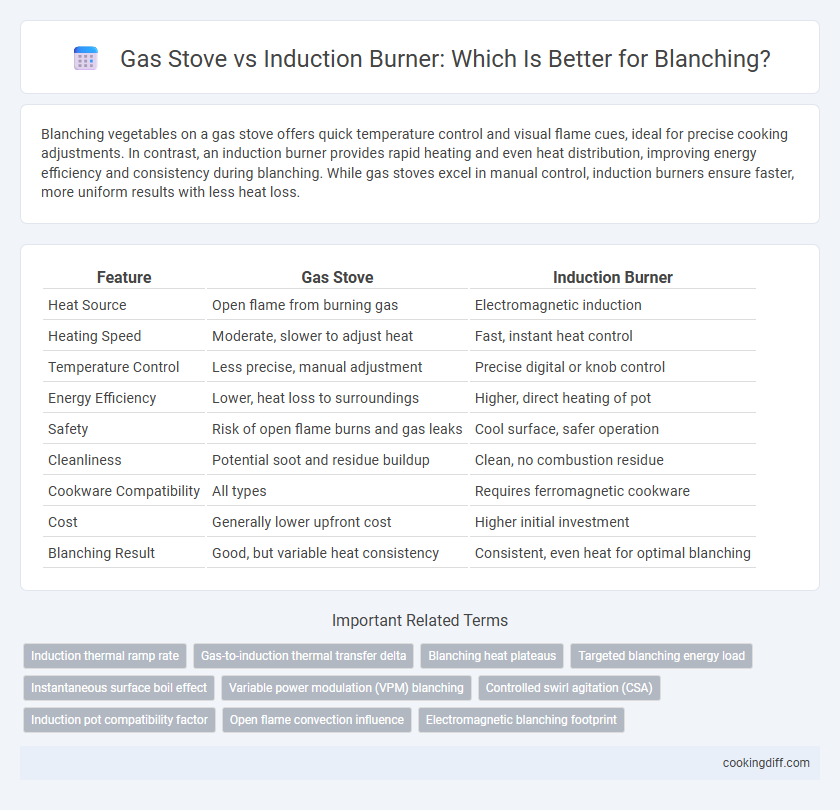
Blanching vegetables on a gas stove offers quick temperature control and visual flame cues, ideal for precise cooking adjustments. In contrast, an induction burner provides rapid heating and even heat distribution, improving energy efficiency and consistency during blanching. While gas stoves excel in manual control, induction burners ensure faster, more uniform results with less heat loss.
Table of Comparison
| Feature | Gas Stove | Induction Burner |
|---|---|---|
| Heat Source | Open flame from burning gas | Electromagnetic induction |
| Heating Speed | Moderate, slower to adjust heat | Fast, instant heat control |
| Temperature Control | Less precise, manual adjustment | Precise digital or knob control |
| Energy Efficiency | Lower, heat loss to surroundings | Higher, direct heating of pot |
| Safety | Risk of open flame burns and gas leaks | Cool surface, safer operation |
| Cleanliness | Potential soot and residue buildup | Clean, no combustion residue |
| Cookware Compatibility | All types | Requires ferromagnetic cookware |
| Cost | Generally lower upfront cost | Higher initial investment |
| Blanching Result | Good, but variable heat consistency | Consistent, even heat for optimal blanching |
Gas Stove vs Induction Burner: Quick Comparison for Blanching
Gas stoves provide immediate flame heat ideal for quick temperature adjustments during blanching, while induction burners offer precise and consistent heat control. Induction burners heat faster and more efficiently, reducing energy consumption compared to gas stoves.
- Heat Control - Gas stoves allow rapid flame adjustments, but induction burners enable precise temperature settings for consistent blanching results.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction burners convert energy directly to cookware, making them more efficient than gas stoves that lose heat to the environment.
- Safety - Induction burners stay cool to the touch and reduce fire hazards, whereas gas stoves expose open flames and hot surfaces.
Heating Speed: Which Heats Water Faster for Blanching?
| Heating Method | Heating Speed | Impact on Blanching |
|---|---|---|
| Gas Stove | Reaches boiling point in approximately 7-10 minutes for 1 liter of water | Provides rapid and adjustable heat, suitable for quick blanching processes |
| Induction Burner | Heats 1 liter of water to boiling in about 4-6 minutes | Delivers faster and more energy-efficient heating, ensuring quicker blanching |
Temperature Control Accuracy in Blanching
Induction burners provide superior temperature control accuracy compared to gas stoves, ensuring precise maintenance of blanching temperatures between 70degC and 100degC. This precision reduces the risk of overcooking or undercooking vegetables, preserving their texture and nutrients more effectively.
- Consistent Heat Distribution - Induction burners generate even heat directly in the cookware, allowing stable blanching temperatures without fluctuations common in gas stoves.
- Rapid Temperature Adjustment - Induction technology responds instantly to control changes, enabling quick corrections to maintain ideal blanching conditions.
- Energy Efficiency - Induction burners convert energy directly to heat in the pan, minimizing energy loss and optimizing temperature control during blanching.
Energy Efficiency: Gas vs Induction When Blanching
Induction burners offer superior energy efficiency compared to gas stoves when blanching due to direct electromagnetic heating. Gas stoves lose significant heat energy to the surrounding air, making them less efficient for rapid temperature control during blanching.
- Induction Efficiency - Transfers nearly 85-90% of energy directly to the pan, minimizing energy loss.
- Gas Stove Waste - Only about 40-55% of the energy heats the cookware, with the rest dissipated as heat into the environment.
- Temperature Precision - Induction burners enable faster and more precise temperature adjustments, essential for consistent blanching results.
Using induction technology for blanching reduces energy consumption and enhances cooking control compared to traditional gas stoves.
Safety Considerations During the Blanching Process
Induction burners offer enhanced safety during blanching by providing precise temperature control and eliminating open flames, reducing the risk of burns and kitchen fires. Gas stoves, while effective, pose a higher risk due to exposed flames and potential gas leaks, which can be hazardous during prolonged boiling tasks like blanching. Choosing an induction burner minimizes accidents and ensures a safer blanching environment by instantly adjusting heat and cooling down rapidly after use.
Consistency of Results: Evenness of Cooking
Gas stoves provide direct flame heat, which can create hot spots causing uneven blanching results, especially with larger or irregularly shaped vegetables. Induction burners offer precise temperature control and consistent heat distribution due to electromagnetic heating, ensuring uniform blanching and preserving texture and color. For chefs prioritizing evenness of cooking, induction burners deliver more reliable and consistent blanching outcomes compared to gas stoves.
Cost Analysis: Blanching with Gas or Induction Burner
Blanching with a gas stove generally incurs lower upfront costs compared to an induction burner, making it more accessible for budget-conscious users. However, gas stoves often have higher ongoing fuel expenses due to less efficient energy usage.
Induction burners, while more expensive initially, offer greater energy efficiency and faster heating times, reducing long-term operating costs. The precise temperature control of induction burners improves blanching consistency and minimizes food waste. Over time, savings on electricity and improved performance can offset the higher initial investment of induction technology.
Convenience and Ease of Use in Blanching Tasks
Gas stoves offer immediate heat control, making it easier to adjust the temperature quickly during blanching. This responsiveness helps prevent overcooking and ensures consistent results when preparing vegetables.
Induction burners provide precise temperature settings and maintain consistent heat, which simplifies controlling blanching times. Their safety features and easy-to-clean surfaces enhance convenience in repetitive blanching tasks.
Maintenance and Cleanup After Blanching
Which appliance is easier to maintain and clean after blanching, a gas stove or an induction burner? Gas stoves often require more intensive cleaning due to exposed flames and greasy grates that accumulate residue. Induction burners feature smooth, flat surfaces that are quick to wipe down and resist staining from blanching spills.
Related Important Terms
Induction thermal ramp rate
Induction burners offer a significantly faster thermal ramp rate compared to gas stoves, allowing for precise temperature control essential for blanching. This rapid and consistent heat transfer minimizes nutrient loss and ensures uniform blanching in a shorter cooking time.
Gas-to-induction thermal transfer delta
Induction burners deliver up to 90% thermal transfer efficiency compared to approximately 40-50% for gas stoves, resulting in faster and more consistent blanching temperatures. This higher energy efficiency minimizes heat loss and ensures precise temperature control, optimizing blanching quality and reducing cooking time.
Blanching heat plateaus
Gas stoves offer rapid heat adjustments and visible flame control, creating ideal heat plateaus for precise blanching, while induction burners provide consistent, energy-efficient heat with faster temperature stabilization but may experience slight heat plateaus due to electromagnetic heating cycles. Optimal blanching requires maintaining a steady temperature plateau around 85-95degC, where the choice between gas and induction impacts heat responsiveness and temperature uniformity.
Targeted blanching energy load
Gas stoves deliver rapid, adjustable heat with direct flame contact, resulting in higher energy loss and less precise control during blanching, whereas induction burners provide efficient, targeted heat transfer directly to the cookware, optimizing energy load and ensuring consistent blanching temperature. Induction technology typically achieves up to 90% energy efficiency compared to gas stoves' approximately 40%, reducing overall energy consumption and improving blanching precision.
Instantaneous surface boil effect
Induction burners provide a rapid and consistent instantaneous surface boil due to their electromagnetic heat generation directly within the cookware, significantly reducing heating time compared to gas stoves. Gas stoves rely on flame heat transfer, which often results in slower, uneven boiling and less energy efficiency during blanching processes.
Variable power modulation (VPM) blanching
Induction burners provide precise Variable Power Modulation (VPM) for blanching, allowing consistent temperature control that prevents overcooking and preserves nutrient quality. Gas stoves lack this fine-tuned power modulation, resulting in less efficient heat management and increased risk of uneven blanching.
Controlled swirl agitation (CSA)
Gas stoves provide a natural flame that can be adjusted for dynamic heat distribution, enabling moderate controlled swirl agitation (CSA) during blanching which helps in maintaining even temperature across the water. Induction burners offer precise temperature control and consistent heat, producing steady CSA that enhances the efficiency of blanching by uniformly agitating the water and preventing hot spots.
Induction pot compatibility factor
Induction burners require induction-compatible pots made of ferrous metals like cast iron or magnetic stainless steel to operate efficiently, ensuring rapid and precise temperature control essential for blanching. In contrast, gas stoves offer compatibility with any pot material but lack the precise heat control that induction burners provide, which can impact blanching consistency.
Open flame convection influence
Gas stoves with open flame provide direct convection heat that rapidly transfers energy to water during blanching, ensuring quicker temperature rise and even cooking. Induction burners rely on electromagnetic fields to heat the pan directly, offering precise temperature control but lacking the intense convection effect of an open flame, which can slightly prolong blanching time.
Gas stove vs Induction burner for blanching. Infographic
 cookingdiff.com
cookingdiff.com