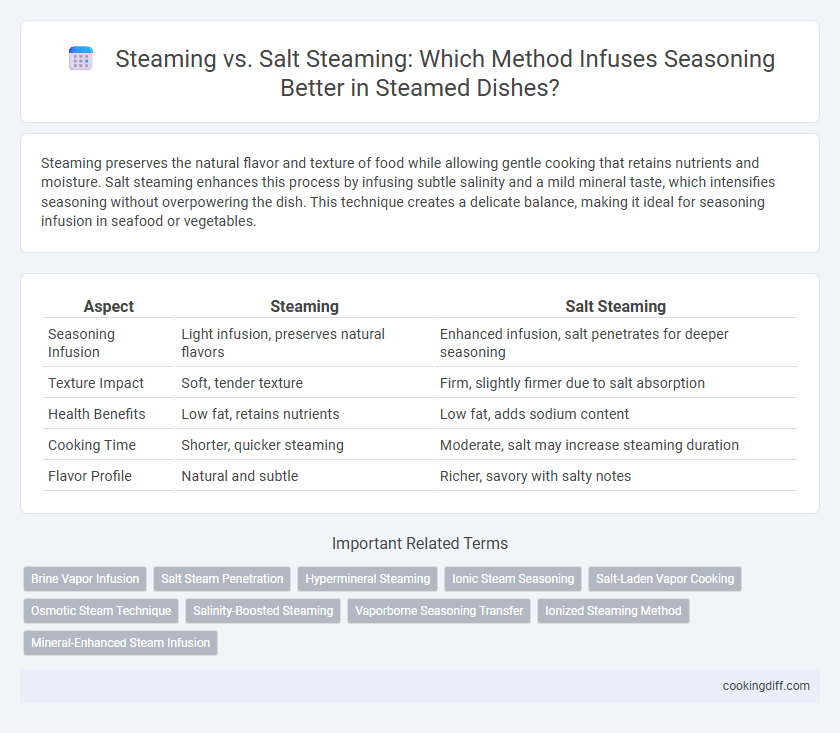
Steaming preserves the natural flavor and texture of food while allowing gentle cooking that retains nutrients and moisture. Salt steaming enhances this process by infusing subtle salinity and a mild mineral taste, which intensifies seasoning without overpowering the dish. This technique creates a delicate balance, making it ideal for seasoning infusion in seafood or vegetables.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Steaming | Salt Steaming |
|---|---|---|
| Seasoning Infusion | Light infusion, preserves natural flavors | Enhanced infusion, salt penetrates for deeper seasoning |
| Texture Impact | Soft, tender texture | Firm, slightly firmer due to salt absorption |
| Health Benefits | Low fat, retains nutrients | Low fat, adds sodium content |
| Cooking Time | Shorter, quicker steaming | Moderate, salt may increase steaming duration |
| Flavor Profile | Natural and subtle | Richer, savory with salty notes |
Introduction to Steaming and Salt Steaming
| Steaming | Steaming is a cooking technique that uses hot steam to gently cook food, preserving moisture and nutrients while allowing seasoning to infuse subtly. It provides an even, consistent heat that enhances the natural flavors of ingredients without drying them out. This method is ideal for delicate vegetables, seafood, and poultry, ensuring a tender and flavorful result. |
| Salt Steaming | Salt steaming involves layering coarse salt beneath or around the food during steaming, which helps to intensify seasoning infusion by slowly releasing salt ions and enhancing flavor penetration. The mineral-rich steam created elevates the taste profile while maintaining food texture, often used for fish and meats to impart a balanced seasoning. This technique offers a controlled salt delivery that can reduce the need for additional seasoning post-cooking. |
How Steaming Works for Seasoning Infusion
Steaming infuses seasoning by gently heating food with vapor, allowing flavors to penetrate without direct contact with water. Salt steaming enhances this process by using salt to absorb moisture and evenly distribute heat, intensifying the seasoning infusion.
- Steam Transfers Heat Uniformly - The vapor surrounds the food, facilitating even heat distribution that opens pores for better flavor absorption.
- Salt Absorbs Moisture - Salt crystals draw out moisture, creating a dry steam environment that concentrates seasoning flavors.
- Enhanced Flavor Penetration - Combining salt with steaming increases seasoning infusion depth due to salt's hygroscopic properties.
The Science Behind Salt Steaming
Salt steaming enhances seasoning infusion by creating a concentrated saline vapor that penetrates food more effectively than water steam alone. The presence of salt in the steam increases the boiling point and alters moisture transfer, promoting deeper flavor absorption and improved texture. This method leverages osmotic pressure differences, which accelerate the diffusion of seasoning molecules into the food matrix during cooking.
Flavor Penetration: Steaming vs Salt Steaming
Steaming allows delicate flavors to infuse uniformly by maintaining moisture and gentle heat, while salt steaming enhances flavor penetration by drawing out natural juices and intensifying seasoning absorption. Salt steaming creates a flavor concentration effect that standard steaming cannot achieve, resulting in a richer taste profile.
- Flavor Penetration - Salt steaming enables deeper infusion by leveraging osmosis, enhancing the seasoning's impact.
- Moisture Retention - Traditional steaming preserves moisture but may dilute subtle flavors due to lack of salt interaction.
- Cooking Time - Salt steaming can reduce cooking time by accelerating the breakdown of food fibers for better flavor absorption.
The choice between steaming and salt steaming depends on whether the goal is subtle moisture preservation or intensified seasoning depth.
Health Implications of Both Methods
Steaming preserves nutrients by gently cooking food without added fats, maintaining vitamins like C and B-complex which are sensitive to heat. Salt steaming can enhance flavor by infusing minerals, but excessive salt intake may increase sodium levels, raising blood pressure and cardiovascular risks. Choosing plain steaming minimizes sodium consumption and supports better heart health while still providing a wholesome seasoning method.
Best Foods for Steaming Infusion
Steaming infusion enhances the natural flavors of vegetables such as broccoli, carrots, and asparagus, making them ideal for seasoning infusion. Salt steaming, which involves adding salt to the steaming water, intensifies the seasoning by allowing the salt to penetrate the food more effectively.
Leafy greens like spinach and kale benefit greatly from salt steaming as it helps retain their vibrant color and texture while infusing subtle seasoning. Fish and shellfish are also excellent candidates for steaming infusion, absorbing delicate herbs and spices without becoming waterlogged. Root vegetables such as sweet potatoes and beets develop a richer flavor profile through this method, balancing sweetness with savory notes from the salt.
Salt Steaming: Enhancing Taste and Texture
Salt steaming enhances seasoning infusion by allowing salt to permeate food items gently, intensifying flavor while preserving natural moisture. This technique improves texture, resulting in a tender yet firm bite that elevates the overall eating experience.
Compared to traditional steaming, salt steaming provides a subtle seasoning boost without overpowering the ingredient's inherent taste. The process reduces cooking time and locks in nutrients, making it a preferred method for delicate proteins and vegetables.
Equipment and Techniques Comparison
Steaming uses a standard steamer basket or rack to cook food with vapor, while salt steaming incorporates a layer of coarse salt between the heat source and the steamer, enhancing flavor infusion. The equipment for salt steaming often requires a heavy-duty pan to contain and evenly distribute heat through the salt, differing significantly from traditional steamers.
- Equipment Durability - Salt steaming demands robust cookware to handle high heat without warping, unlike typical lightweight steamers.
- Flavor Penetration - Salt steaming infuses seasoning more deeply by direct contact with heated salt, compared to passive vapor in standard steaming.
- Heat Distribution - Salt provides consistent, even heat that reduces hot spots, improving the seasoning process relative to conventional steaming techniques.
Common Mistakes and How to Avoid Them
What are common mistakes when using steaming versus salt steaming for seasoning infusion? Over-steaming can cause herbs and spices to lose their potency, while under-steaming may result in uneven seasoning absorption. Avoid these issues by carefully controlling steaming time and ensuring salt is evenly distributed for consistent flavor infusion.
Related Important Terms
Brine Vapor Infusion
Steaming with brine vapor infusion enhances flavor penetration by circulating salt-infused steam that tenderizes and seasons food more evenly than traditional salt steaming, which simply relies on salt granules without vapor interaction. This method improves moisture retention and intensifies seasoning absorption, resulting in juicier, well-flavored dishes due to the molecular action of salt ions in steam.
Salt Steam Penetration
Salt steaming enhances seasoning infusion by allowing salt particles to penetrate deeper into food compared to traditional steaming, creating a more intense and uniform flavor profile. The saline vapor breaks down cell walls more effectively, resulting in faster absorption and improved texture.
Hypermineral Steaming
Hypermineral steaming enhances seasoning infusion by using mineral-rich steam that penetrates food more effectively than traditional salt steaming, resulting in deeper flavor absorption and improved texture. The high mineral content in hypermineral steam activates natural enzymes, accelerating seasoning fusion and boosting the overall taste profile without the need for added salt.
Ionic Steam Seasoning
Ionic steam seasoning enhances flavor infusion by using charged steam particles to penetrate ingredients more deeply than traditional salt steaming, which relies on salt concentration and moisture to season food. This method improves nutrient retention and seasoning uniformity while reducing sodium content and preserving natural textures.
Salt-Laden Vapor Cooking
Salt steaming enhances seasoning infusion by generating salt-laden vapor that penetrates food more deeply than plain steaming, resulting in intensified flavor profiles. This method promotes even seasoning distribution and retains moisture, creating a tender texture while imparting a subtle salty taste directly through the vapor.
Osmotic Steam Technique
The Osmotic Steam Technique enhances seasoning infusion by combining steam's heat with controlled salt concentration, promoting deeper flavor absorption through osmotic pressure. Unlike traditional steaming, this method enables precise seasoning penetration, improving texture and taste by balancing moisture retention and salt diffusion.
Salinity-Boosted Steaming
Salinity-boosted steaming enhances seasoning infusion by using salt vapor to penetrate food more deeply, resulting in intensified flavor and improved texture compared to traditional steaming. This method promotes better salt distribution without overwhelming surface salinity, balancing moisture retention and taste infusion efficiently.
Vaporborne Seasoning Transfer
Vaporborne seasoning transfer during steaming efficiently infuses flavors by allowing aromatic compounds to permeate food surfaces, while salt steaming enhances this process by creating a microenvironment that intensifies vapor absorption and seasoning penetration. The presence of salt alters the vapor's chemical composition, facilitating deeper infusion and more uniform seasoning distribution compared to traditional steaming methods.
Ionized Steaming Method
Ionized steaming enhances seasoning infusion by generating charged steam particles that penetrate food more effectively than traditional salt steaming, elevating flavor absorption and texture. This method improves ion exchange, accelerating seasoning uptake and preserving nutrient integrity, making it a preferred choice for culinary precision and health-conscious preparation.
Steaming vs Salt Steaming for seasoning infusion. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com