An ice bath bowl is a simple and effective method for shocking blanched food, rapidly halting the cooking process and preserving texture and color. A rapid chill tray, however, offers a more efficient cooling surface designed to quickly reduce the temperature of blanched items and improve food safety by minimizing time in the temperature danger zone. Choosing between the two depends on batch size and the desired speed of chilling, with rapid chill trays being ideal for larger quantities or commercial use.
Table of Comparison
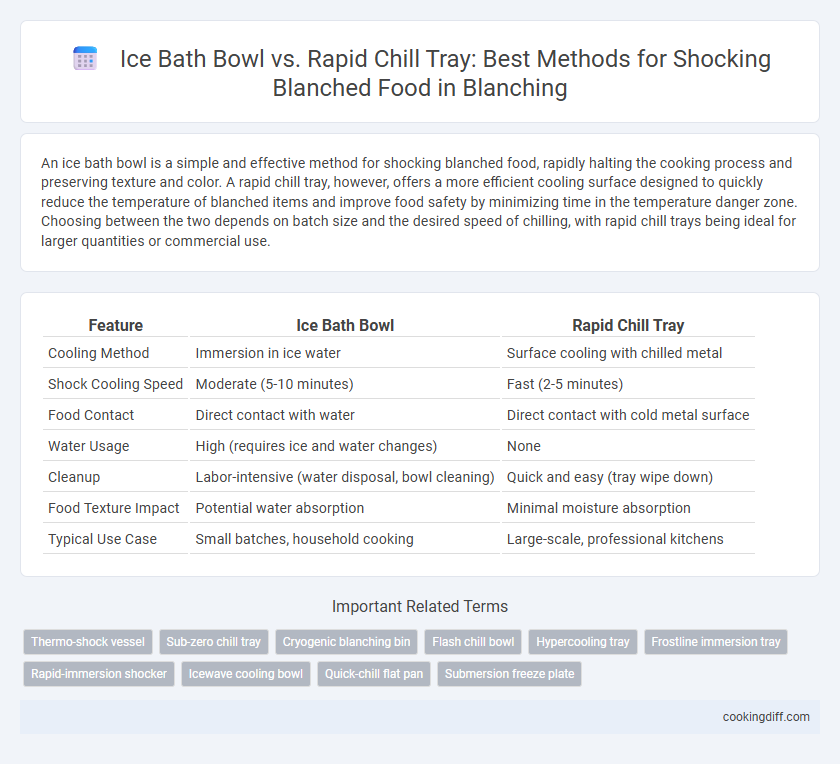
| Feature | Ice Bath Bowl | Rapid Chill Tray |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Method | Immersion in ice water | Surface cooling with chilled metal |
| Shock Cooling Speed | Moderate (5-10 minutes) | Fast (2-5 minutes) |
| Food Contact | Direct contact with water | Direct contact with cold metal surface |
| Water Usage | High (requires ice and water changes) | None |
| Cleanup | Labor-intensive (water disposal, bowl cleaning) | Quick and easy (tray wipe down) |
| Food Texture Impact | Potential water absorption | Minimal moisture absorption |
| Typical Use Case | Small batches, household cooking | Large-scale, professional kitchens |
Introduction: The Importance of Shocking Blanched Food
Shocking blanched food immediately after boiling halts the cooking process, preserving texture, color, and nutrient content. An ice bath bowl offers a simple and effective method for rapid cooling by submerging food in ice water, ensuring even temperature reduction. Rapid chill trays, engineered for quick heat extraction, provide a more efficient and hygienic alternative for maintaining food quality in professional kitchens.
How Ice Bath Bowls Work in the Blanching Process
Ice bath bowls rapidly cool blanched foods by immersing them in cold water, halting the cooking process and preserving texture and color. The cold water absorbs heat efficiently, preventing overcooking and maintaining the nutritional quality of vegetables and fruits.
This method allows for uniform cooling as the food is fully submerged, ensuring every piece reaches the ideal temperature quickly. Ice bath bowls are especially effective for small batches and delicate produce that require gentle handling after blanching.
Rapid Chill Trays: Innovative Approach to Food Cooling
Rapid chill trays provide an innovative approach to shocking blanched food by enabling faster temperature reduction compared to traditional ice bath bowls. These trays use conductive cooling surfaces that rapidly absorb heat, preserving food texture and color more effectively.
Unlike ice bath bowls that rely on water immersion, rapid chill trays minimize water usage and reduce the risk of cross-contamination. Their design ensures uniform cooling across all food items, enhancing efficiency in commercial kitchens. This technology supports food safety standards by quickly bringing temperatures below critical thresholds.
Key Differences: Ice Bath Bowl vs Rapid Chill Tray
Ice bath bowls and rapid chill trays are common methods for shocking blanched food to halt the cooking process quickly. Each offers distinct advantages in cooling efficiency and convenience, impacting texture and color retention in vegetables.
- Cooling Speed - Rapid chill trays cool food faster by maximizing surface contact, reducing the risk of overcooking.
- Water Usage - Ice bath bowls require more water and ice replenishment compared to the minimal water usage of rapid chill trays.
- Space and Portability - Ice bath bowls are typically more portable and easier to use in small kitchens, whereas rapid chill trays demand more counter space.
Choosing between these methods depends on kitchen setup, volume of food, and the desired quality of blanched ingredients.
Speed and Efficiency in Food Chilling
Rapid chill trays cool blanched food significantly faster than traditional ice bath bowls, reducing cooling time and preserving texture and color. This speed enhances kitchen efficiency and food safety by minimizing the time food spends in the temperature danger zone.
- Rapid chilling - Uses metal trays that quickly absorb heat, cooling food up to 50% faster than ice baths.
- Space-efficient - Rapid chill trays require less counter space and simplify handling during the shocking process.
- Improved food safety - Faster cooling reduces bacterial growth risks associated with prolonged warm exposure.
Food Texture and Quality Outcomes
| Ice Bath Bowl | Rapidly cools blanched food using cold water immersion, preserving crisp texture and preventing overcooking. Helps maintain vibrant color and overall food quality by halting the cooking process effectively. Can cause slight water absorption affecting delicate textures if immersion time is excessive. |
| Rapid Chill Tray | Uses cold metal surfaces for fast, uniform chilling, reducing moisture contact to maintain dry, crispy texture. Enhances food quality by minimizing nutrient loss and color degradation compared to water immersion. Particularly beneficial for leafy greens and delicate vegetables requiring texture retention without water absorption. |
Equipment Convenience and Space Requirements
An ice bath bowl is typically more compact and easy to store, making it ideal for small kitchens or limited workspace. Rapid chill trays require more countertop space but offer efficient cooling by spreading food in a thin layer for faster temperature reduction.
- Ice Bath Bowl Convenience - Portable and simple to use, the ice bath bowl facilitates quick setup and cleanup.
- Rapid Chill Tray Efficiency - Designed for high-volume kitchens, rapid chill trays accelerate chilling by maximizing surface area exposure.
- Space Requirements Comparison - Ice bath bowls conserve counter space, whereas rapid chill trays require a larger footprint and dedicated storage.
Cleaning and Maintenance Considerations
Ice bath bowls require frequent draining and thorough cleaning to prevent bacterial growth, making maintenance more labor-intensive. Rapid chill trays are designed with smooth, non-porous surfaces that simplify cleaning and reduce the risk of cross-contamination. Choosing equipment with dishwasher-safe components further enhances sanitation efficiency in commercial kitchens.
Cost Analysis: Ice Bath Bowl vs Rapid Chill Tray
Which option offers a more cost-effective solution for shocking blanched food: an ice bath bowl or a rapid chill tray? Ice bath bowls are generally less expensive upfront but require frequent ice replenishment, increasing ongoing operational costs. Rapid chill trays involve higher initial investment but provide consistent chilling efficiency and lower labor expenses over time.
Related Important Terms
Thermo-shock vessel
Ice bath bowls provide effective thermal shock by immersing blanched food in cold water, rapidly lowering its temperature to halt cooking and preserve texture; however, rapid chill trays offer superior temperature control with circulating cold air, reducing moisture retention and improving food crispness. Thermo-shock vessels optimize the cooling process by combining rapid heat extraction with minimal moisture contact, enhancing the quality and shelf life of blanched produce.
Sub-zero chill tray
Sub-zero chill trays offer faster and more consistent cooling for shocked blanched food compared to ice bath bowls, reducing bacterial growth and preserving texture and color. These trays maintain temperatures below freezing, ensuring rapid heat transfer and enhancing food safety in commercial kitchens.
Cryogenic blanching bin
Cryogenic blanching bins utilize extremely low temperatures using liquid nitrogen or carbon dioxide to rapidly cool blanched food, offering superior thermal shock compared to traditional ice bath bowls or rapid chill trays. This method preserves texture, color, and nutritional value more effectively while significantly reducing chilling time and minimizing microbial growth during the cooling phase.
Flash chill bowl
Flash chill bowls provide superior thermal conductivity compared to traditional ice bath bowls, enabling faster and more uniform cooling of blanched food, which preserves texture and nutritional quality more effectively. Their design minimizes water usage and reduces the risk of cross-contamination, making them an efficient and hygienic choice for rapid chilling in professional kitchens.
Hypercooling tray
Hypercooling trays provide uniform and rapid chilling by maximizing surface contact and cold air circulation, significantly reducing the temperature of blanched food more efficiently than traditional ice bath bowls. This method minimizes water absorption and nutrient loss while enhancing texture, making it an optimized choice for post-blanching shock cooling.
Frostline immersion tray
Frostline immersion trays provide rapid chilling for blanched foods by maximizing surface contact with ice-cold water, significantly reducing cooling time compared to traditional ice bath bowls. This efficient heat extraction preserves texture, color, and nutritional value, making Frostline trays ideal for commercial kitchens aiming to optimize the shocking process after blanching.
Rapid-immersion shocker
Rapid-immersion shockers offer superior cooling efficiency compared to ice bath bowls by quickly reducing the temperature of blanched food, preserving texture and nutritional value. These rapid chill trays maintain consistent cold temperatures, minimize water usage, and enhance food safety by preventing bacterial growth during the shocking process.
Icewave cooling bowl
The Icewave cooling bowl offers superior heat extraction for shocking blanched food compared to traditional ice bath bowls, utilizing advanced cooling technology to rapidly lower temperatures and preserve texture and color more effectively. Its design enhances chilling efficiency, reducing moisture loss and minimizing microbial growth during the cooling process.
Quick-chill flat pan
Quick-chill flat pans provide efficient heat transfer for shocking blanched food, promoting rapid temperature reduction and preserving texture and color better than traditional ice bath bowls. Their flat design allows uniform cooling, reducing the risk of overcooking and enhancing overall food quality during the blanching process.
Ice bath bowl vs rapid chill tray for shocking blanched food. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com