Sauteing involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil or fat, which enhances flavor and promotes browning through the Maillard reaction. Oil-free sauteing uses alternative methods such as water or broth to cook ingredients, reducing fat content but often resulting in less browning and a different texture. Choosing between these techniques depends on dietary preferences and desired flavor intensity.
Table of Comparison
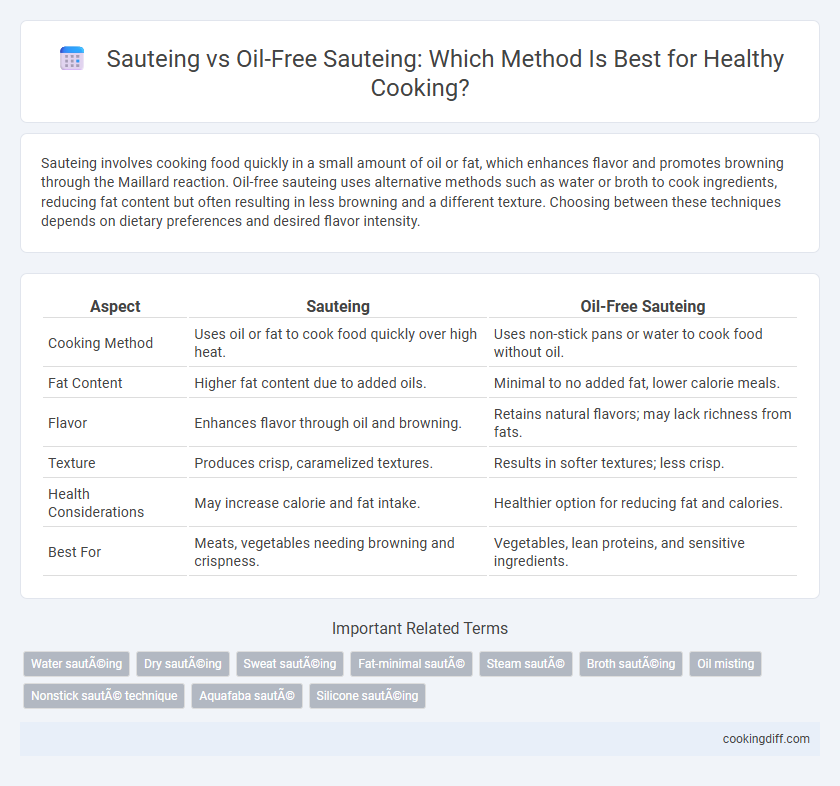
| Aspect | Sauteing | Oil-Free Sauteing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Uses oil or fat to cook food quickly over high heat. | Uses non-stick pans or water to cook food without oil. |
| Fat Content | Higher fat content due to added oils. | Minimal to no added fat, lower calorie meals. |
| Flavor | Enhances flavor through oil and browning. | Retains natural flavors; may lack richness from fats. |
| Texture | Produces crisp, caramelized textures. | Results in softer textures; less crisp. |
| Health Considerations | May increase calorie and fat intake. | Healthier option for reducing fat and calories. |
| Best For | Meats, vegetables needing browning and crispness. | Vegetables, lean proteins, and sensitive ingredients. |
Understanding Sautéing: Traditional Techniques
Sauteing traditionally involves cooking food quickly in a small amount of oil or fat over high heat, which enhances flavor through caramelization. Oil-free sauteing utilizes alternative methods like water or broth to prevent sticking, focusing on retaining natural food flavors without added fats.
- Heat Control - Maintaining high heat is crucial in traditional sauteing to achieve proper browning and texture.
- Fat Usage - Traditional techniques rely on oil or butter to conduct heat and develop rich flavors.
- Moisture Management - Oil-free sauteing avoids added fats by managing moisture to prevent sticking and preserve nutrients.
What is Oil-Free Sautéing?
Oil-free sauteing involves cooking food quickly over high heat without the use of oil or fat. This method relies on natural moisture from vegetables or minimal added liquids to prevent sticking and promote even cooking.
Unlike traditional sauteing, which uses oil to enhance flavor and texture, oil-free sauteing is ideal for those seeking lower calorie and heart-healthy meals. Techniques such as using non-stick pans, stirring frequently, and adding small amounts of water or broth help maintain food's texture and taste. This approach preserves the natural flavors and nutrients of ingredients while reducing fat intake.
Key Differences: Sautéing with Oil vs Without Oil
| Aspect | Sauteing with Oil | Oil-Free Sauteing |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Medium | Uses oil or fat to prevent sticking and enhance flavor | Relies on water, broth, or steam to cook without added fat |
| Flavor | Offers rich, enhanced taste due to oil's flavor absorption and browning | Maintains natural flavors with less richness, often lighter taste |
| Health Aspects | Increases calorie content due to added fats but provides essential fatty acids | Lower calorie and fat content, supporting low-fat diet goals |
| Cooking Technique | Requires moderate to high heat with frequent stirring to avoid burning | Uses lower heat and more moisture to prevent sticking and ensure even cooking |
| Texture | Produces crispy, browned exterior with tender interiors | Results in softer textures with less browning and a steamed consistency |
Health Impact: Oil-Free Sautéing Compared to Classic Sautéing
Oil-free sauteing reduces calorie intake and lowers exposure to unhealthy fats compared to classic sauteing, which typically uses oils high in saturated and trans fats. This method preserves the natural nutrients of vegetables while minimizing the risk of inflammation associated with excessive oil consumption.
- Lower Caloric Density - Oil-free sauteing eliminates added fats, significantly reducing the calorie content of dishes.
- Reduced Inflammatory Risk - Avoiding oils high in omega-6 fatty acids helps decrease inflammation linked to certain chronic diseases.
- Enhanced Nutrient Retention - Cooking without oil preserves heat-sensitive vitamins and antioxidants in vegetables more effectively.
Flavor Profile: How Oil Affects Taste and Texture
How does oil influence the flavor and texture in sauteing compared to oil-free methods? Oil enhances the taste by carrying fat-soluble flavors and creating a richer, more complex profile, while also promoting a crisp, golden-brown texture through Maillard reactions. In contrast, oil-free sauteing preserves the natural moisture of ingredients but may result in a softer texture and a less intense flavor development.
Best Ingredients for Oil-Free Sautéing
Sauteing with oil enhances flavor and promotes even browning, while oil-free sauteing relies on moisture-rich ingredients like mushrooms, zucchini, and bell peppers to prevent sticking and maintain texture. Using non-stick cookware or a well-seasoned cast iron pan is essential for oil-free sauteing to ensure ingredients cook evenly without burning. Incorporating vegetable broth or water can also aid in deglazing and keeping ingredients tender during oil-free sauteing.
Equipment and Tools for Effective Sautéing
Choosing the right equipment is crucial for both traditional sauteing and oil-free sauteing methods to ensure even cooking and prevent sticking. Non-stick pans and stainless steel skillets are preferred tools, while a good spatula aids in proper food turning and sauteing control.
- Non-stick pans - Provide a smooth surface crucial for oil-free sauteing to prevent ingredients from sticking and burning.
- Stainless steel skillets - Offer excellent heat distribution important for traditional sauteing with oil, enhancing flavor development.
- Heat-resistant spatulas - Allow careful turning and stirring of food without scratching cookware, improving cooking efficiency.
Proper selection and maintenance of sauteing equipment optimize cooking results and preserve the quality of ingredients.
Step-by-Step Guide: Sautéing with Oil
Sauteing with oil involves heating a small amount of oil in a pan over medium-high heat before adding ingredients for quick cooking that enhances flavor and texture. Common oils used include olive oil, canola oil, and avocado oil, chosen for their high smoke points and health benefits. Proper technique includes preheating the oil until shimmering, stirring frequently to prevent burning, and ensuring even heat distribution for optimal sauteing results.
Step-by-Step Guide: Oil-Free Sautéing
Begin oil-free sauteing by preheating a nonstick or well-seasoned cast-iron skillet over medium heat to ensure even cooking without sticking. Add chopped vegetables directly to the hot pan, stirring frequently to prevent burning and promote uniform caramelization.
Use a small amount of water or vegetable broth to deglaze the pan when ingredients start to dry out, which helps maintain moisture and enhances flavor without oil. Cook until vegetables are tender and lightly browned, approximately 5-7 minutes depending on the type and size of the pieces.
Related Important Terms
Water sautéing
Water sauteing uses water or broth instead of oil, reducing fat content while still achieving tender, flavorful vegetables through high-heat cooking. This technique is ideal for health-conscious individuals seeking low-calorie alternatives without sacrificing the caramelization and texture typical of traditional oil sauteing.
Dry sautéing
Dry sauteing, a technique involving cooking food in a hot pan without oil, preserves the natural flavors and nutrients while reducing calorie intake compared to traditional oil-based sauteing. This method relies on controlled heat and frequent stirring to prevent sticking and achieve even browning, making it ideal for vegetables and lean proteins.
Sweat sautéing
Sweat sauteing involves cooking vegetables gently over low heat with a small amount of fat to release moisture and enhance flavor without browning, contrasting with oil-free sauteing which relies solely on water or broth to prevent sticking but may lack the rich taste developed by fat. The presence of oil in sweat sauteing aids in dissolving fat-soluble nutrients and achieving a tender texture, whereas oil-free methods prioritize minimal fat intake and reduced calories.
Fat-minimal sauté
Fat-minimal sauteing uses a small amount of healthy oils like olive or avocado oil to enhance flavor and texture while reducing overall fat content compared to traditional sauteing that often requires more oil or butter. Oil-free sauteing relies on techniques such as steaming or using non-stick cookware to cook ingredients without added fats, preserving the natural taste and nutrients with minimal calorie intake.
Steam sauté
Steam saute uses minimal oil and relies on steam to cook food quickly, preserving nutrients and enhancing natural flavors compared to traditional sauteing, which often requires more oil and higher temperatures. This method is particularly beneficial for delicate vegetables, maintaining texture while reducing calorie intake and promoting healthier meals.
Broth sautéing
Broth sauteing uses flavorful liquid instead of oil to cook vegetables and proteins, enhancing moisture and reducing fat content while preserving texture and nutrients. This oil-free technique offers a healthier alternative to traditional sauteing by minimizing added calories and promoting a lighter, more vibrant dish.
Oil misting
Oil misting in sauteing creates a thin, even layer of fat that promotes efficient heat transfer and prevents food from sticking, preserving texture and flavor while reducing overall oil usage. In oil-free sauteing, the absence of oil misting requires precise temperature control and the use of non-stick surfaces or moisture-rich ingredients to prevent sticking and achieve similar browning effects.
Nonstick sauté technique
Nonstick sauteing utilizes high-quality nonstick pans allowing food to cook evenly with minimal or no oil, preserving natural flavors and reducing fat intake. This oil-free technique enhances browning and texture by preventing food from sticking, making it ideal for healthier meal preparation without sacrificing taste or texture.
Aquafaba sauté
Aquafaba saute uses the viscous liquid from cooked legumes as a fat substitute, providing moisture and binding without added oils, making it ideal for oil-free sauteing while preserving flavor and texture. This method enhances nutrient retention and reduces calorie intake compared to traditional oil-based sauteing, appealing to health-conscious and vegan cooks.
Sautéing vs Oil-Free Sautéing for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com