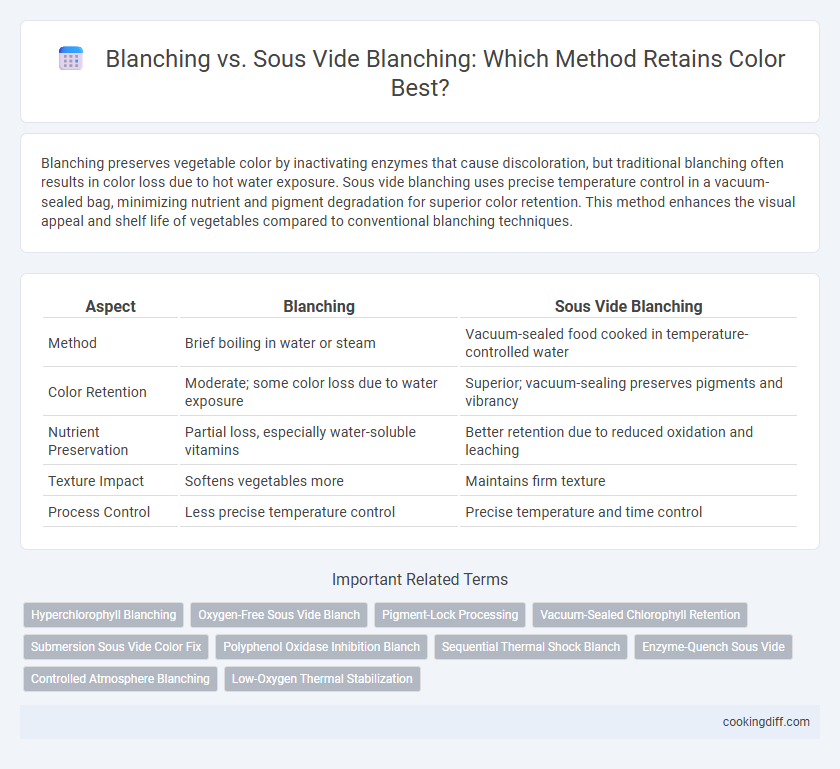
Blanching preserves vegetable color by inactivating enzymes that cause discoloration, but traditional blanching often results in color loss due to hot water exposure. Sous vide blanching uses precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed bag, minimizing nutrient and pigment degradation for superior color retention. This method enhances the visual appeal and shelf life of vegetables compared to conventional blanching techniques.
Table of Comparison
| Aspect | Blanching | Sous Vide Blanching |
|---|---|---|
| Method | Brief boiling in water or steam | Vacuum-sealed food cooked in temperature-controlled water |
| Color Retention | Moderate; some color loss due to water exposure | Superior; vacuum-sealing preserves pigments and vibrancy |
| Nutrient Preservation | Partial loss, especially water-soluble vitamins | Better retention due to reduced oxidation and leaching |
| Texture Impact | Softens vegetables more | Maintains firm texture |
| Process Control | Less precise temperature control | Precise temperature and time control |
Understanding Blanching: Traditional Method
Traditional blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables to inactivate enzymes that cause spoilage and color degradation, effectively preserving their natural vibrancy. This method uses high heat for a short time, which can result in some nutrient loss and slight color fading due to water exposure.
In comparison, sous vide blanching employs precise temperature control with vacuum-sealed food, reducing color loss by minimizing oxidation and leaching. The controlled environment helps retain chlorophyll and carotenoids, essential pigments responsible for the bright green and orange hues in vegetables.
Introduction to Sous Vide Blanching
Sous vide blanching uses precise temperature control in a vacuum-sealed environment to preserve the vibrant color of vegetables better than traditional blanching. This method minimizes nutrient leaching and oxidation, resulting in enhanced color retention and texture. By maintaining consistent heat levels, sous vide blanching ensures more uniform cooking and superior aesthetic quality in processed foods.
Importance of Color Retention in Vegetables
Color retention in vegetables is crucial for consumer appeal and perceived freshness, directly impacting marketability and nutritional quality. Blanching typically causes more color degradation due to higher temperatures and longer exposure times, leading to leaching of pigments like chlorophyll. Sous vide blanching preserves vibrant colors effectively by using precise, lower-temperature water baths that minimize pigment loss and maintain cell structure integrity.
How Traditional Blanching Works
How does traditional blanching affect color retention in vegetables? Traditional blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables followed by rapid cooling, which helps deactivate enzymes that cause color degradation. This process can lead to some nutrient and pigment loss due to heat exposure, affecting overall color vibrancy compared to sous vide blanching techniques.
Sous Vide Blanching Process Explained
Sous vide blanching enhances color retention by gently heating vegetables in vacuum-sealed bags at precise, lower temperatures compared to traditional blanching methods. This controlled environment minimizes pigment degradation and preserves vibrant hues more effectively.
- Temperature control - Sous vide blanching uses exact temperature settings, typically between 70-85degC, to avoid overcooking and color loss.
- Vacuum sealing - Removing air reduces oxidation, which helps maintain the natural color of the produce.
- Extended cooking time - Longer, lower-temperature cooking allows enzyme inactivation without excessive pigment breakdown.
Implementing sous vide blanching improves visual quality and nutritional value through superior color preservation.
Effects on Pigments: A Scientific Overview
Blanching traditionally uses boiling water or steam to inactivate enzymes, which can cause leaching and partial degradation of pigments like chlorophyll and carotenoids. Sous vide blanching employs precise temperature control, significantly enhancing pigment retention by minimizing pigment degradation and preventing color loss.
- Chlorophyll Stability - Sous vide blanching maintains higher chlorophyll levels by avoiding excessive heat exposure that typically leads to pheophytin formation in conventional blanching.
- Carotenoid Preservation - The vacuum-sealed environment in sous vide reduces oxidative degradation, preserving carotenoid pigments more effectively than traditional methods.
- Enzymatic Inactivation - Both techniques deactivate oxidative enzymes, but sous vide achieves this with less pigment leaching due to reduced water contact.
Comparative Results: Color Preservation
| Method | Color Retention (%) | Key Observations |
|---|---|---|
| Traditional Blanching | 70-75% | Heat exposure causes moderate pigment degradation, leading to noticeable color loss in vegetables. |
| Sous Vide Blanching | 85-90% | Precise temperature control minimizes pigment breakdown, significantly enhancing vibrant color retention. |
Texture and Nutrient Retention Differences
Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables, which can soften texture and cause some nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins like vitamin C. Sous vide blanching cooks vegetables in vacuum-sealed bags at precise temperatures, better preserving firmness and nutrient content.
Texture retention is superior with sous vide blanching due to gentle heat application that prevents cell wall breakdown. Nutrient retention improves because vitamins and minerals remain trapped within the sealed environment, minimizing leaching into water.
Practical Applications in Home Cooking
Blanching quickly cooks vegetables in boiling water, often causing some color loss due to oxidation, while sous vide blanching uses precise temperature control to better preserve vibrant hues. Home cooks benefit from sous vide blanching by achieving superior color retention and enhanced texture in vegetables without overcooking.
- Blanching - Involves immersing vegetables in boiling water for a short period to inactivate enzymes and set color, but some pigment degradation may occur.
- Sous Vide Blanching - Uses vacuum-sealed bags and a controlled water bath to maintain optimal temperatures, preserving chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments effectively.
- Home Cooking Application - Sous vide blanching offers consistent results with minimal color loss, making it ideal for meal prep and improving visual appeal in home-prepared dishes.
Related Important Terms
Hyperchlorophyll Blanching
Hyperchlorophyll blanching, a method involving chlorophyll-preserving solutions, significantly enhances the green color retention in vegetables compared to traditional blanching techniques. When combined with sous vide blanching, this approach offers precise temperature control that further minimizes pigment degradation and maintains vibrant color intensity.
Oxygen-Free Sous Vide Blanch
Oxygen-free sous vide blanching significantly enhances color retention in vegetables by minimizing oxidative degradation compared to traditional blanching methods. This technique utilizes vacuum-sealed, oxygen-deprived environments combined with precise temperature control to preserve chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments effectively.
Pigment-Lock Processing
Pigment-Lock Processing enhances color retention by using controlled temperature and time parameters during blanching to preserve chlorophyll and other plant pigments more effectively than traditional blanching methods. Compared to Sous Vide Blanching, Pigment-Lock offers optimized thermal treatment that minimizes pigment degradation while maintaining texture and nutritional quality.
Vacuum-Sealed Chlorophyll Retention
Vacuum-sealed sous vide blanching significantly enhances chlorophyll retention by minimizing oxygen exposure, preserving vibrant green color better than traditional blanching methods. This controlled, low-temperature process reduces pigment degradation while maintaining nutrient integrity and extending shelf life.
Submersion Sous Vide Color Fix
Submersion sous vide blanching significantly enhances color retention by precisely controlling temperature and preventing nutrient leaching, unlike conventional blanching methods. This technique creates an optimal environment for maintaining vibrant hues in vegetables through vacuum-sealed immersion in heated water.
Polyphenol Oxidase Inhibition Blanch
Blanching effectively inhibits polyphenol oxidase (PPO), preventing enzymatic browning and preserving color in vegetables, whereas sous vide blanching allows more precise temperature control that enhances PPO inactivation while minimizing pigment loss. Research shows sous vide blanching maintains higher chlorophyll and carotenoid retention compared to traditional blanching methods, optimizing color stability during storage and cooking.
Sequential Thermal Shock Blanch
Sequential Thermal Shock Blanching enhances color retention by rapidly alternating hot and cold water exposure, preserving chlorophyll and carotenoids in vegetables more effectively than traditional blanching. Compared to sous vide blanching, this method achieves superior pigment stability through immediate temperature shifts that minimize enzymatic degradation.
Enzyme-Quench Sous Vide
Enzyme-Quench Sous Vide blanching significantly improves color retention by precisely controlling temperature to halt enzymatic activity without overcooking, preserving chlorophyll and carotenoid pigments better than traditional blanching. This method enhances the vibrant appearance and nutritional quality of vegetables by minimizing pigment degradation and oxidation during the heat treatment.
Controlled Atmosphere Blanching
Controlled Atmosphere Blanching (CAB) significantly enhances color retention by using an inert gas environment to minimize oxidation and enzymatic browning during blanching, outperforming traditional blanching and Sous Vide Blanching methods. CAB maintains high levels of chlorophyll and carotenoids, preserving the vibrant green and natural hues in vegetables more effectively than the heat and water-based Sous Vide process.
Blanching vs Sous Vide Blanching for color retention. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com