainless steel. Their non-reactive surface provides gentle, even cooking, although they may struggle to maintain high temperatures for extended frying sessions.
Nonstick Performance: Stainless Steel vs Ceramic-Coated
Stainless steel pans offer a natural nonstick surface when properly preheated and oiled, while ceramic-coated pans provide an initially slick, chemical-free nonstick layer. Over time, ceramic coatings tend to wear down, reducing their nonstick effectiveness compared to the durable surface of stainless steel.
- Durability - Stainless steel maintains nonstick properties longer due to its solid metal surface.
- Coating wear - Ceramic coatings degrade with use and high heat, affecting performance.
- Maintenance - Stainless steel requires seasoning and proper technique to prevent sticking.
Oil Usage and Food Release While Frying
Stainless steel pans require more oil to prevent food from sticking due to their less non-stick surface compared to ceramic-coated pans. Ceramic-coated pans allow for healthier cooking with minimal oil usage because their smooth, non-porous surface enhances food release. While stainless steel excels at browning and searing, ceramic-coated pans offer easier cleanup and consistent non-stick performance during frying.
Durability and Scratch Resistance in Frying Applications
Which pan offers better durability and scratch resistance for frying: stainless steel or ceramic-coated? Stainless steel pans excel in durability and resist scratches effectively, making them ideal for frequent frying with metal utensils. Ceramic-coated pans, while non-stick and easy to clean, tend to wear down and scratch more quickly under high-heat frying conditions.
Maintenance and Cleaning After Frying
Stainless steel pans require thorough cleaning to remove food residues and prevent discoloration, often needing scrubbing with abrasive pads. Ceramic-coated pans are easier to clean due to their non-stick surface, which resists food sticking and simplifies maintenance.
- Durability - Stainless steel withstands high-temperature scrubbing better than ceramic coatings that can wear off.
- Cleaning method - Ceramic pans usually require gentle sponges and avoid metal utensils, unlike stainless steel.
- Residue removal - Stainless steel may need soaking or stainless steel cleaners to remove burnt-on food, whereas ceramic coatings typically rinse clean with mild detergent.
Safety and Health Concerns: Coatings and Materials
Stainless steel pans are praised for their durability and non-reactive surface, making them a safe choice that doesn't release harmful chemicals during frying. Ceramic-coated pans feature a non-stick surface derived from inorganic materials, reducing the need for excessive oil and lowering health risks associated with traditional non-stick coatings. Both options avoid toxic substances like PFOA and PTFE, but stainless steel requires proper oiling to prevent sticking, ensuring safer cooking temperatures and minimizing potential health concerns.
Versatility for Different Frying Techniques
Stainless steel pans offer excellent versatility for various frying techniques, including searing, sauteing, and deglazing, due to their high heat tolerance and durability. They maintain consistent heat, making them ideal for achieving crispy textures and browning.
Ceramic-coated pans excel in non-stick frying and are perfect for delicate foods like eggs and fish, requiring less oil and easier cleanup. However, they are less suited for high-heat searing or techniques that demand metal utensils, as the coating can degrade over time.
Price Comparison and Long-Term Value
Stainless steel pans generally have a higher initial cost compared to ceramic-coated pans, but their durability often leads to better long-term value. Ceramic-coated pans are more affordable upfront but may require replacement sooner due to coating wear over time.
- Cost Efficiency - Stainless steel pans, despite a higher price, last longer making them cost-effective in the long run.
- Upfront Price - Ceramic-coated pans offer a budget-friendly option for immediate purchase.
- Durability - Stainless steel resists scratches and high heat, preserving its functionality over years of use.
Choosing between the two depends on balancing initial cost with expected longevity and maintenance.
Related Important Terms
Thermal conductivity spike
Stainless steel pans exhibit a rapid thermal conductivity spike, allowing for quick heat retention and even frying surfaces, which prevents hotspots and ensures consistent browning. Ceramic-coated pans, however, have a slower thermal response with lower conductivity, resulting in more gradual heat changes that reduce the risk of burning but may lead to uneven frying temperatures.
Hard-sear zone
Stainless steel pans excel in creating a hard-sear zone due to their superior heat retention and even distribution, allowing for precise temperature control and enhanced browning of foods. Ceramic-coated pans offer non-stick properties but typically generate a softer sear zone because their heat conductivity is less efficient compared to stainless steel.
Oil beading effect
Stainless steel pans tend to exhibit minimal oil beading due to their smooth, non-porous surface, promoting even heat distribution and consistent frying results. Ceramic-coated pans often show pronounced oil beading, which can enhance non-stick properties but might cause uneven heat transfer and localized frying inconsistencies.
Micro-crisp layering
Stainless steel pans excel in achieving micro-crisp layering due to their superior heat conductivity and ability to maintain high temperatures without coating breakdown, resulting in even browning and a distinct crunch. Ceramic-coated pans provide a non-stick surface that requires less oil, but their lower heat tolerance often limits micro-crisp texture development compared to stainless steel counterparts.
Reactive-flavor retention
Stainless steel pans excel at reactive-flavor retention due to their non-porous surface that does not interact with acidic or alkaline ingredients, preserving the original taste of food during frying. Ceramic-coated pans offer a non-reactive surface as well, but their porous nature can sometimes trap oils and flavors, potentially altering the seasoning profile over time.
Gossamer stick-slip
Stainless steel pans often exhibit gossamer stick-slip behavior during frying, causing uneven food release and requiring precise temperature control to minimize adhesion. Ceramic-coated pans provide a smoother non-stick surface that reduces gossamer stick-slip effects, enhancing consistent food release and easier cleanup.
Eco-glaze lifecycle
Stainless steel pans offer durability and resistance to wear but often require more oil for frying, whereas ceramic-coated pans, featuring an eco-glaze lifecycle, minimize the need for fats and release fewer toxins due to their non-stick, eco-friendly surface. The eco-glaze coating extends the pan's lifespan by reducing surface degradation and environmental impact compared to traditional non-stick options.
Deglaze efficiency
Stainless steel pans excel in deglazing as their non-porous surface allows for easy caramelization and release of fond, enhancing sauce flavor intensity. Ceramic-coated pans tend to retain residue due to their smoother, less reactive surface, which can reduce deglaze efficiency and flavor depth.
PFAS-free browning
Stainless steel pans offer excellent PFAS-free browning by allowing high heat retention and even cooking without chemical coatings, making them ideal for searing and frying. Ceramic-coated pans provide a naturally non-stick surface free from PFAS chemicals but may not achieve the same high-temperature browning due to their lower heat tolerance.
Stainless steel pan vs Ceramic-coated pan for frying. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com