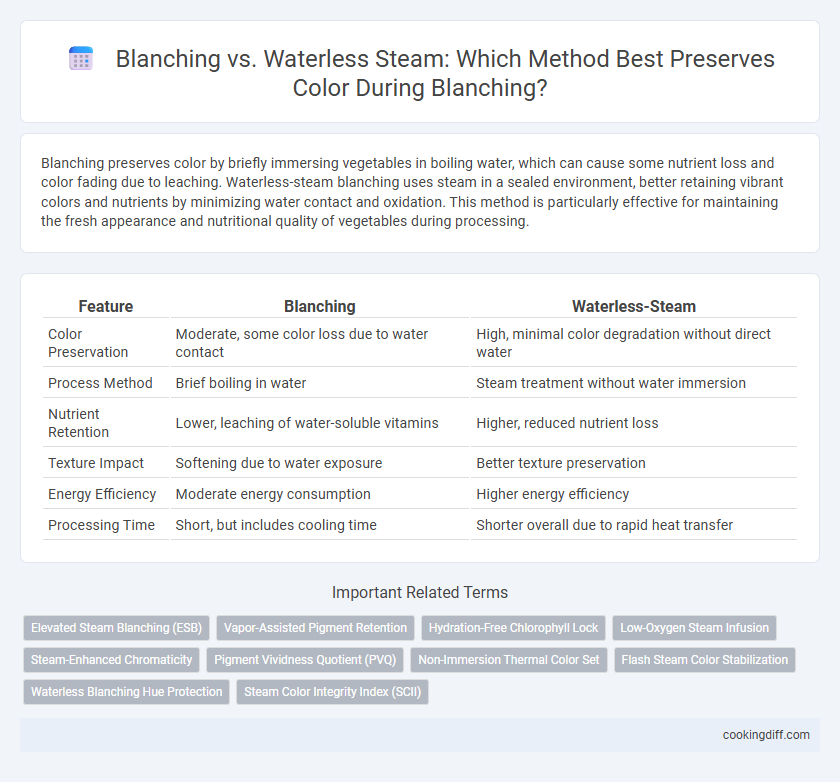
Blanching preserves color by briefly immersing vegetables in boiling water, which can cause some nutrient loss and color fading due to leaching. Waterless-steam blanching uses steam in a sealed environment, better retaining vibrant colors and nutrients by minimizing water contact and oxidation. This method is particularly effective for maintaining the fresh appearance and nutritional quality of vegetables during processing.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Blanching | Waterless-Steam |
|---|---|---|
| Color Preservation | Moderate, some color loss due to water contact | High, minimal color degradation without direct water |
| Process Method | Brief boiling in water | Steam treatment without water immersion |
| Nutrient Retention | Lower, leaching of water-soluble vitamins | Higher, reduced nutrient loss |
| Texture Impact | Softening due to water exposure | Better texture preservation |
| Energy Efficiency | Moderate energy consumption | Higher energy efficiency |
| Processing Time | Short, but includes cooling time | Shorter overall due to rapid heat transfer |
Understanding Blanching and Waterless-Steam Methods
| Blanching involves briefly boiling vegetables to inactivate enzymes, effectively preserving vibrant colors by halting oxidation and enzymatic browning, while also improving texture and shelf life. Waterless-steam blanching utilizes steam under pressure without direct water contact, enhancing color retention by minimizing leaching of water-soluble pigments and nutrients, thus maintaining visual and nutritional quality. Comparing both, waterless-steam offers superior color preservation due to reduced nutrient loss, making it optimal for vegetables with delicate pigments such as leafy greens and broccoli. |
The Science of Color Preservation in Vegetables
Blanching and waterless-steam methods both affect the color preservation of vegetables by targeting enzyme inactivation, but waterless-steam better retains chlorophyll and carotenoids due to reduced leaching. The science reveals that minimizing exposure to water and oxygen during heating preserves vibrant vegetable hues more effectively.
- Enzyme Inactivation - Both methods deactivate polyphenol oxidase and peroxidase enzymes responsible for color degradation.
- Reduced Nutrient Loss - Waterless-steam limits nutrient leaching compared to blanching in boiling water.
- Chlorophyll Stability - Waterless-steam better maintains chlorophyll's Mg2+ center, preserving green coloration.
Waterless-steam offers superior color retention by combining effective enzyme inactivation with minimal pigment degradation.
How Blanching Affects Color Retention
Blanching involves briefly exposing vegetables to boiling water or steam, effectively inactivating enzymes that cause color degradation. This process helps maintain the bright green, red, or orange hues by preventing chlorophyll and carotenoid breakdown during storage and cooking.
Waterless-steam blanching preserves color more effectively by minimizing nutrient leaching and reducing exposure to oxygen. This method retains higher levels of natural pigments compared to traditional hot water blanching, resulting in more vibrant and appealing produce.
Waterless-Steam: A Modern Approach to Vibrant Vegetables
Waterless-steam blanching uses minimal water and high-pressure steam to preserve vegetables' vibrant color more effectively than traditional water blanching. This modern technique reduces nutrient loss and prevents color leaching by maintaining the vegetable's natural pigments. As a result, waterless-steam blanching offers superior color retention and enhanced nutritional value in processed vegetables.
Comparing Nutrient Loss: Blanching vs Waterless-Steam
Blanching commonly causes greater nutrient loss, especially water-soluble vitamins such as vitamin C, due to direct exposure to hot water. Waterless-steam preserves nutrients more effectively by using steam under pressure, reducing leaching and maintaining vibrant color.
- Blanching nutrient loss - Water immersion during blanching leads to significant leaching of antioxidants and vitamins from vegetables.
- Waterless-steam preservation - Steam treatment limits nutrient escape by avoiding direct water contact, resulting in better retention of vitamin C and chlorophyll.
- Color retention correlation - Higher nutrient retention in waterless-steam processed foods contributes to enhanced natural color stability compared to blanching.
Texture and Flavor: Side Effects of Each Technique
Blanching preserves vibrant color but can cause slight softening of texture due to water exposure, which may leach some flavor compounds. Waterless-steam methods maintain a firmer texture and more intense natural flavors by minimizing nutrient loss during processing.
While blanching risks overcooking and flavor dilution, waterless-steam reduces oxidation and preserves phytochemicals that enhance taste. Each technique affects texture and flavor differently, making selection crucial based on the desired quality of the final product.
Energy and Time Efficiency in Blanching vs Waterless-Steam
Blanching typically consumes more energy due to prolonged exposure to boiling water, whereas waterless-steam methods use less energy by leveraging steam's higher heat transfer efficiency. Time efficiency also favors waterless-steam, as it reduces processing time by rapidly heating and cooling vegetables without water immersion.
Waterless-steam blanching preserves color more effectively by minimizing pigment leaching compared to traditional water blanching. The shorter processing time in steam blanching reduces nutrient degradation, improving overall product quality. Energy savings from waterless-steam systems contribute to lower operational costs and environmental impact during industrial food processing.
Common Mistakes and Best Practices
Blanching often leads to color loss when done too long or at excessively high temperatures, causing nutrient degradation. Waterless-steam blanching preserves vibrant color by using controlled steam environments that minimize oxidation and leaching. Best practices include monitoring precise time-temperature parameters and avoiding overexposure to hot water to maintain optimal color retention in vegetables.
Which Method is Better for Different Types of Foods?
Blanching effectively preserves color in vegetables with high pigment content such as green beans and spinach by quickly deactivating enzymes. Waterless-steam blanching is better suited for delicate foods like berries, as it minimizes nutrient loss and maintains vibrant color without water immersion.
- Blanching for leafy greens - Rapid heat exposure preserves chlorophyll and bright green color.
- Waterless-steam for delicate fruits - Gentle steaming retains natural colors and antioxidants more effectively.
- Food texture impact - Blanching may cause slight softening, while waterless-steam maintains firmer texture for sensitive produce.
Related Important Terms
Elevated Steam Blanching (ESB)
Elevated Steam Blanching (ESB) preserves color more effectively than traditional water blanching by minimizing nutrient leaching and enzymatic discoloration through precise temperature and steam control. Compared to waterless-steam methods, ESB offers enhanced uniform heat distribution and reduced oxidative damage, resulting in superior color retention in vegetables.
Vapor-Assisted Pigment Retention
Blanching using waterless-steam methods significantly enhances color preservation by leveraging vapor-assisted pigment retention, which minimizes pigment leaching compared to traditional water blanching. This technique maintains chlorophyll and carotenoid integrity, resulting in brighter, more vibrant vegetables while reducing nutrient loss and improving overall product quality.
Hydration-Free Chlorophyll Lock
Blanching utilizes hot water to penetrate and hydrate plant cells, often leading to chlorophyll degradation and color loss, whereas waterless-steam blanching preserves vibrant green hues by maintaining a hydration-free chlorophyll lock. This method minimizes pigment leaching and enzymatic browning, ensuring superior color retention and enhanced visual appeal in vegetables.
Low-Oxygen Steam Infusion
Low-oxygen steam infusion preserves vegetable color more effectively than traditional water blanching by minimizing pigment degradation and enzymatic browning. This method utilizes steam with reduced oxygen content to maintain vibrancy and nutritional quality while preventing color loss during processing.
Steam-Enhanced Chromaticity
Steam-enhanced chromaticity during blanching provides superior color preservation by rapidly inactivating enzymes responsible for pigment degradation, compared to traditional water blanching which often leads to color leaching. Waterless steam blanching maintains the natural vibrancy of vegetables by minimizing pigment loss and preserving chlorophyll integrity more effectively than immersion methods.
Pigment Vividness Quotient (PVQ)
Blanching often leads to a moderate Pigment Vividness Quotient (PVQ), causing some color loss in vegetables due to water leaching and heat exposure. Waterless-steam blanching significantly enhances PVQ by preserving natural pigments, maintaining vivid colors and improving overall visual appeal in processed foods.
Non-Immersion Thermal Color Set
Non-immersion thermal color set methods like waterless-steam blanching preserve vegetable chlorophyll and carotenoids more effectively than traditional water immersion blanching, minimizing color leaching and nutrient loss. Steam blanching creates less oxidative degradation and maintains vibrant, natural hues by avoiding direct water contact and reducing thermal shock.
Flash Steam Color Stabilization
Flash steam color stabilization preserves vibrant vegetable hues more effectively than traditional blanching by minimizing pigment loss and enzymatic oxidation. This waterless-steam method rapidly deactivates enzymes while maintaining cellular structure, resulting in superior color retention and enhanced product quality.
Waterless Blanching Hue Protection
Waterless blanching enhances hue protection by utilizing steam pressure, which prevents pigment loss and preserves vibrant vegetable colors more effectively than traditional water blanching. This method minimizes nutrient leaching and oxidation, resulting in superior color retention and improved visual appeal in processed vegetables.
Blanching vs Waterless-steam for color preservation. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com