Steaming fish preserves moisture and nutrients, delivering a tender texture and delicate flavor without added fats. Steam ovens offer precise temperature control and even heat distribution, reducing cooking time and enhancing consistency compared to traditional stovetop steaming. The enclosed environment of a steam oven also minimizes flavor loss, making it ideal for delicate fish varieties.
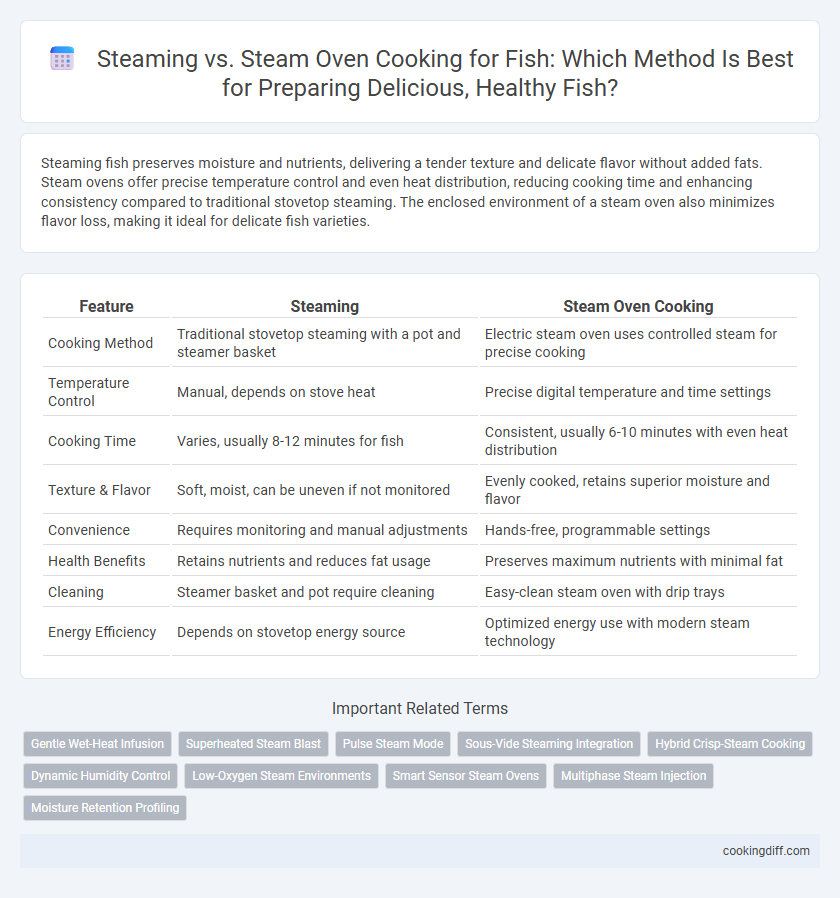
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Steaming | Steam Oven Cooking |
|---|---|---|
| Cooking Method | Traditional stovetop steaming with a pot and steamer basket | Electric steam oven uses controlled steam for precise cooking |
| Temperature Control | Manual, depends on stove heat | Precise digital temperature and time settings |
| Cooking Time | Varies, usually 8-12 minutes for fish | Consistent, usually 6-10 minutes with even heat distribution |
| Texture & Flavor | Soft, moist, can be uneven if not monitored | Evenly cooked, retains superior moisture and flavor |
| Convenience | Requires monitoring and manual adjustments | Hands-free, programmable settings |
| Health Benefits | Retains nutrients and reduces fat usage | Preserves maximum nutrients with minimal fat |
| Cleaning | Steamer basket and pot require cleaning | Easy-clean steam oven with drip trays |
| Energy Efficiency | Depends on stovetop energy source | Optimized energy use with modern steam technology |
Introduction to Steaming and Steam Oven Cooking for Fish
| Steaming is a traditional cooking method that uses vaporized water to gently cook fish, preserving moisture and nutrients effectively. |
| Steam oven cooking combines controlled steam with convection heat, providing consistent temperatures and enhanced flavor retention for fish dishes. |
| Both techniques reduce the need for added fats and offer a healthy, efficient way to prepare tender, flaky fish with minimal nutrient loss. |
Key Differences Between Traditional Steaming and Steam Oven Methods
Steaming fish traditionally uses boiling water and a bamboo or metal steamer, imparting a delicate texture and subtle flavor. Steam ovens utilize precise temperature and humidity controls, ensuring consistent results with minimal nutrient loss.
- Temperature Control - Steam ovens maintain exact temperatures, preventing overcooking, unlike traditional steaming which depends on the boiling point of water.
- Cooking Time - Steam ovens often reduce cooking time through even steam distribution compared to traditional methods.
- Flavor and Texture - Traditional steaming imparts a more natural aroma while steam ovens preserve moisture with a firmer texture.
Flavor and Texture: Steamed Fish vs. Steam Oven Fish
Steamed fish retains a delicate, moist texture with subtle flavors that come through gently, preserving its natural taste. Steam oven cooking often enhances the fish's firmness, allowing for a slightly more intense flavor concentration due to controlled temperature and consistent steam circulation.
Steaming fish on the stovetop typically produces a softer, more tender bite, which is ideal for delicate white fish like cod or sole. Steam ovens provide even heat distribution, which helps maintain the fish's moisture while developing a firmer exterior, perfect for heartier types such as salmon or tuna. The steam oven's precise control also reduces the risk of overcooking, resulting in a balanced texture and richer flavor profile.
Nutrient Retention in Steaming vs. Steam Oven Cooking
Steaming fish preserves more water-soluble vitamins such as B vitamins and vitamin C compared to steam oven cooking, which often exposes fish to higher and less controlled temperatures. The gentle and consistent heat in traditional steaming minimizes nutrient degradation and preserves the fish's natural moisture.
Steam oven cooking allows for even cooking but can lead to slight nutrient loss due to prolonged exposure to higher heat levels and potential air circulation effects. Nutrient retention in fish is maximized when steaming is done at lower temperatures with minimal cooking time, ensuring essential omega-3 fatty acids remain intact.
Equipment Overview: Steamers Versus Steam Ovens
Traditional steamers use a pot and basket system that directs steam from boiling water to cook fish gently, preserving moisture and nutrients. Steam ovens combine steam with precise temperature controls and convection heating, allowing for more consistent cooking and versatility in preparation. While steamers are more affordable and portable, steam ovens offer advanced features such as programmable settings and faster cooking times for delicate fish dishes.
Cooking Time and Efficiency for Both Methods
Steaming fish using a traditional pot typically takes less time and uses less energy compared to a steam oven, which requires preheating and longer cooking cycles. However, steam ovens offer more consistent temperature control, improving cooking precision and texture.
- Traditional Steaming Efficiency - Direct steam transfer cooks fish faster, reducing overall cooking time and energy consumption.
- Steam Oven Cooking Time - Steam ovens need about 5-10 minutes of preheat, extending total cooking duration despite steady heat application.
- Energy Use Comparison - Steam ovens consume more electricity but provide uniform cooking, improving quality for delicate fish cuts.
Choosing between steaming and steam oven cooking depends on whether speed or precision is prioritized in fish preparation.
Versatility: What Types of Fish Work Best
Steaming and steam oven cooking both excel at preserving the delicate texture and flavor of fish, but their versatility varies depending on the fish type. While traditional steaming suits tender white fish like cod and sole, steam ovens handle a wider range including oily fish and thicker cuts.
- Tender White Fish - Cod, sole, and haddock maintain moisture best with gentle steaming methods.
- Oily Fish - Salmon and mackerel benefit from steam ovens that evenly cook and enhance natural oils.
- Thicker Cuts - Steam ovens allow uniform heat penetration for species like tuna or halibut, ensuring consistent doneness.
Ease of Use and Cleanup Comparison
Which method offers greater ease of use and cleanup when cooking fish, steaming or using a steam oven? Traditional steaming requires careful water monitoring and often multiple pots, making cleanup more intensive. Steam ovens provide a streamlined cooking process with built-in timers and drip trays, significantly reducing post-cooking cleanup time.
Energy Consumption: Traditional Steamer vs. Steam Oven
Traditional steamers typically consume less electricity due to their simpler design and shorter preheating times, making them energy-efficient for small, quick meals like fish. In contrast, steam ovens require more power because of their larger size and advanced features, though they offer precise temperature control and even cooking.
Energy consumption in steam ovens increases with their multifunctional use, often balancing out efficiency with cooking versatility. Choosing between the two depends on whether energy savings or cooking performance is the priority when preparing fish.
Related Important Terms
Gentle Wet-Heat Infusion
Steaming fish uses gentle wet-heat infusion, preserving moisture, texture, and nutrients by surrounding the fish with steam at consistent temperatures, unlike traditional steam ovens that may apply higher heat and variability, potentially altering delicate flavors. This method ensures a tender, evenly cooked result, maintaining the fish's natural taste and integrity.
Superheated Steam Blast
Superheated Steam Blast in steam ovens cooks fish faster by achieving higher temperatures above 212degF, resulting in a crispier texture and enhanced flavor compared to traditional steaming, which uses saturated steam at boiling point. This method also reduces cooking time while preserving moisture and nutrients, making it a superior choice for delicate fish dishes.
Pulse Steam Mode
Pulse Steam Mode in steam ovens offers precise temperature control and intermittent steam bursts, ensuring fish cooks evenly while retaining moisture and delicate texture. Compared to traditional steaming, this mode reduces overcooking risks and enhances flavor absorption, delivering a tender, flavorful result every time.
Sous-Vide Steaming Integration
Sous-vide steaming offers precise temperature control for perfectly tender and evenly cooked fish, surpassing traditional steaming's variable heat distribution. Integrating sous-vide techniques within steam ovens enhances flavor infusion and texture consistency by maintaining optimal moisture levels throughout the cooking process.
Hybrid Crisp-Steam Cooking
Hybrid crisp-steam cooking combines the gentle, nutrient-preserving benefits of traditional steaming with the high-temperature crisping capabilities of a steam oven, producing fish with a tender interior and a perfectly crispy exterior. This method enhances flavor retention and texture contrast, outperforming conventional steaming in delivering restaurant-quality results.
Dynamic Humidity Control
Steaming fish using a traditional method offers consistent moisture retention, but steam ovens with dynamic humidity control precisely regulate steam levels to prevent overcooking and enhance texture. This technology adapts humidity in real-time, ensuring even cooking and flaky, tender fish every time.
Low-Oxygen Steam Environments
Low-oxygen steam environments enhance fish cooking by minimizing oxidation, preserving delicate flavors and nutrients compared to traditional steaming methods. Steam ovens utilize controlled low-oxygen steam chambers that maintain consistent temperature and moisture levels, resulting in tender, evenly cooked fish with superior texture and color retention.
Smart Sensor Steam Ovens
Smart Sensor Steam Ovens provide precise temperature and humidity control, enhancing the texture and flavor of fish by maintaining optimal steaming conditions. This technology outperforms traditional steaming by automatically adjusting steam levels, ensuring even cooking and preserving nutrients more effectively.
Multiphase Steam Injection
Multiphase steam injection in steam ovens delivers precise temperature and moisture control, ensuring even cooking and enhanced flavor retention in fish compared to traditional steaming methods. This advanced technology enables rapid heating and consistent steam distribution, resulting in tender, juicy fish with optimal texture and nutrients preserved.
Steaming vs Steam Oven Cooking for fish. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com