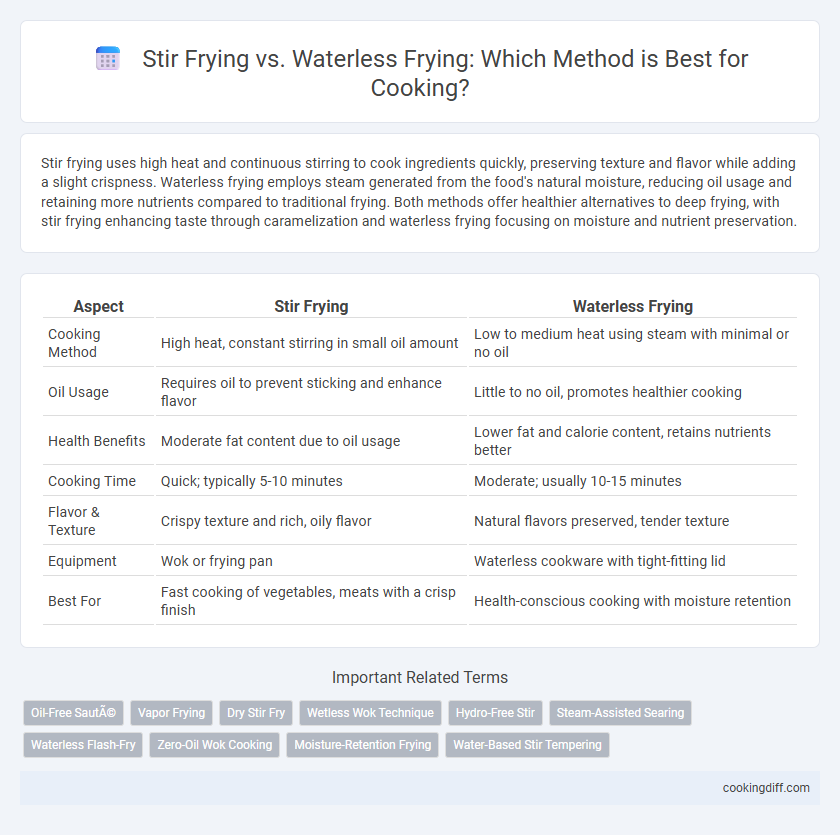
Stir frying uses high heat and continuous stirring to cook ingredients quickly, preserving texture and flavor while adding a slight crispness. Waterless frying employs steam generated from the food's natural moisture, reducing oil usage and retaining more nutrients compared to traditional frying. Both methods offer healthier alternatives to deep frying, with stir frying enhancing taste through caramelization and waterless frying focusing on moisture and nutrient preservation.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Stir Frying | Waterless Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | High heat, constant stirring in small oil amount | Low to medium heat using steam with minimal or no oil |
| Oil Usage | Requires oil to prevent sticking and enhance flavor | Little to no oil, promotes healthier cooking |
| Health Benefits | Moderate fat content due to oil usage | Lower fat and calorie content, retains nutrients better |
| Cooking Time | Quick; typically 5-10 minutes | Moderate; usually 10-15 minutes |
| Flavor & Texture | Crispy texture and rich, oily flavor | Natural flavors preserved, tender texture |
| Equipment | Wok or frying pan | Waterless cookware with tight-fitting lid |
| Best For | Fast cooking of vegetables, meats with a crisp finish | Health-conscious cooking with moisture retention |
Introduction to Stir Frying and Waterless Frying
Stir frying is a high-heat cooking technique that uses a small amount of oil to quickly cook bite-sized ingredients, preserving texture and flavor. Waterless frying relies on the natural moisture of food and closed cookware to cook without added fats, promoting healthier meals with fewer calories. Both methods offer distinct benefits for preparing vegetables, meats, and seafood efficiently while enhancing nutrient retention.
Core Principles of Stir Frying
| Core Principles of Stir Frying |
| Stir frying relies on high heat, continuous stirring, and small, uniform ingredient pieces to ensure quick, even cooking while preserving texture and flavor. The method uses minimal oil to create a non-stick surface and to enhance the Maillard reaction, which develops complex flavors through caramelization. In contrast to waterless frying, which uses steam and lower temperatures, stir frying emphasizes fast cooking over direct heat for maximum crispness and color. |
Understanding Waterless Frying Techniques
Waterless frying uses the natural moisture in food to cook without added oils, preserving nutrients and flavors better than traditional stir frying. This technique requires non-stick cookware or heavy pans to prevent sticking and allows food to steam in its own juices at lower temperatures.
- Moisture Retention - Waterless frying retains vitamins and minerals by avoiding oil and high heat that typically degrade nutrients.
- Equipment Requirements - Specialized non-stick pans or heavy-bottomed cookware are essential to maintain moisture and prevent burning during waterless frying.
- Temperature Control - Lower cooking temperatures minimize nutrient loss and help evenly cook food using the steam generated from the food's own water content.
Key Differences Between Stir Frying and Waterless Frying
What are the key differences between stir frying and waterless frying in cooking? Stir frying involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil at high heat, ensuring crisp textures and rapid browning. Waterless frying uses moisture from the food itself and minimal or no added water, focusing on preserving nutrients and natural flavors without added fats.
Equipment Needed for Each Method
Stir frying requires a wok or a large, heavy-bottomed skillet to ensure even heat distribution and quick cooking at high temperatures. Waterless frying utilizes specially designed pans with tight-fitting lids and nonstick surfaces to cook food using its own moisture without added water or oil.
- Wok for Stir Frying - A round-bottomed wok allows rapid heat conduction and easy tossing of ingredients.
- Heavy-Bottomed Skillet - Essential for maintaining high and steady heat during stir frying.
- Waterless Frying Pan - Equipped with a sealed lid and nonstick surface to retain moisture and cook food gently.
Choosing the right equipment enhances cooking efficiency and flavor retention in each frying method.
Types of Foods Best Suited for Stir Frying
Stir frying is best suited for small, uniformly cut pieces of vegetables, lean meats, and seafood that cook quickly and retain their texture. Foods like bell peppers, broccoli, snap peas, chicken breast, and shrimp excel in stir frying due to the high heat and short cooking time. These ingredients benefit from the rapid searing that preserves nutrients and enhances flavor while maintaining a crisp-tender bite.
Foods Ideal for Waterless Frying
Waterless frying is ideal for cooking delicate vegetables such as zucchini, spinach, and mushrooms, which retain their nutrients and texture without requiring added fats. This method uses the natural moisture of the food, making it perfect for lean proteins like chicken breast and fish fillets that benefit from gentle cooking.
In contrast, stir frying suits tougher vegetables like bell peppers and broccoli, which require high heat for a short time to stay crisp. Stir frying also enhances the flavors of marinated meats and tofu by quickly searing their surfaces.
Nutritional Impact: Stir Frying vs Waterless Frying
Stir frying preserves vitamins and minerals by using high heat for a short duration, which minimizes nutrient loss. Waterless frying utilizes the natural moisture of foods, reducing oil usage and retaining more antioxidants and water-soluble vitamins.
- Higher nutrient retention in stir frying - Rapid cooking at high temperatures helps maintain vitamin C and B-complex levels.
- Reduced fat absorption in waterless frying - Cooking without added oil lowers overall calorie content and saturated fat intake.
- Enhanced antioxidant preservation in waterless frying - Minimal oxidation preserves polyphenols and flavonoids crucial for health.
Flavor Profiles and Texture Comparison
Stir frying enhances flavor profiles by quickly searing ingredients at high heat, which caramelizes sugars and preserves crunchy textures in vegetables and meats. Waterless frying, relying on the natural moisture of ingredients without added oil, tends to produce a more delicate flavor and softer texture due to gentle cooking.
Stir frying creates a vibrant, complex taste through Maillard reactions and retains a crisp bite, ideal for dishes with distinct ingredient contrasts. Waterless frying emphasizes the pure, intrinsic flavors of food, often resulting in a juicier but less crispy texture. Choosing between these methods depends on whether a bold, crunchy experience or a tender, subtle flavor is desired in the final dish.
Related Important Terms
Oil-Free Sauté
Stir frying uses high heat with a small amount of oil to quickly cook vegetables and proteins, preserving texture and flavor, while waterless frying relies on the natural moisture in food to saute without oil, promoting healthier, low-fat meals. Oil-free saute techniques enhance nutrient retention and reduce calorie intake by eliminating added fats.
Vapor Frying
Vapor frying, a subset of waterless frying, uses the natural moisture in food to create steam that cooks ingredients quickly while preserving nutrients and flavor without added oils. Stir frying typically requires higher heat and oil to achieve a crispy texture, whereas vapor frying emphasizes gentle steam heat for healthier, lower-fat dishes.
Dry Stir Fry
Dry stir frying uses minimal oil and high heat to quickly cook vegetables and proteins, preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors through rapid searing. Unlike waterless frying that relies on steam and moisture retention, dry stir frying ensures a crisp texture and caramelization without added liquids.
Wetless Wok Technique
Waterless frying using the wetless wok technique enhances flavor retention by cooking vegetables at high heat without added water or oil, preserving nutrients and natural textures. This method contrasts with traditional stir frying by minimizing moisture loss and oxidation, resulting in vibrant, crisp dishes with concentrated taste and improved health benefits.
Hydro-Free Stir
Hydro-free stir frying uses minimal oil and high heat to cook food quickly while preserving nutrients and texture, unlike traditional stir frying that may involve more oil and moisture. This method enhances flavors through rapid caramelization and reduces calorie intake by avoiding water or oil-based cooking fluids.
Steam-Assisted Searing
Steam-assisted searing enhances stir frying by rapidly cooking ingredients while locking in moisture, resulting in crisp, flavorful textures without added oils. Waterless frying uses the natural moisture from food, steaming and searing simultaneously, which preserves nutrients and creates a healthier, evenly cooked dish.
Waterless Flash-Fry
Waterless flash-fry cooking uses minimal or no oil, relying on high heat and steam from the food's natural moisture to quickly cook ingredients while preserving nutrients and flavors. This method contrasts with traditional stir frying, which typically uses more oil and constant stirring to prevent burning and ensure even cooking.
Zero-Oil Wok Cooking
Stir frying uses high heat and small amounts of oil to quickly cook food, preserving texture and flavor, while waterless frying relies on steam and the natural moisture of ingredients to cook without oil, ideal for zero-oil wok cooking that promotes healthier meals with fewer calories. Zero-oil wok cooking enhances nutrient retention and reduces fat intake, making waterless frying a superior technique for health-conscious culinary practices.
Moisture-Retention Frying
Stir frying uses high heat and constant stirring to quickly cook food, preserving texture while allowing some moisture evaporation for crispness. Waterless frying relies on the natural moisture of ingredients, cooking at lower temperatures to retain maximum juices and nutrients, resulting in juicier, more flavorful dishes.
Stir Frying vs Waterless Frying for Cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com