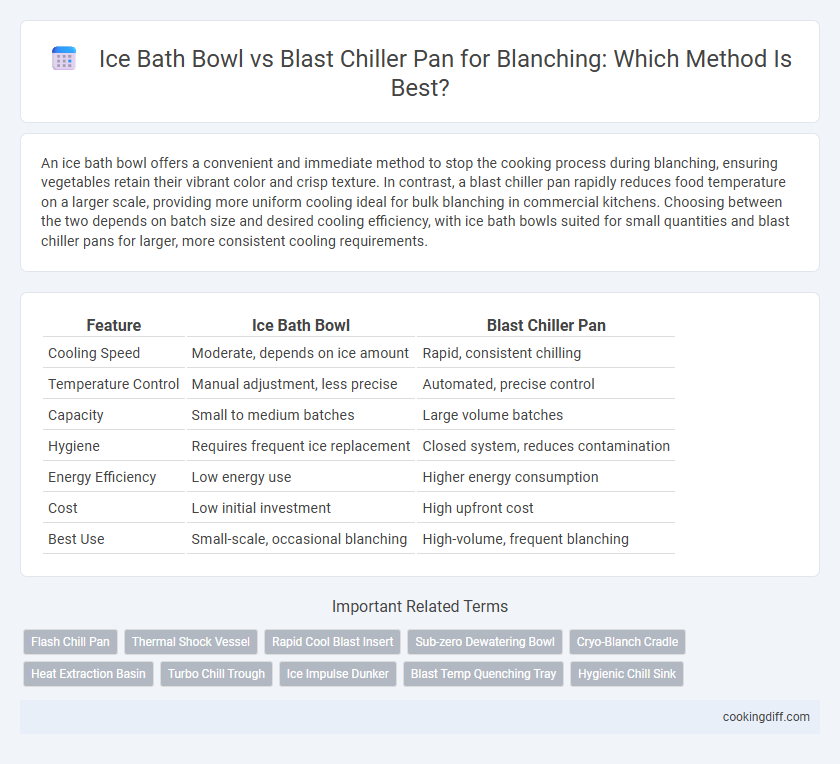
An ice bath bowl offers a convenient and immediate method to stop the cooking process during blanching, ensuring vegetables retain their vibrant color and crisp texture. In contrast, a blast chiller pan rapidly reduces food temperature on a larger scale, providing more uniform cooling ideal for bulk blanching in commercial kitchens. Choosing between the two depends on batch size and desired cooling efficiency, with ice bath bowls suited for small quantities and blast chiller pans for larger, more consistent cooling requirements.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Ice Bath Bowl | Blast Chiller Pan |
|---|---|---|
| Cooling Speed | Moderate, depends on ice amount | Rapid, consistent chilling |
| Temperature Control | Manual adjustment, less precise | Automated, precise control |
| Capacity | Small to medium batches | Large volume batches |
| Hygiene | Requires frequent ice replacement | Closed system, reduces contamination |
| Energy Efficiency | Low energy use | Higher energy consumption |
| Cost | Low initial investment | High upfront cost |
| Best Use | Small-scale, occasional blanching | High-volume, frequent blanching |
Overview: Ice Bath Bowl vs Blast Chiller Pan in Blanching
Ice bath bowls and blast chiller pans serve distinct roles in the blanching process, impacting cooling speed and efficiency. Selection depends on batch size, cooling time requirements, and kitchen workflow.
- Ice Bath Bowl - Provides immediate, direct cooling by submerging blanched produce in ice water, ideal for small batches and quick temperature reduction.
- Blast Chiller Pan - Uses controlled cold air circulation to rapidly reduce food temperature, suitable for larger quantities and consistent results in commercial kitchens.
- Efficiency Comparison - Ice bath bowls offer faster cooling for delicate items but require manual monitoring, whereas blast chiller pans ensure uniform cooling with minimal labor.
Blanching Basics: Why Cooling Matters
Blanching requires rapid cooling to halt the cooking process and preserve texture, color, and nutrients. An ice bath bowl provides immediate temperature reduction by immersing vegetables in cold water, while a blast chiller pan uses forced air to cool more evenly and efficiently. Choosing the right cooling method impacts food safety and quality by preventing overcooking and bacterial growth during blanching.
Ice Bath Bowl: Traditional Cooling Method
| Ice Bath Bowl | Traditional cooling method used in blanching to rapidly stop the cooking process of vegetables. |
| Cooling Efficiency | Relies on manual ice replacement and water agitation to maintain low temperatures, typically around 0degC (32degF). |
| Usage | Common in home kitchens and small-scale operations for its simplicity and low cost despite limited temperature control compared to blast chiller pans. |
Blast Chiller Pan: Modern Rapid Cooling Solution
Blast chiller pans provide a cutting-edge solution for rapid cooling after blanching, preserving food texture and nutritional quality. Unlike traditional ice bath bowls, they significantly reduce cooling time by using controlled cold air circulation.
- Efficient Temperature Reduction - Blast chiller pans quickly lower food temperature to safe levels, minimizing bacterial growth.
- Consistent Cooling - The controlled environment ensures even cooling, preventing over-soaking or uneven texture.
- Space-Saving Design - Their stackable pans optimize kitchen workflow and reduce the need for large volumes of ice.
Blast chiller pans represent a modern, hygienic, and efficient tool for professional blanching and cooling processes.
Speed and Efficiency: Comparing Cooling Times
Which cooling method offers faster efficiency in blanching, an ice bath bowl or a blast chiller pan? Ice bath bowls typically cool vegetables quickly by immersing them in chilled water, but blast chiller pans use rapid air circulation to reduce temperature in a fraction of the time. Blast chiller pans generally provide superior speed and energy efficiency, making them ideal for high-volume or professional kitchen settings.
Food Quality: Impact on Texture and Color
Immersing vegetables in an ice bath bowl immediately after blanching rapidly cools them, preserving vibrant color and crisp texture by halting enzymatic activity quickly. This method effectively maintains the visual appeal and firmness crucial for high-quality produce in short-term storage.
Using a blast chiller pan provides a controlled, rapid cooling environment that ensures uniform temperature reduction, significantly reducing color degradation and texture softening during extended storage. The precise temperature control helps retain cellular structure and nutrient content, optimizing overall food quality for commercial applications.
Safety and Hygiene: Reducing Bacterial Growth
Using a blast chiller pan for blanching significantly reduces bacterial growth compared to an ice bath bowl due to faster cooling rates. Blast chiller pans maintain consistent low temperatures, enhancing food safety and hygiene by limiting the time vegetables spend in the danger zone.
- Rapid Cooling - Blast chiller pans cool blanched vegetables quickly, minimizing microbial proliferation risks.
- Temperature Control - Precise temperature regulation in blast chiller pans inhibits bacterial growth more effectively than ice bath bowls.
- Sanitation - Stainless steel blast chiller pans are easier to clean and sanitize, reducing cross-contamination hazards.
Space and Equipment Requirements
Ice bath bowls require minimal space and basic kitchen equipment, making them suitable for small-scale blanching tasks. They can be easily stored and are portable, but may limit the quantity of food processed at one time.
Blast chiller pans demand a dedicated refrigeration unit and more kitchen space, suited for high-volume blanching operations. They offer faster cooling and better temperature control, but entail higher initial equipment investment and space allocation.
Cost Analysis: Ice Bath vs Blast Chiller Investment
Ice bath bowls offer a low-cost solution for blanching with minimal upfront investment, making them ideal for small-scale or home use. Blast chiller pans require significant capital expenditure but provide rapid cooling and improved food safety, reducing labor costs and spoilage in commercial kitchens. Over time, the energy efficiency and operational benefits of blast chillers can justify their higher initial price compared to the recurring costs of ice and manual handling associated with ice baths.
Related Important Terms
Flash Chill Pan
Flash chill pans offer superior temperature control during blanching compared to traditional ice bath bowls, rapidly lowering food temperature to inhibit microbial growth and preserve texture. The stainless steel construction of flash chill pans ensures even cooling and durability, making them an efficient choice for commercial kitchens aiming for consistent food safety and quality.
Thermal Shock Vessel
An ice bath bowl provides rapid cooling through immediate thermal shock, effectively halting the cooking process during blanching by quickly lowering the temperature of vegetables, preserving color and texture. In contrast, a blast chiller pan offers controlled, uniform cooling with precise temperature settings but delivers a less intense thermal shock, making it ideal for large batches requiring gradual heat reduction without compromising quality.
Rapid Cool Blast Insert
A Rapid Cool Blast Insert in a blast chiller pan offers significantly faster cooling after blanching compared to an ice bath bowl, minimizing nutrient loss and maintaining optimal food texture. Its efficient cold air circulation ensures uniform temperature reduction, enhancing food safety and quality during industrial-scale blanching processes.
Sub-zero Dewatering Bowl
The Sub-zero dewatering bowl offers superior temperature control and rapid cooling compared to a traditional ice bath bowl, ensuring optimal texture and nutrient retention during blanching. Unlike blast chiller pans, it combines efficient ice-water circulation with sub-zero conditions to minimize thermal shock and enhance post-blanching freshness.
Cryo-Blanch Cradle
The Cryo-Blanch Cradle offers superior temperature control compared to traditional ice bath bowls, enabling rapid cooling of blanched vegetables and preserving texture and nutrients more effectively. Unlike blast chiller pans, the Cryo-Blanch Cradle is specifically designed to optimize cryogenic cooling efficiency, reducing cooling time and minimizing thermal shock during the blanching process.
Heat Extraction Basin
An ice bath bowl provides rapid cooling for blanching by immersing vegetables directly in cold water, efficiently removing heat through conduction and maintaining texture and color. In contrast, a blast chiller pan relies on forced cold air circulation for heat extraction, offering precise temperature control but generally slower cooling rates compared to direct ice bath immersion.
Turbo Chill Trough
The Turbo Chill Trough provides a more consistent and rapid cooling rate compared to traditional ice bath bowls, ensuring optimal blanching results by immediately halting the cooking process and preserving texture and color. Unlike blast chiller pans, the Turbo Chill Trough's design maximizes surface contact and circulation, enhancing heat extraction and reducing cooling time for high-volume blanching operations.
Ice Impulse Dunker
The Ice Impulse Dunker provides rapid cooling with an ice bath bowl, preserving texture and color better than traditional blast chiller pans designed for gradual temperature reduction. Its efficient ice water circulation accelerates heat removal during blanching, optimizing food quality and safety in commercial kitchens.
Blast Temp Quenching Tray
The Blast Temp Quenching Tray offers superior heat extraction compared to traditional ice bath bowls by rapidly cooling blanched vegetables, preserving texture and nutrient retention more effectively. Its design enables consistent temperature control and faster quenching times, reducing microbial growth risks and enhancing food safety in commercial blanching processes.
Ice bath bowl vs blast chiller pan for blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com