Stovetop frying provides direct heat through gas or electric burners, allowing precise temperature control and a traditional cooking experience. Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, resulting in faster heating, improved energy efficiency, and safer surface temperatures. Both methods offer distinct advantages, with induction providing speed and safety, while stovetop frying delivers familiar control and versatility.
Table of Comparison
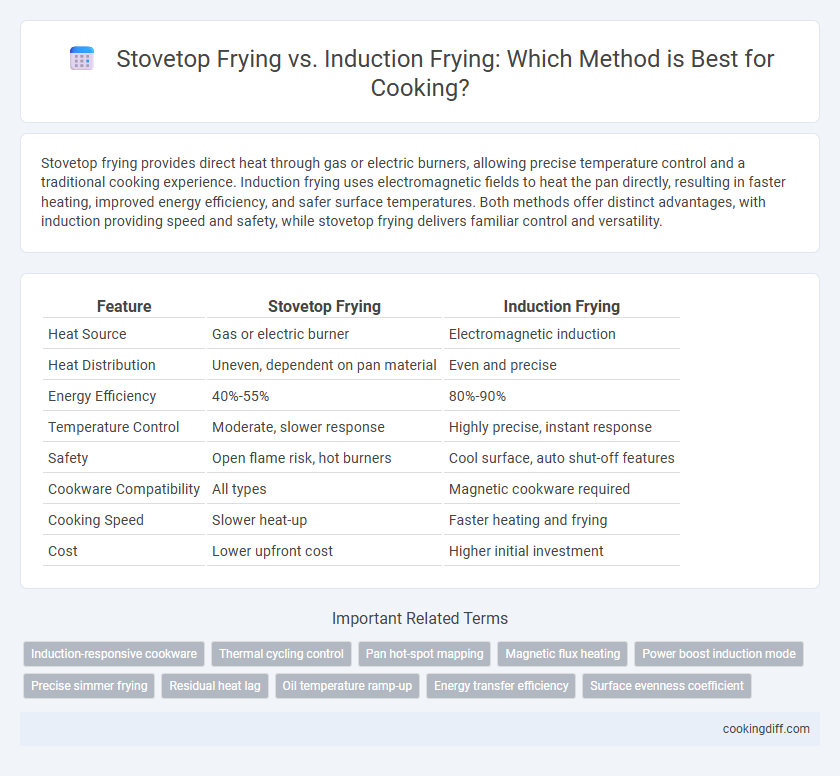
| Feature | Stovetop Frying | Induction Frying |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Gas or electric burner | Electromagnetic induction |
| Heat Distribution | Uneven, dependent on pan material | Even and precise |
| Energy Efficiency | 40%-55% | 80%-90% |
| Temperature Control | Moderate, slower response | Highly precise, instant response |
| Safety | Open flame risk, hot burners | Cool surface, auto shut-off features |
| Cookware Compatibility | All types | Magnetic cookware required |
| Cooking Speed | Slower heat-up | Faster heating and frying |
| Cost | Lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
Introduction to Stovetop and Induction Frying
What are the main differences between stovetop frying and induction frying methods? Stovetop frying uses direct heat from gas or electric burners, allowing precise temperature control with visible flames or heating elements. Induction frying utilizes electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, offering faster heating times and increased energy efficiency during cooking.
How Stovetop Frying Works
Stovetop frying involves heating a pan directly on a gas or electric burner, where heat transfers through conduction to cook food evenly. The temperature is controlled by adjusting the burner's flame or heat setting, allowing for precise frying conditions. This method relies on surface contact between the pan and the heat source to generate the high temperatures essential for frying techniques like sauteing or searing.
How Induction Frying Works
Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to directly heat pots and pans, providing rapid and precise temperature control. Unlike stovetop frying, it heats the cookware itself rather than relying on a flame or electric coil.
When an induction cooktop is activated, alternating current passes through a coil beneath the cooking surface, creating a magnetic field that induces an electric current in the ferromagnetic cookware. This current generates heat within the pan, allowing for efficient energy transfer and consistent cooking temperatures. Induction frying reduces heat loss and provides faster response times compared to traditional stovetop methods.
Heat Distribution and Temperature Control
Induction frying offers superior heat distribution by directly heating the cookware, resulting in more even cooking compared to traditional stovetop frying. Temperature control is more precise with induction, allowing for rapid adjustments and consistent heat levels throughout the cooking process.
- Heat Distribution - Induction frying evenly distributes heat across the pan due to electromagnetic energy, minimizing hotspots common in stovetop cooking.
- Temperature Control - Induction cooktops provide immediate and accurate temperature adjustments, enhancing cooking precision.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction frying is more energy-efficient by transferring heat directly to the pan, reducing energy loss.
Choosing induction frying improves cooking performance through enhanced heat distribution and precise temperature management.
Energy Efficiency Comparison
Stovetop frying typically uses more energy as it relies on gas or electric coil elements, which lose heat during transfer. Induction frying offers superior energy efficiency by directly heating the cookware through electromagnetic fields, minimizing heat loss.
Induction cooktops can convert about 85-90% of energy into heat for cooking, whereas conventional stovetops convert only around 40-55%. This higher efficiency reduces cooking time and overall energy consumption, making induction frying a more sustainable choice.
Safety Features and Considerations
Stovetop frying requires careful monitoring of open flames and hot surfaces to prevent burns and kitchen fires, with many models featuring flame failure devices for enhanced safety. Induction frying offers a safer alternative by using electromagnetic fields to heat cookware directly, significantly reducing the risk of accidental burns and eliminating open flames. Both methods benefit from using heat-resistant utensils and proper ventilation to maintain a safe cooking environment.
Cooking Results: Texture, Taste, and Consistency
Stovetop frying provides a traditional cooking experience with direct heat, often resulting in a crispy texture and rich flavor profile. Induction frying offers precise temperature control, enhancing consistency and reducing the risk of burning or uneven cooking.
- Texture - Stovetop frying tends to create a more varied texture due to fluctuating heat levels, ideal for foods requiring a crisp outer layer.
- Taste - Induction frying preserves delicate flavors better by maintaining steady temperatures, preventing overcooking and bitterness.
- Consistency - Induction frying excels in delivering uniform cooking results through precise heat regulation, ensuring even browning and moisture retention.
Suitable Cookware for Stovetop vs. Induction
Stovetop frying is compatible with a wide range of cookware, including stainless steel, cast iron, and aluminum pans. These materials distribute heat evenly but may require thicker bottoms to avoid hotspots on gas or electric burners.
Induction frying demands ferromagnetic cookware such as cast iron or magnetic stainless steel to generate heat through electromagnetic fields. Non-ferrous materials like aluminum or copper require induction-compatible bases for efficient cooking.
Maintenance and Cleaning Differences
| Stovetop Frying | Requires regular scrubbing to remove grease buildup on burners; glass or ceramic surfaces may crack if cleaning is too abrasive. |
| Induction Frying | Features a smooth, flat surface that is easier to wipe clean; no open flames reduce soot and grease accumulation, minimizing maintenance. |
Related Important Terms
Induction-responsive cookware
Induction frying offers precise temperature control and faster heat response due to electromagnetic technology, requiring cookware made from ferromagnetic materials such as cast iron or stainless steel. Only induction-responsive cookware can efficiently transfer heat on induction stovetops, enhancing cooking performance and energy efficiency compared to traditional stovetop frying methods.
Thermal cycling control
Stovetop frying offers less precise thermal cycling control, causing temperature fluctuations that may lead to uneven cooking or burning, while induction frying provides rapid and consistent heat adjustments through electromagnetic energy for precise temperature regulation. This precise thermal cycling capability in induction cooking enhances energy efficiency and improves food quality by maintaining stable heat levels throughout the frying process.
Pan hot-spot mapping
Stovetop frying often results in uneven pan hot-spots due to direct flame contact, causing inconsistent cooking temperatures across the surface. Induction frying provides uniform heat distribution by generating heat directly within the pan's material, minimizing hot-spot formation and ensuring consistent cooking performance.
Magnetic flux heating
Stovetop frying using traditional gas or electric burners relies on direct heat transfer, whereas induction frying utilizes magnetic flux to generate heat directly within the cookware, resulting in faster and more energy-efficient cooking. Magnetic flux heating creates an electromagnetic field that induces eddy currents in ferromagnetic pans, providing precise temperature control and reduced heat loss compared to conventional stovetop methods.
Power boost induction mode
Power boost induction mode delivers rapid, intense heat directly to cookware, enabling faster stovetop frying with precise temperature control compared to traditional electric or gas stovetops. This efficient energy transfer reduces cooking time and enhances browning and crisping, making induction frying superior for quick and consistent results.
Precise simmer frying
Induction frying offers precise temperature control for simmer frying, maintaining consistent low heat ideal for delicate sauces and gentle cooking. Stovetop frying on gas or electric burners often lacks this exact temperature accuracy, which can lead to uneven cooking or overheating during simmering.
Residual heat lag
Stovetop frying often experiences significant residual heat lag due to the slower cooling of traditional burners, which can lead to overcooking or uneven temperature control. Induction frying offers precise heat management with minimal residual heat lag, as the cookware itself heats directly through electromagnetic induction, allowing for faster cooldown and improved cooking accuracy.
Oil temperature ramp-up
Stovetop frying relies on direct flame or electric coil heat, resulting in a variable oil temperature ramp-up that depends on burner power and pan material, often leading to slower and less consistent heating. Induction frying uses electromagnetic fields to heat the pan quickly and uniformly, enabling faster and more precise oil temperature control, which improves cooking efficiency and food quality.
Energy transfer efficiency
Induction frying offers significantly higher energy transfer efficiency, typically around 80-90%, by using electromagnetic fields to directly heat the cookware, minimizing heat loss compared to stovetop frying, which usually transfers only 40-55% of energy through gas or electric coils. This efficient energy use results in faster cooking times and reduced energy consumption, making induction frying more cost-effective and environmentally friendly than traditional stovetop methods.
Stovetop frying vs induction frying for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com