Sous vide cooking ensures precise temperature control by vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath, preserving flavor and texture. Low-oxygen sous vide takes this method further by reducing oxygen exposure during cooking, which helps minimize oxidation and extends shelf life. This technique enhances color retention and improves the overall quality of delicate proteins compared to traditional sous vide.
Table of Comparison
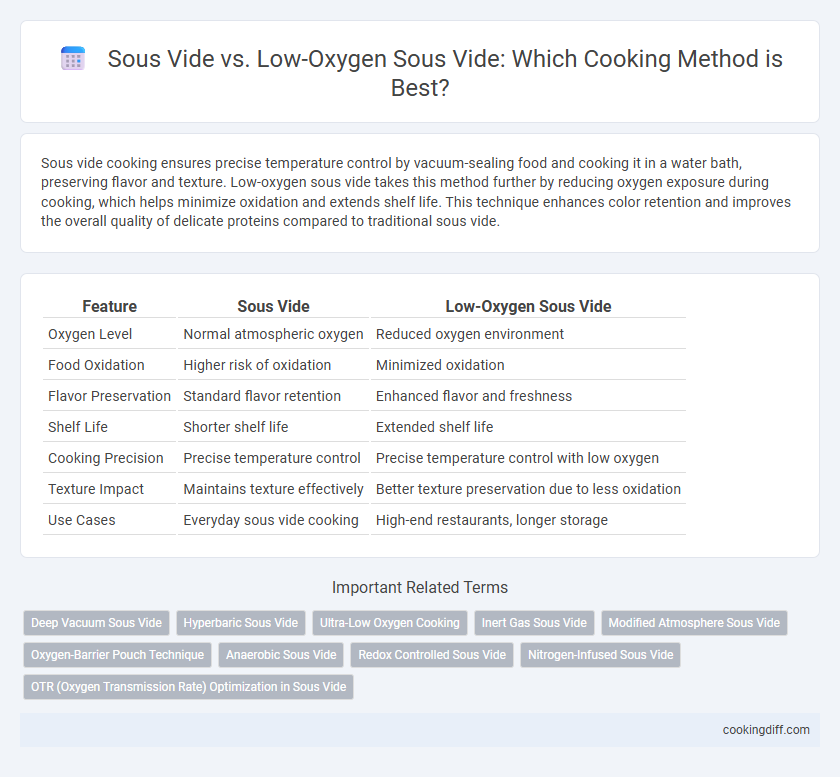
| Feature | Sous Vide | Low-Oxygen Sous Vide |
|---|---|---|
| Oxygen Level | Normal atmospheric oxygen | Reduced oxygen environment |
| Food Oxidation | Higher risk of oxidation | Minimized oxidation |
| Flavor Preservation | Standard flavor retention | Enhanced flavor and freshness |
| Shelf Life | Shorter shelf life | Extended shelf life |
| Cooking Precision | Precise temperature control | Precise temperature control with low oxygen |
| Texture Impact | Maintains texture effectively | Better texture preservation due to less oxidation |
| Use Cases | Everyday sous vide cooking | High-end restaurants, longer storage |
Introduction to Sous Vide and Low-Oxygen Sous Vide
Sous vide is a cooking technique that involves vacuum-sealing food and cooking it in a water bath at a precise, consistent temperature to ensure even doneness. Low-oxygen sous vide enhances this method by reducing oxygen levels to limit oxidation and improve flavor and texture retention during the cooking process.
- Sous vide technique - Uses vacuum-sealed bags and controlled temperature water baths for precise cooking.
- Low-oxygen sous vide - Minimizes oxygen exposure to prevent oxidation and enhance food quality.
- Cooking benefits - Both methods promote tender, flavorful results with improved nutrient retention compared to traditional cooking.
Understanding Standard Sous Vide Techniques
Standard sous vide techniques involve vacuum-sealing food in plastic bags and cooking it in a precisely controlled water bath, ensuring even temperature distribution for consistent results. This method reduces oxidation and preserves moisture and flavor by minimizing air exposure around the food. Compared to low-oxygen sous vide, which further reduces oxygen levels using inert gases, standard sous vide remains the most widely accessible and effective technique for tenderizing proteins and enhancing taste.
What Is Low-Oxygen Sous Vide?
Low-oxygen sous vide is a cooking technique that reduces oxygen exposure during the vacuum-sealing process, minimizing oxidation and preserving food quality. This method enhances flavor retention, texture, and nutrient preservation compared to traditional sous vide.
By using specialized vacuum bags or oxygen scavengers, low-oxygen sous vide creates an anaerobic environment that prevents spoilage and extends shelf life. It is especially beneficial for cooking delicate proteins and vegetables, ensuring optimal taste and safety.
Equipment Comparison: Traditional vs. Low-Oxygen Sous Vide
Traditional sous vide equipment utilizes precise temperature control with water baths to ensure even cooking without oxygen control, which can lead to slight oxidation in certain foods. Low-oxygen sous vide systems incorporate vacuum-sealed bags and oxygen-reducing technology to minimize oxidation, preserving color, texture, and flavor for delicate ingredients like seafood and leafy greens. Both methods require immersion circulators, but low-oxygen setups often involve specialized vacuum chambers or oxygen scavengers to enhance food quality and shelf life.
Safety Considerations: Foodborne Risks and Prevention
Both sous vide and low-oxygen sous vide cooking methods reduce foodborne risks by maintaining precise temperature control to inhibit pathogen growth. Low-oxygen sous vide further minimizes oxidation but requires stringent vacuum sealing to prevent anaerobic bacteria like Clostridium botulinum.
- Temperature control - Ensures cooked foods reach safe internal temperatures to eliminate harmful bacteria.
- Vacuum sealing quality - Critical in low-oxygen sous vide to prevent contamination while limiting oxygen exposure.
- Time-temperature synergy - Applying adequate cooking times at controlled temperatures is essential to mitigate foodborne illness risks.
Proper adherence to safety protocols in both methods is vital to prevent foodborne hazards and ensure safe consumption.
Cooking Results: Texture, Flavor, and Juiciness
Traditional sous vide cooking maintains precise temperature control, resulting in consistently tender texture and enhanced juiciness by evenly cooking proteins while retaining natural flavors. Low-oxygen sous vide, by removing oxygen, minimizes oxidation and flavor degradation, preserving a fresher taste and deeper umami notes in meats and vegetables.
Low-oxygen sous vide also improves texture by reducing enzymatic browning, which maintains the meat's vibrant color and smooth mouthfeel. Both methods excel in juiciness, but low-oxygen sous vide offers superior flavor retention, particularly for delicate seafood and aromatic herbs.
Suitable Foods for Each Method
Sous vide cooking excels with tender meats, fish, and vegetables that benefit from precise temperature control and moisture retention. Low-oxygen sous vide is optimal for foods prone to oxidation, such as delicate seafood and fruits, preserving freshness and color effectively.
- Sous vide suits lean meats - Cuts like chicken breast and steak maintain juiciness and texture with traditional sous vide.
- Low-oxygen sous vide benefits seafood - Oxygen-sensitive fish like salmon retain vibrant color and delicate flavor longer.
- Vegetables vary by method - Root vegetables thrive under normal sous vide while low-oxygen sous vide suits fragile greens prone to discoloration.
Time and Temperature Differences
| Cooking Method | Time Range | Temperature Range |
|---|---|---|
| Sous Vide | 1 to 48 hours depending on food type | 50degC to 85degC (122degF to 185degF) |
| Low-Oxygen Sous Vide | Typically 2 to 72 hours for enhanced preservation | 45degC to 75degC (113degF to 167degF), lower due to oxygen reduction |
Energy Efficiency and Resource Usage
How do Sous vide and low-oxygen sous vide compare in terms of energy efficiency and resource usage? Traditional Sous vide cooking typically consumes more energy due to longer cooking times at stable temperatures. Low-oxygen sous vide reduces cooking duration and oxygen exposure, which minimizes energy consumption and optimizes water and vacuum bag usage for a more sustainable cooking process.
Related Important Terms
Deep Vacuum Sous Vide
Deep Vacuum Sous Vide enhances traditional sous vide by employing ultra-low oxygen environments, which minimizes oxidation and extends food freshness while preserving texture and flavor more effectively. Compared to standard sous vide, this method intensifies nutrient retention and improves shelf life, making it ideal for precision cooking of meats, seafood, and vegetables.
Hyperbaric Sous Vide
Hyperbaric sous vide enhances traditional sous vide by cooking food in a pressurized, low-oxygen environment, which intensifies flavor infusion and accelerates cooking times while preserving nutrient integrity. This method minimizes oxidation and bacterial growth, resulting in superior texture and extended shelf life compared to conventional sous vide techniques.
Ultra-Low Oxygen Cooking
Ultra-low oxygen sous vide cooking significantly reduces oxidation and bacterial growth compared to traditional sous vide methods by maintaining oxygen levels below 0.1%, enhancing food preservation and flavor intensity. This innovative approach prolongs shelf life, improves color retention, and allows for precise control over texture and tenderness, revolutionizing professional and home cooking techniques.
Inert Gas Sous Vide
Inert gas sous vide cooking utilizes an oxygen-free environment by replacing air with inert gases like nitrogen or argon to prevent oxidation and preserve flavor, resulting in better texture and extended shelf life compared to traditional sous vide. This method enhances food safety and quality by minimizing microbial growth and maintaining nutrient integrity during the low-temperature, long-time cooking process.
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide
Modified Atmosphere Sous Vide (MASV) enhances traditional sous vide cooking by replacing the bag's oxygen with gases like nitrogen or carbon dioxide, significantly reducing oxidation and spoilage. This technique preserves food texture, color, and flavor more effectively than low-oxygen sous vide, extending shelf life while maintaining optimal cooking precision.
Oxygen-Barrier Pouch Technique
The oxygen-barrier pouch technique in low-oxygen sous vide cooking minimizes oxygen exposure by using special vacuum-sealed bags that prevent oxidative damage and enhance flavor retention. Compared to traditional sous vide, this method extends shelf life and improves texture by creating a near-perfect anaerobic environment during precise temperature control.
Anaerobic Sous Vide
Anaerobic sous vide cooking uses vacuum-sealed bags to create an oxygen-free environment, enhancing flavor retention and extending shelf life by reducing oxidation compared to traditional sous vide methods. This technique improves food safety by inhibiting aerobic bacteria growth while maintaining precise temperature control for optimal texture and tenderness.
Redox Controlled Sous Vide
Redox Controlled Sous Vide utilizes a precise balance of oxidation-reduction potential to enhance flavor development and microbial safety, outperforming traditional low-oxygen sous vide techniques by maintaining optimal redox conditions during cooking. This method enables superior texture retention and nutrient preservation by dynamically adjusting oxygen levels, ensuring consistent culinary results and extended shelf life.
Nitrogen-Infused Sous Vide
Nitrogen-infused sous vide cooking enhances traditional sous vide by incorporating nitrogen gas to create a low-oxygen environment, which significantly reduces oxidation and extends the freshness of the food. This method preserves color, texture, and flavor while maintaining precise temperature control for optimal nutrient retention and tender results.
Sous vide vs low-oxygen sous vide for cooking. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com