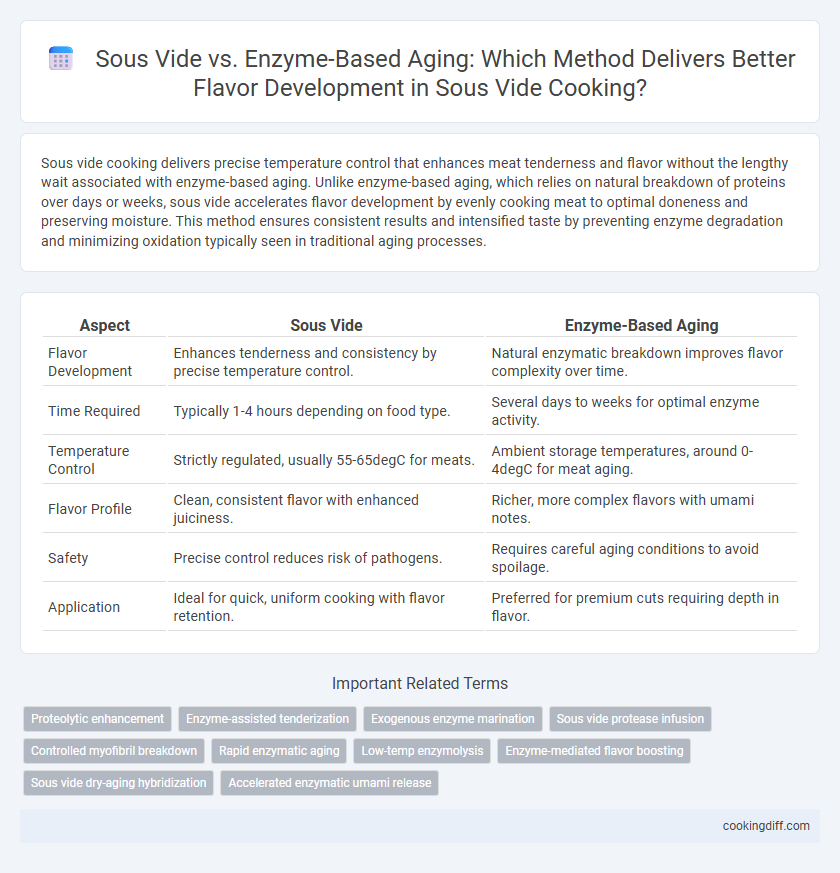
Sous vide cooking delivers precise temperature control that enhances meat tenderness and flavor without the lengthy wait associated with enzyme-based aging. Unlike enzyme-based aging, which relies on natural breakdown of proteins over days or weeks, sous vide accelerates flavor development by evenly cooking meat to optimal doneness and preserving moisture. This method ensures consistent results and intensified taste by preventing enzyme degradation and minimizing oxidation typically seen in traditional aging processes.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Sous Vide | Enzyme-Based Aging |
|---|---|---|
| Flavor Development | Enhances tenderness and consistency by precise temperature control. | Natural enzymatic breakdown improves flavor complexity over time. |
| Time Required | Typically 1-4 hours depending on food type. | Several days to weeks for optimal enzyme activity. |
| Temperature Control | Strictly regulated, usually 55-65degC for meats. | Ambient storage temperatures, around 0-4degC for meat aging. |
| Flavor Profile | Clean, consistent flavor with enhanced juiciness. | Richer, more complex flavors with umami notes. |
| Safety | Precise control reduces risk of pathogens. | Requires careful aging conditions to avoid spoilage. |
| Application | Ideal for quick, uniform cooking with flavor retention. | Preferred for premium cuts requiring depth in flavor. |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Enzyme-Based Aging
Sous vide is a precise cooking technique that uses controlled low temperatures to enhance flavor and texture by evenly cooking food in vacuum-sealed bags. Enzyme-based aging relies on natural enzymatic processes to break down proteins and fats over time, intensifying flavors and tenderizing meat. Both methods aim to improve taste profiles, with sous vide focusing on temperature control and enzyme-based aging emphasizing biochemical reactions.
Understanding Flavor Development in Cooking
Sous vide cooking and enzyme-based aging both enhance meat flavor through different mechanisms; sous vide uses precise temperature control to tenderize and develop flavors during cooking, while enzyme-based aging relies on natural enzymatic breakdown over time. Understanding how proteins and fats transform in each method helps chefs optimize flavor profiles for desired taste and texture.
- Sous Vide Temperature Control - Maintains consistent low heat to preserve moisture and promote gradual protein denaturation for enhanced tenderness.
- Enzyme-Based Aging - Utilizes proteolytic enzymes to break down muscle fibers and intensify umami compounds over a prolonged resting period.
- Flavor Compound Formation - Sous vide favors Maillard reactions post-cooking, whereas aging enriches intrinsic flavor precursors through enzymatic activity.
Both techniques uniquely influence the biochemical pathways that define flavor development in cooking, offering complementary approaches to meat preparation.
How Sous Vide Enhances Food Flavors
Sous vide cooking intensifies food flavors by maintaining precise temperatures that promote the even breakdown of proteins and fats, enhancing taste and texture. It locks in moisture and concentrates natural juices, resulting in deeply rich and consistent flavors throughout the dish.
Unlike enzyme-based aging, which relies on time and natural enzymatic activity to develop flavor, sous vide accelerates this process through controlled heat exposure. This method prevents oxidative damage and nutrient loss, preserving the food's original aromatic compounds. The consistent temperature control in sous vide contributes to uniform flavor profiles that enzyme aging can sometimes fail to achieve due to its variability.
The Science Behind Enzyme-Based Aging
Enzyme-based aging enhances meat flavor through proteolysis, breaking down muscle proteins into flavorful peptides and amino acids. This biochemical process occurs naturally over several days, intensifying taste and tenderness more gradually than sous vide methods.
- Proteolytic enzymes - Endogenous enzymes like cathepsins and calpains degrade muscle fibers, releasing umami-rich compounds.
- Flavor precursor formation - Enzymatic breakdown generates amino acids and small peptides that act as flavor precursors during cooking.
- Controlled aging conditions - Temperature and humidity regulated aging chambers optimize enzyme activity for consistent flavor development.
Texture Differences: Sous Vide vs Enzyme Aging
How do texture differences compare between sous vide cooking and enzyme-based aging for flavor development? Sous vide cooking results in a consistently tender texture by precisely controlling temperature and time, preventing overcooking and moisture loss. Enzyme-based aging naturally breaks down connective tissues over time, creating a more complex, variable texture with enhanced bite and chewiness.
Impact on Meat Juiciness and Tenderness
Both sous vide and enzyme-based aging significantly enhance meat tenderness by breaking down muscle fibers, but sous vide offers precise temperature control that preserves natural juiciness. Enzyme-based aging relies on proteolytic activity over time, which can improve flavor complexity but may result in some moisture loss.
Sous vide cooking at low, consistent temperatures minimizes water loss, ensuring the meat remains succulent and tender throughout the cooking process. Enzyme-based aging, while effective in softening meat, often requires careful handling to avoid over-tenderization and preserve optimal juiciness levels.
Flavor Complexity: Comparing Both Techniques
Sous vide cooking enhances flavor complexity by precisely controlling temperature and time, allowing enzymes in meat to break down proteins and develop rich, tender textures. Enzyme-based aging relies on natural enzymatic activity over days or weeks to intensify umami and deepen flavor profiles. Combining sous vide with enzyme-based aging can maximize flavor development by balancing enzymatic breakdown and moisture retention.
Time and Safety Considerations
Sous vide cooking accelerates flavor development by precisely controlling low temperatures, reducing the time needed compared to traditional enzyme-based aging, which often spans days or weeks. Safety is enhanced in sous vide through consistent temperature maintenance, minimizing bacterial growth that can occur during prolonged enzyme aging processes.
- Reduced Timeframe - Sous vide typically requires hours, while enzyme aging may take several days to weeks for optimal flavor.
- Temperature Control - Precise sous vide temperatures prevent pathogen proliferation, unlike variable conditions in enzyme aging.
- Enhanced Food Safety - Sous vide's sealed, controlled environment lowers contamination risks compared to open-air enzyme aging.
Cost and Practicality for Home Cooks
| Sous vide equipment, including precision cookers and vacuum sealers, typically ranges from $100 to $300, making it a cost-effective method for consistent flavor development at home. Enzyme-based aging requires specialized enzymes and controlled storage conditions, often needing investment in humidity and temperature control systems exceeding $200, which may be less practical for casual cooks. Sous vide's user-friendly interface and shorter processing times provide home cooks with a convenient and repeatable approach to enhancing meat tenderness and flavor without extensive expertise. |
Related Important Terms
Proteolytic enhancement
Sous vide cooking precisely controls temperature to optimize proteolytic enzyme activity, enhancing meat tenderness and flavor complexity by preserving endogenous enzymes during low-temperature aging. Enzyme-based aging relies on exogenous proteases to break down muscle proteins, but sous vide's gentle heat activation of natural proteolytic pathways results in more uniform flavor development and improved texture.
Enzyme-assisted tenderization
Enzyme-assisted tenderization enhances meat flavor development by breaking down muscle fibers and connective tissues through proteolytic enzymes like bromelain and papain, complementing the precise temperature control of sous vide cooking. This combination intensifies tenderness and flavor complexity, as enzymes accelerate aging processes that sous vide alone achieves more slowly, optimizing texture and taste.
Exogenous enzyme marination
Exogenous enzyme marination accelerates protein breakdown in meat, enhancing tenderness and flavor development more rapidly than traditional sous vide cooking, which relies on precise temperature control over extended times to achieve similar effects. Combining enzyme marination with sous vide can optimize flavor profiles by leveraging enzymatic activity before thermal processing, resulting in improved taste complexity and texture.
Sous vide protease infusion
Sous vide protease infusion enhances flavor development by precisely controlling temperature to activate enzymes that tenderize meat and intensify umami profiles without overprocessing. This technique outperforms traditional enzyme-based aging by accelerating protein breakdown while maintaining moisture and texture integrity through airtight cooking conditions.
Controlled myofibril breakdown
Sous vide cooking enables precise temperature control that promotes controlled myofibril breakdown, enhancing flavor and tenderness through gradual protein denaturation. In contrast, enzyme-based aging relies on natural enzymatic activity to break down muscle fibers over time, but offers less consistency and precision compared to sous vide methods.
Rapid enzymatic aging
Rapid enzymatic aging accelerates tenderization and flavor enhancement by activating natural enzymes at controlled temperatures, often achieved through sous vide precision. This method intensifies beef's umami and complexity within hours, contrasting the longer timelines of traditional dry or wet aging processes.
Low-temp enzymolysis
Low-temp enzymolysis in sous vide cooking enhances flavor development by activating specific proteolytic enzymes at controlled temperatures, resulting in improved tenderness and complex meat flavors. This method offers precise temperature control superior to traditional enzyme-based aging, accelerating enzymatic breakdown while preserving moisture and texture.
Enzyme-mediated flavor boosting
Enzyme-mediated flavor boosting in sous vide cooking enhances meat tenderness and depth by activating proteolytic enzymes such as cathepsins and calpains at precise low temperatures, accelerating the breakdown of muscle fibers and connective tissues. Unlike traditional enzyme-based aging, sous vide offers controlled thermal conditions that optimize enzymatic activity, resulting in consistent flavor development and improved juiciness without prolonged aging times.
Sous vide dry-aging hybridization
Sous vide dry-aging hybridization combines precise temperature control with enzymatic breakdown to enhance meat flavor and tenderness more efficiently than traditional enzyme-based aging alone. This method promotes uniform enzyme activation and moisture retention, resulting in intensified umami profiles and consistent texture throughout the cut.
Sous vide vs enzyme-based aging for flavor development. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com